Physics - Electromagnetism - Magnetic field of current-carrying conductors
Image source: http://bolvan.ph.utexas.edu/~vadim/Classes/2018f/MagneticFieldLines.html
Introduction
Hello it's a me again Drifter Programming! Today we continue with Electromagnetism to get into another source of magnetic fields. I'm of course talking about current-carrying conductors, which will be very easy to understand, cause we already covered the magnetic field of moving charges last time! So, without further do, let's get straight into it!
Magnetic field of current
As we already know from previous articles, current is build up of moving charges that are oriented to flow in one direction. Due to the superposition principle the total magnetic field of more then one charges is equal to the vector sum of all those separate magnetic fields.
Last time we saw that the magnetic field around a moving charged particle is:
which are a vector and "magnitude" form...
Consider a point on a conductive wire where the section has an Area A with a infinitesmal length dl. N-charges pass through this section and all charges have the same charge q. The total charge is that way as we already know:
The moving charges are equivalent to this total charge that we calculated right now. That way by substituting dQ as q in the magnetic field equation we get:
The component: nqvdA is of course equal to the current I that flows in the section of length dl which means that we can re-write the equation as:
"magnitude" and vector forms...
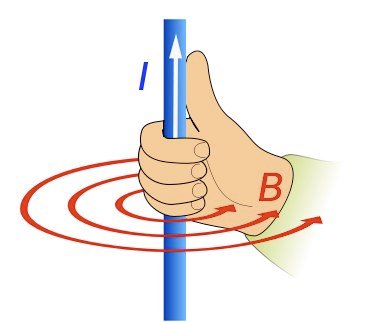
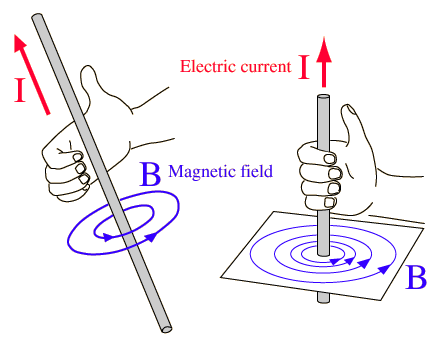
The component dl is of course a vector that points in the trajectory where the infinitesmal current flows and so because of the cross product between dl and r (which is the normal to the area) we can clearly see that the magnetic field is again perpendicular to the current and section A. This means that the magnetic field will again be in a circular form around the wire, like we had with charges! To find the actual direction of the field lines we use the same right-hand rule that we had with charges, but this time the velocity is replaced by the current. This looks like this:
Biot-Savart law
By integrating this previous equation we end up with the so caleld Biot-Savart law which states:
When applying this law you should be cautious and should always check the following:
- The vector directions are very important. As already told before dl is always pointing in the direction of the current. The unit vector r is moving from dl to the points where we want to calculate the magnetic field (from the source to the observation point).
- The elementary charges and dB fields can have the same direction, which means that the total magnetic field is a simple sum of the magnitudes. But, these two vectors mostly have different directions which makes the integration much more difficult and takes us to an integral for each axis/component. For this second case symmetry is key and makes our calculations much much easier!
- Don't ever forget to use the superposition principle! Knowing the magnetic field of a simple case can sometimes help us when finding the magnetic field of another more complicated case.
So, yes this law applies to current-carrying conductors of a elementary length dl, what happens in other cases?
Finite length
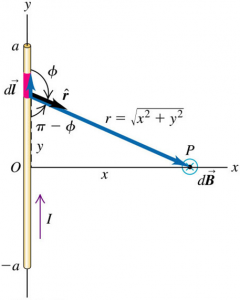
Suppose we have a straight current-carrying conductor of finite length 2a:
Image source: https://www.miniphysics.com/uy1-magnetic-field-of-a-straight-current-carrying-conductor.html
By doing the calculations using Biot-Savart's and the Euclid theorem at the triangle we end up with:
where of course: r^2 = a^2 + b^2.
Infinite length
Let's consider that the length of the conductor is infinite!
For a-> ∞ we get:
where r is the distance of the point from the conductor/source.
As you can see, calculations where left out, cause we don't need them anyways now :P
REFERENCES:
- http://www.quantumstudy.com/physics/magnetic-effect-of-current-2/
- http://eeedrmcet.zohosites.com/files/II%20Year/SEM%203/EMT/EMT_L23.pdf
- https://www.miniphysics.com/uy1-magnetic-field-of-a-straight-current-carrying-conductor.html
- https://gradestack.com/JEE-Main-2015-Complete/Moving-Charges-and/Magnetic-Field-due-to-a/19509-3784-41491-study-wtw
- https://www.britannica.com/science/Biot-Savart-law
- http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/magnetic/Biosav.html
Mathematical equations that I had in this post where drawn using quicklatex!
Previous posts about Electromagnetism
Electric fields:
Getting into Electromagnetism -> electromagnetim, electric charge, conductors, insulators, quantization
Coulomb's law with examples -> Coulomb's law, superposition principle, Coulomb constant, how to solve problems, examples
Electric fields and field lines -> Electric fields, Solving problems around Electric fields and field lines
Electric dipoles -> Electric dipole, torque, potential and field
Electric charge and field Exercises -> examples in electric charges and fields
Electric flux:
Electric flux and Gauss's law -> Electric flux, Gauss's law
Applications of Gauss's law (part 1) -> applying Gauss's law, Gauss applications
Applications of Gauss's law (part 2) -> more Gauss applications
Electric flux exercises -> examples in electric flux and Gauss's law
Electric potential:
Electric potential energy -> explanation of work-energy, electric potential energy
Calculating electric potentials -> more stuff about potential energy, potential, calculating potentials
Equipotential surfaces and potential gradient -> Equipotential surface, potential gradient
Millikan's Oil Drop Experiment -> Millikan's experiment, electronvolt
Cathode ray tubes explained using electric potential -> cathode ray tube explanation
Electric potential exercises (part 1) -> applications of potential
Electric potential exercises (part 2) -> applications of potential gradient, advanced examples
Capacitance:
Capacitors (Condensers) and Capacitance -> Capacitors, capacitance, calculating capacitance
How to solve problems around Capacitors -> combination, solving problems, simple example
Electric field energy and density -> Electric field energy, energy density
Dielectric materials -> Dielectrics, dielectric constant, permittivity and strength, how to solve problems
Electric capacitance exercises -> examples in capacitance, energy density and dielectrics
Current, resistance and EMF:
Electric current -> Electric current, current density
Electrical resistivity and conductivity -> Electrical resistivity, conductivity, thermal coefficient of resistivity, hyperconductivity
Electric resistance -> Resistance, temperature, resistors
Electromotive Force (EMF) and Internal resistance -> Electromotive force, internal resistance
Power and Wattage of Electronic Circuits -> Power in general, power/wattage of electronic circuits
Electric current, resistance and emf exercises -> exampes in all those topics
Direct current (DC) circuits:
Resistor Combinations -> Resistor combinations, how to solve problems
Kirchhoff's laws with applications -> Kirchhoff's laws, how to solve problems, applications
Electrical measuring instruments -> what are they?, types list, getting into some of them, an application
Electronic circuits with resistors and capacitors (R-C) -> R-C Circuit, charging, time constant, discharging, how to apply
RC circuit exercises -> examples in Kirchhoff, charging, discharging capacitor with/without internal resistance
Magnetic field and forces:
Magnetic fields -> Magnetism, Magnetic field
Magnetic field lines and Gauss's law of Magnetism -> magnetic field lines, mono- and dipoles, Flux, Gauss's law of magnetism
The motion of charged particles inside of a magnetic field -> straight-line, spiral and helical particle motion
Applications of charged particle motion -> CERN, Cyclotrons, Synchrotrons, Cavity Magetron, Mass Spectrometry and Magnetic lens
Magnetic force applied on Current-Carrying Conductors -> magnetic force on current-carrying conductors/wires, proofs
Magnetic force and torque applied on current loops (circuits) -> magnetic force on current loops, magnetic moment and torque
Explaining the Physics behind Electromotors -> tesla, history and explaining the physics behind them
Magnetic field exercises -> examples in magnetic force, magnetic flux, particle motion and forces/torque on current-carrying conductors
Magnetic field sources:
Magnetic field of a moving charged particle -> moving charge, magnetic field, force between parallel charged particles
And this is actually it for today's post! Next time I'm thinking of getting into the force between two parallel conductors and maybe even the magnetic field of current loops...
Bye!
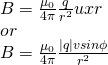
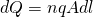
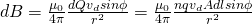
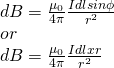

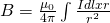
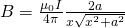
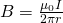
This post has been voted on by the steemstem curation team and voting trail.
There is more to SteemSTEM than just writing posts, check here for some more tips on being a community member. You can also join our discord here to get to know the rest of the community!
Hi @drifter1!
Your post was upvoted by utopian.io in cooperation with steemstem - supporting knowledge, innovation and technological advancement on the Steem Blockchain.
Contribute to Open Source with utopian.io
Learn how to contribute on our website and join the new open source economy.
Want to chat? Join the Utopian Community on Discord https://discord.gg/h52nFrV
Nothing to add, but many thanks for posting these.
lol
Good post