Writing a simple Compiler on my own - Semantic Analysis Theory [C][Flex][Bison]
 GitHub repository:
https://github.com/drifter1/compiler
GitHub repository:
https://github.com/drifter1/compiler
Introduction
Hello it's a me again @drifter1! Today we continue with my Compiler Series, a series where we implement a complete compiler for a simple C-like language by using the C-tools Flex and Bison. This article will be about covering what Semantic Analysis is all about "in theory". Practical stuff will be covered from next time on..The topics that we will cover today are:
- What Semantic Analysis is all about
- Context-Sensitive Grammars (CSG) and Languages (CSL)
- Attribute Grammars (synthesized and inherited attributes)
- S- and L-attributed Syntax Directed Translations (SDT)
Requirements:
Actually you need to read and understand all the topics that I covered in the series as a whole, as these articles will give you access to knowledge about:- What Compiler Design is (mainly the steps)
- For which exact Language the Compiler is build for (Tokens and Grammar)
- How to use Flex and Bison
- How to implement a lexer and parser for the language using those tools
- What the Symbol Table is and how we implement it
- How we combine Flex and Bison together
- How we can pass information from the Lexer to the Parser
- How we define operator priorities, precedencies and associativity
Difficulty:
Talking about the series in general this series can be rated:- Intermediate to Advanced
- Easy
Actual Tutorial Content
What Semantic Analysis is all about
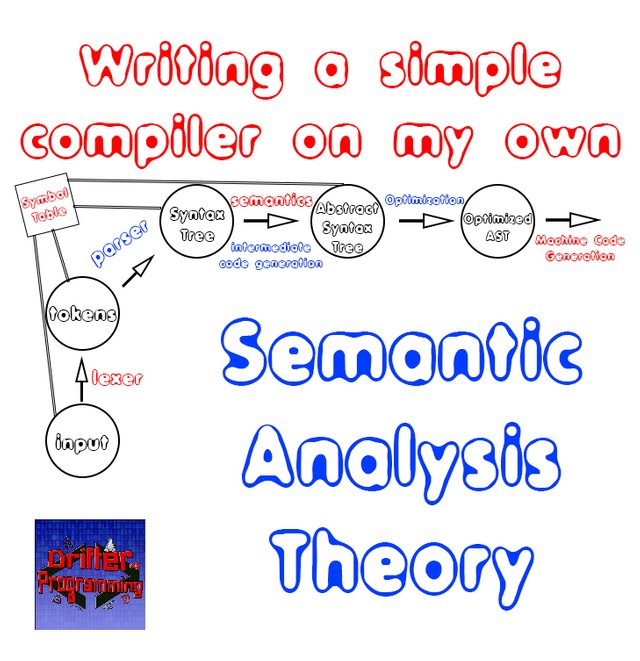
Until now we covered how we turn the character stream that we get from the source program into lexical units or tokens, which is the so called Lexical Analysis. Afterwards, we combined these tokens to form the syntax of the language, which is the Syntax Analysis part of Compiler Design. Doing all that we are not quite finished, as the parse- or syntax-tree constructed in the current phase, doesn't really evaluate the tokens used in the parsing process.You might remember that:
- Lexical analysis uses a regular grammar/language, which can be expressed using regular expressions and in the end turns into a deterministic finite automaton (DFA)
- Syntax analysis uses a context-free grammar/language, which can be expressed using the so called production rules, which in the end become push-down or shift-reduce automata (Bison uses LALR)
- a token is valid (something that the lexer does for it - sortoff)
- a token was declared before being used
- a token was initialized before being used
- a operation performed on a specific token is allowed or not
- Scope resolution, which helps us recognize if an variable is being accessed out of scope, if a variable has been declared multiple times in the same scope and if an variable is undeclared
- Type checking, which let's us recognize type mismatch, identifier misuse, actual and formal parameter mismatch etc.
- Array-bound checking
One last thing that I would like to mention is that the semantic analysis can be of two forms:
- Static: Semantics are checked at compile-time
- Dynamic: Semantics are checked at run-time, using generated semantic error-checking code
Context-Sensitive Grammars (CSG) and Languages (CSL)
From the Chomsky hierarchy, we know that context-sensitive languages (CSL) are more powerful than the context-free languages (CFL) used for the syntax analysis. Such languages can describe more grammars, but are much more difficult to work and implemented in code, cause they need a linear bounded automaton, which is a restricted form of a Turing machine.Either way, a CSG has the following 4-tuple:
G = {N, Σ, P, S}, where:
- N is the set of non-terminal symbols
- Σ is the set of terminal symbols
- S is the start symbol of the production
- P is a finite set of productions
α -> β
or
α1Aα2 -> α1βα2
where α and β can be terminal or non-terminal symbols.
In context-free grammars the left-part was always a non-terminal!
Attribute Grammars
Getting into an CSG would make the compiler design procedure even more difficult and so we needed to find another way. To provide context-sensitive information to non-terminal symbols, we extend the context-free grammar and turn it into a so called Attribute Grammar. Such a grammar is a special form of CFG, where additional information, in form of attributes, is appended to one or more of the non-terminals. These attributes are well-defined domains of values, which can be integers, floats, characters, strings or even expressions. I guess that you see now that an CSG is not actually needed, cause adding attributes to non-terminals, we provide semantics to an CFG, helping us specify not only the syntax, but also the semantics of a programming language. This final form of parse-tree, which also contains attributes, is mostly called a decorated parse-tree.Talking about the parse-tree of the Attribute grammar, we understand that we can easily use and pass values or information between the different nodes of this tree. The only restriction we have is that information can only be passed directly between nodes of the same production rule, while parsing. After finishing the syntax Analysis, we can off course access all the rules as we like! These attributes will be accessed and modified in the actions of each grammar production of non-terminals. Depending on how exactly attributes get their values, we divide attributes into two categories:
- Synthesized attributes
- Inherited attributes
Synthesized attributes
Such attributes get values only from attribute values of their child nodes. So, when having a rule A -> BC, A is only taking values from it's childs B and C. The values of B and C are synthesized into A. So, such attributes cannot take values from their parent nodes or any sibling nodes. This all shows us that synthesized attributes can only flow upwards in the syntax tree.Inherited attributes
Such attributes can get values from parent and/or siblings. So, in the previous example rule, B could take a value from A and/or C. In the same way, C could take a value from A and/or B.Syntax Directed Translations (SDT)
For the Syntax Analysis we define the following two terms:- Expansion: when a non-terminal is expanded to terminals according to a grammatical rule
- Reduction: When a terminal is reduced to it's corresponding non-terminal.
- S-attributed SDT
- L-attributed SDT
S-attributed SDT
Such an SDT uses only synthesized attributes, which is why we call it S-attributed. The semantic rules in a S-attributed SDT are written right after the production (right hand side). This shows us that the attributes can only be evaluated in bottom-up parsing, cause only then the parent nodes can get the values of the child nodes they depend on.L-attributed SDT
Such an SDT uses both types of attributes, with one very important restriction of not taking values from right siblings. So, a node can get values from it's parent, child and "left" sibling nodes. Considering the example of before (A -> BC), A can of course take values from B and C (synthesized), B can only take a value from A (C is to the right!) and C can take a value from both A and B! This shows us that L-attributed SDT's are evaluated depth-first and left-to-right. This is the most practical and essential grammar property for an one-pass compiler, cause semantic rules can therefore be applied directly during parsing. There is no need for keeping the entire parse-tree in memory!I guess it's also worth noting that S-attributed SDT's are also L-attributed SDT's, BUT an L-attributed is not always an S-attributed SDT! So, the L-attributed definition encloses the S-attributed definitions. The way Bison works (LALR parser) allows the use of both types, which means that the grammar that we created in Bison can be extended into an L-attributed grammar!
RESOURCES
References:
The following helped me refresh my knowledge around Semantics:- https://www.tutorialspoint.com/compiler_design/compiler_design_syntax_analysis.htm
- https://www.tutorialspoint.com/compiler_design/compiler_design_semantic_analysis.htm
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/toc-context-sensitive-grammar-csg-language-csl/
- https://www.cs.fsu.edu/~engelen/courses/COP402003/notes4.html
- https://web.cs.wpi.edu/~kal/courses/cs4533/module4/mysa.html
Images:
All of the images are custom-made!Previous parts of the series
- Introduction -> What is a compiler, what you have to know and what you will learn
- A simple C Language -> Simplified C, comparison with C, tokens, basic structure
- Lexical Analysis using Flex -> Theory, Regular Expressions, Flex, Lexer
- Symbol Table (basic structure) ->Why Symbol Tables, Basic Implementation
- Using Symbol Table in the Lexer -> Flex and Symbol Table combination
- Syntax Analysis Theory -> Syntax Analysis, grammar types and parsing
- Bison basics -> Bison tutorial actually
- Creating a grammar for our Language -> Grammar and first Parser
- Combine Flex and Bison -> lexer and parser combined
- Passing information from Lexer to Parser -> Bug Fix, yylval variable, YYSTYPE union, Setting up the Parser, Passing information "directly" and through the symbol table (special case) with examples.
- Finishing Off The Grammar/Parser (part 1) -> Adding the missing grammar rules, small fixes
- Finishing Off The Grammar/Parser (part 2) -> Operator priorities, precedencies and associativity, complete example file (for testing), grammar rule visualization, finish off grammar/parser
Final words | Next up on the project
And this is actually it for today's post! I hope that I explained everything as much as I needed to, meaning that you learned something out of it.Next up on this series are:
- Semantic analysis (visualization of semantics for our grammar rules, "extending" the symbol table for scope resolution and creating/using semantic rules in Bison)
- Intermediate Code generation (Abstract Syntax Tree)
- Machine Code generation (MIPS Assembly)
So, see ya next time!
GitHub Account:
https://github.com/drifter1
Keep on drifting! ;)
Thank you for your contribution @drifter1.
We've been reviewing your tutorial and we've just suggested this below:
Tutorial very well structured and explained. Excellent work in the development of this article.
We are waiting for more tutorials.
Your contribution has been evaluated according to Utopian policies and guidelines, as well as a predefined set of questions pertaining to the category.
To view those questions and the relevant answers related to your post, click here.
Need help? Write a ticket on https://support.utopian.io/.
Chat with us on Discord.
[utopian-moderator]
Thank you for your review, @portugalcoin!
So far this week you've reviewed 8 contributions. Keep up the good work!
This post has been voted on by the SteemSTEM curation team and voting trail in collaboration with @curie.
If you appreciate the work we are doing then consider voting both projects for witness by selecting stem.witness and curie!
For additional information please join us on the SteemSTEM discord and to get to know the rest of the community!
Hi @drifter1!
Your post was upvoted by @steem-ua, new Steem dApp, using UserAuthority for algorithmic post curation!
Your post is eligible for our upvote, thanks to our collaboration with @utopian-io!
Feel free to join our @steem-ua Discord server
Hello! Your post has been resteemed and upvoted by @ilovecoding because we love coding! Keep up good work! Consider upvoting this comment to support the @ilovecoding and increase your future rewards! ^_^ Steem On!

Reply !stop to disable the comment. Thanks!
Hey, @drifter1!
Thanks for contributing on Utopian.
We’re already looking forward to your next contribution!
Get higher incentives and support Utopian.io!
Simply set @utopian.pay as a 5% (or higher) payout beneficiary on your contribution post (via SteemPlus or Steeditor).
Want to chat? Join us on Discord https://discord.gg/h52nFrV.
Vote for Utopian Witness!