Understanding cryptography part 1
Para versão em português deste post clique aqui.
All cryptocurrencies, protocols and new technologies have a similar base, encryption. For this reason and for being one of the bases of information security I decided to make a series of posts on the subject. We will start from the basics to understand enough how such protocols work, up to something more advanced and technical within the main algorithms.
Introduction
Cryptography is a study of ways to transform a legible and meaningful information into illegible and meaningless. The readable message must be known only to the destination, sender, and other authorized parties. The purpose of cryptography in general is to prevent unauthorized people from having access to this information, that is, secrecy.

Source
Couldn't understand? Let's take a few practical examples:
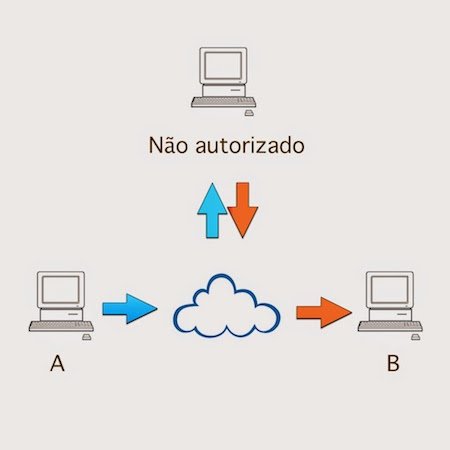
User A sends information to User B. User C intercepts the communication and views without having been authorized.
Well, here we can clearly see the problem. You send something to someone and in the middle of the way someone else, without authorization, visualizes this information. If this information is confidential you do not want to show out there, so to make sure no one sees you apply a security measure. We are not talking here exclusively of communication through computers, but of any type of communication. A practical example of this is in a company. An HR employee send employee payroll to the Financial sector, another employee intercepts and sees the salary of all employees.
User A sends information to user B. User C intercepts, changes information and delivery to B.
Here we have another problem, similar in some ways to the previous one. In this case in addition to an unauthorized person see information that should not it still alters the information in order to cause some harm, get some advantage, etc. The practical example we can use here is on a school. The teacher completes the notes and forwards to the secretary, a student intercepts, exchanges his grade and hands the book to the secretary.
User C impersonating user A, sends a message to User B requesting some information. User B believing to be User A, delivers the information to User C.
A simple example of this type of problem is those scams by email and telephone. It may sound silly, but many people fall into this kind scheme. If you did not know, most of the major social networking hacks went through such a social engineering attack. I have one of these to post sometime.
Brief history
You may find that by using encryption on our systems, servers, and computers, encryption is something new and modern, right?
On the contrary! Encryption is already used for hundreds or even thousands of years. Since the purpose of cryptography is to create secret communications, a number of evidence has been found of the use of cryptography to hide information in antiquity, such as unusual hieroglyphs found in tombs in Egypt, in Mesopotamian clay plates, messages between Spartan military, Roman army (the famous Caesar Cipher) and so on.
Obviously the methods used were evolving over time along with mathematics, moving from the basic forms of antiquity to ciphers known today as classical as Caesar's cipher and the Enigma machine used in World War II, up to modern cryptographic algorithms. In future in other posts we will see more about some of the classic techniques, but if you want to take a quick look at the subject I recommend the two films about Alan Turing and the Enigma machine, The Enigma (2001) and the Imitation Game (2014)

Source
Digital documents vs Physical documents
Now having a sense of what kind of problems we can encounter, let's start introducing the digital world into history. First let's compare the digital world with the physical world. There are some details that make all the difference in digital security and physical security, which completely changes the approach we have to use, here are some:
Physical documents are better protected than digital documents: Look at the company you work in or companies you know about. In most cases this statement is true. Physical documents are stored in iron file cabinets, Inside a possibly locked room. To get a document you would have to get the key and physically enter that location. In digital world, documents are stored on servers and workstations with outdated versions and cracked operating systems and other services, in most cases without any security knowledge applied to them. I do not even need to comment on how easy it is to access and obtain this data, right? :)
Possibility of identifying the original of a copy: In general, it is possible to identify an original document and a copy physically. For example, if you compare a handmade signature in a document and the copy of that signature will notice small differences. In digital, everything is a sequence of bits and no difference can be noticed between two documents. If you duplicate a document, you can not initially identify the original. Of course we are not taking into account forensic expertise, which can identify the slightest sign of modification, we are talking here of normal people, who would not notice this kind of modification.
Physical alterations leave evidence, digital alterations do not: Another case similar to above, to the eye of an ordinary person, a mark in a document may indicate a modification for example, in a digital document we can not easily identify this evidence.

Source
Majors attacks against information
Active Interception: When an unauthorized party intercepts a message between two parties and reads the contents of messages.
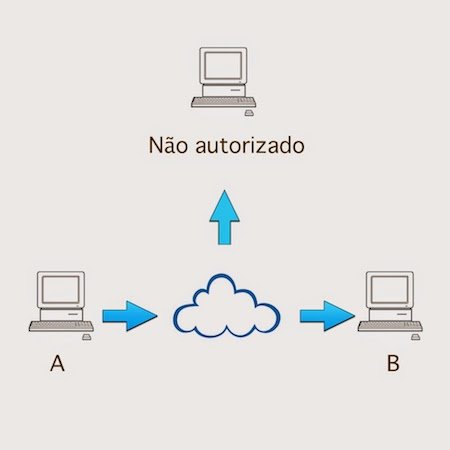
Traffic analysis: Also known as passive interception, where the attacker only observes and analyzes communication looking for patterns.
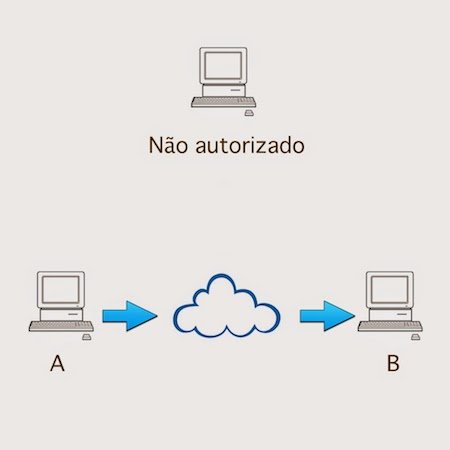
Fabrication: Also known as personification, when the attacker try to personificate one of the parties to obtain information.
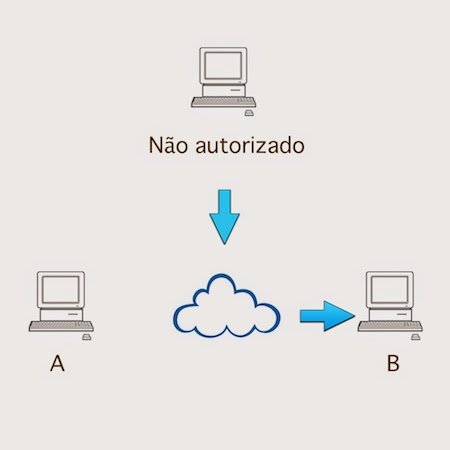
Replay: When the attacker intercepts a valid message from a party and later resends in the hope that the recipient will resend the message response.
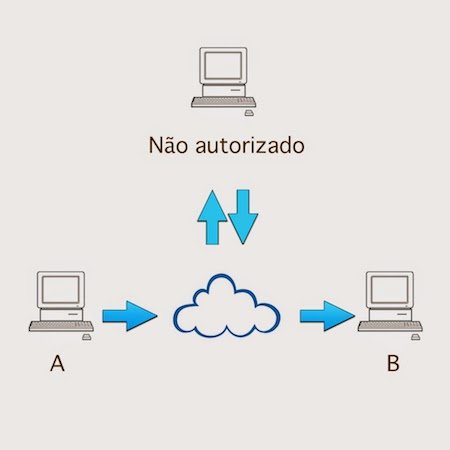
Modification: In this case, the attacker intercepts the message, changes its contents and then forwards the target.












Sneaky Ninja Attack! You have just been defended with a 2.99% upvote!
I was summoned by @deividluchi. I have done their bidding and now I will vanish...
woosh
A portion of the proceeds from your bid was used in support of youarehope and tarc.
Abuse Policy
Rules
How to use Sneaky Ninja
How it works
Victim of grumpycat?
Well done @deividluchi! You successfully guessed the match result.
Click on the badge to view your Board of Honor.
Do not miss the last post from @steemitboard!
Well done @deividluchi! You successfully guessed the match result.
Click on the badge to view your Board of Honor.
Do not miss the last post from @steemitboard!
Congratulations @deividluchi! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on the badge to view your Board of Honor.
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPDo not miss the last post from @steemitboard!
Participate in the SteemitBoard World Cup Contest!
Collect World Cup badges and win free SBD
Support the Gold Sponsors of the contest: @good-karma and @lukestokes