STEEMIT CRYPTO ACADEMY [BEGINNERS’ LEVEL] | SEASON 3 WEEK 4 | BLOCKCHAIN FORKS BY @AWESONONSO | HOMEWORK POST BY @A-LASS-WONDERS🙋♂👇
Greetings from @a-lass-wonders!! 🙏
Hello, my fellow steemians!
Today I am planning to post my homework task article for Steemit Crypto Academy [Beginners’ Level] | Season 3 Week 4 | Blockchain Forks assigned by Professor @awesononso.

If you need to get an idea about BLOCKCHAIN FORKS, I would like to invite you all to read this article.
HOMEWORK TASKS
1.What is a Fork? (In your own Words)
2.Explain in detail what a Hard Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain)
3.Explain in detail what a Soft Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain)
4.What are the differences between Hard Forks and Soft Forks?
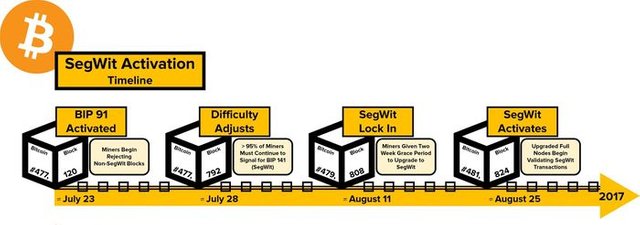
5.Explain the following Bitcoin Forks and explore the blockchain where necessary. Indicate if they are hard forks or soft forks.
• Bitcoin Cash
• Segregated Witnesses
6.Write on the Steem and Hive Hard fork and show similarities in their Genesis Blocks (Provide screenshots).
I will explain above homework tasks one by one.
1.What is a Fork? (In your own Words)
WHAT IS A FORK?
Every cryptocurrency has its own protocol that everyone in the network should follow. Below I mentioned some examples for your reference:
- Block size
- Reward amount that miners, harvesters, or other network participants receive
- Fee calculation method
Also, we know that since all cryptocurrencies are software projects, their development will never be fully finished. Because developers of these projects will work and try to fix issues and also, they will take their maximum effort to increase the performance.
Sometimes these updates will tend to initiate an argument between most influential stakeholders (mainly miners and developers) due to disagreement with the above-mentioned updates. At this point, some members can decide to go their own way and initiate a fork.
See above image of real fork. It has one long handle, and then it divides into a bunch of branches. Same happens in the above-mentioned cryptocurrency fork.
2. Explain in detail what a Hard Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain)
Actually, two types of forks can happen in a cryptocurrency:
- HARD FORK
- SOFT FORK
First, I will explain about HARD FORK.
Simply, HARD FORK is a permanent separation from previous version of the blockchain. In this scenario, nodes which are running older version won’t accept transactions created on the new version.
This means two different versions of the blockchain will create. One version will keep continue to run on the old blockchain while the other version initiates to operate on the new path.
As we all know, there are two pillows in all cryptocurrencies.
- The Protocol (set of rules)
- The Blockchain (which stores all the transactions that have ever happened)
As I mentioned earlier, after a HARD FORK happened, the team which is created new version of blockchain will start their works by copying the original protocol code. Actually, I would like to specially highlight that to copy this original protocol code this chain must be completely open-source. After copying this code, they can make changes to it.
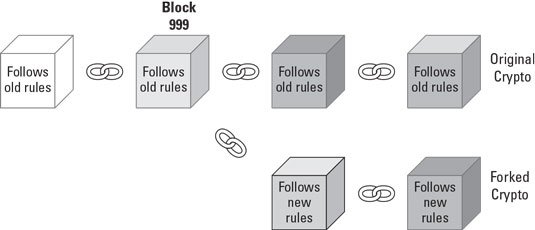
After making their desired changes to the blockchain, they can define a point (separation point) to active their fork. Actually, they define a block number to start the forking. Please find above mentioned figure to get a better idea.
As you can see in the figure, the team which is created new version of blockchain can tell that their fresh protocol will be active once the BLOCK 999 is published to the cryptocurrency blockchain. When the currency reaches that block number, the community splits in two.
From this point onwards, one version will keep continue to run on the old blockchain while the other version initiates to operate on the new path. Simply it means that, both groups can starts adding fresh blocks to the fork it supports.
Also note that both blockchains are incompatible with each other at this point. Nodes won’t ever interact with each other again as well. Actually, they don’t even acknowledge the nodes or transactions on the old blockchain. So that means hard fork is a backward-incompatible upgrade to the blockchain.
Now I will brief you about a real HARD FORK that happened in recent history.
BITCOIN VS BITCOIN CASH FORK
Since the bitcoin blockchain is an open-source software, this hard fork happened in 2017.
The major reason for this hard fork is an argument between team members regarding the of size of each block in bitcoin’s blockchain.
Opinion of the Bitcoin core developers was that increasing bitcoin’s block size from 1 Mb to 2 Mb is enough, while some members of the team argued on this point. Their opinion was to increase it to 8 Mb.
Differences between two cryptocurrencies
| Point | Bitcoin | Bitcoin Cash |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Fee | High | Low |
| Transaction Processing Speed | Slow | Fast |
| Transactions per second | Low | High |
| Token price | High | Low |
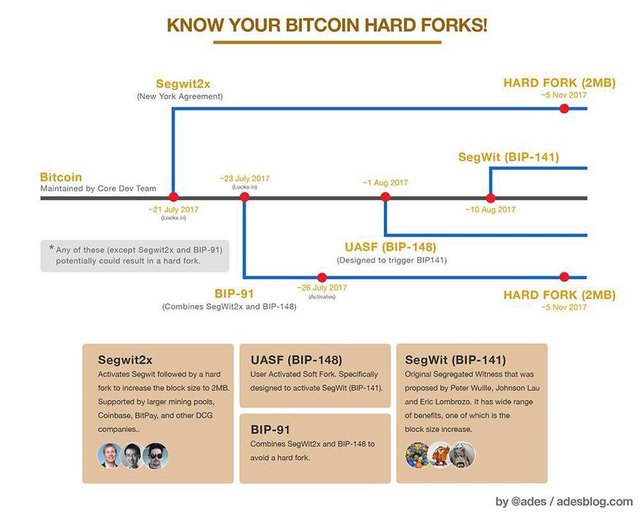
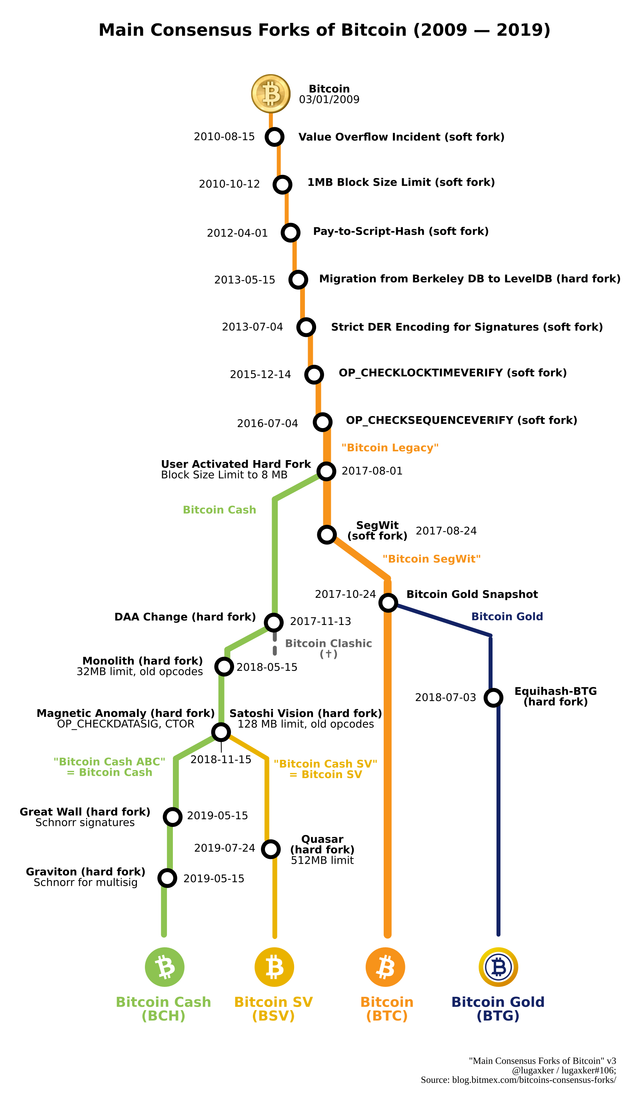
Hope you had an idea about this HARD FORK now. I have attached below images of bitcoin fork history just for your further knowledge.
3. Explain in detail what a Soft Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain)
Actually, I can give a short and sweet but funny explanation for this SOFT FORK. It is some sort of a breakup where you remain friends with your ex-girlfriend. HA! HA!
If I technically elaborate more, when the developers decide to fork the cryptocurrency and make the changes compatible with the old one, this situation is called as SOFT FORK.
Let’s refer below image for further clarifications.
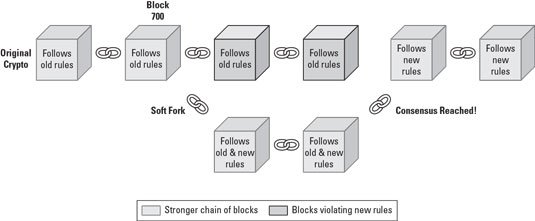
As you can see in the figure, the team can tell that their soft fork will be active once the BLOCK 700 is published to the cryptocurrency blockchain. In this case, the majority of the blockchain may support the stronger chain of blocks following both the new and old rules.
Actually, soft fork is a forward-compatible change to the rules. Because as I mentioned earlier, the old version will continue to accept blocks which are publishing from the newly updated blockchain protocol, even though there is a change in the rules because of the new updates. That means soft fork is totally different than the hard fork, because soft fork maintains the old blockchain by maintaining two paths with different sets of rules.
Now I will brief about a real SOFT FORK happened in recent history.
Segregated Witness (SegWit) fork is a perfect example for the SOFT FORK. This fork happened after the Bitcoin/Bitcoin Cash HARD FORK.
This update was taken place to change the format of blocks and transactions. Since this is a soft fork to the blockchain, old nodes could still validate blocks and transactions.
4.What are the differences between Hard Forks and Soft Forks?
| SOFT FORK | HARD FORK |
|---|---|
| An update of a cryptocurrency protocol’s software | A radical change to a network’s protocol |
| Miner software update compatible with old versions | Major software update incompatible with old versions |
| Backward compatible | Backward incompatible |
| Consensus rules are more restrictive | Consensus rules are less restrictive |
| Compatible with legacy rules | Incompatible with legacy rules |
| Friendly to Users | Friendly to Developers |
5. Explain the following Bitcoin Forks.
Since I have already spoke about this, I am planning to mention some important points of this question.
Bitcoin Cash
WHY USE BITCOIN CASH?
- We can send or transfer money to anywhere in the world without any charge.
- We can control our own money that means we don’t need anyone’s approval.
- We have higher privacy and also can operate anonymously.
- There are lots of exclusive discounts.
- This is a scarce digital currency with a Known Fixed Supply
BENEFITS FOR MERCHANTS
- Ultra-Low Fees
- No Charge backs
- New Customers
- Free Marketing and Press
Segregated Witnesses
We already know that SegWit is a soft fork to the bitcoin blockchain and this means it introduces very important backward compatibility. In this fork, block is measured using “units” instead of bytes so that block can hide its size increment.
Also, the witness signature data would be separated from the Merkle tree recordand moved to the end. In here, each byte of it would only count as one quarter of a "unit".
Purpose of doing all these things was changing the size of block.
6. Write on the Steem and Hive Hard fork and show similarities in their Genesis Blocks (Provide screenshots).
First, let’s take a look on the Interfaces.
STEEMIT PLATFORM MAIN PAGE 
HIVE BLOG PLATFORM MAIN PAGE Here we can see similar interfaces in both platforms.
GENESIS BLOCK
Below are the Genesis block of Steem.
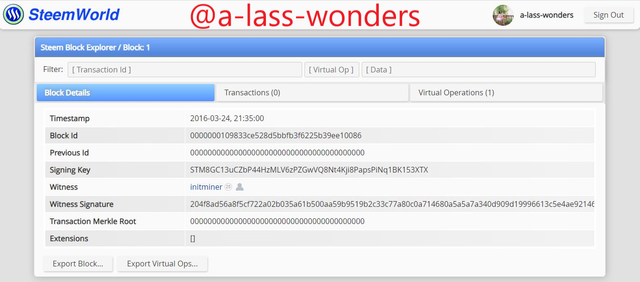
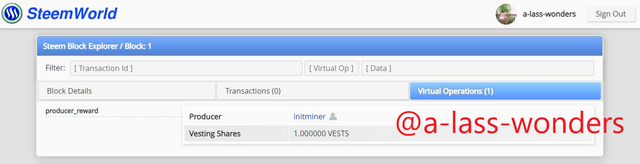
GENESIS BLOCK OF STEEM Below is the Genesis block of Hive.
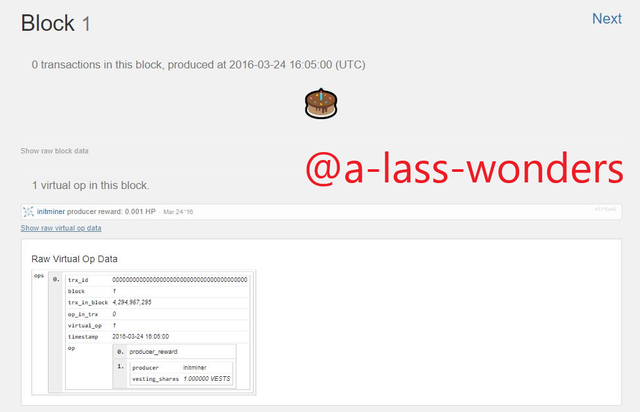
GENESIS BLOCK OF HIVE Above images clearly shows that the producer and vesting shares are equal in both blockchains.
Furthermore, I took another block to prove these similarities. Here are the screenshots of the Block 10000 of both blockchains.
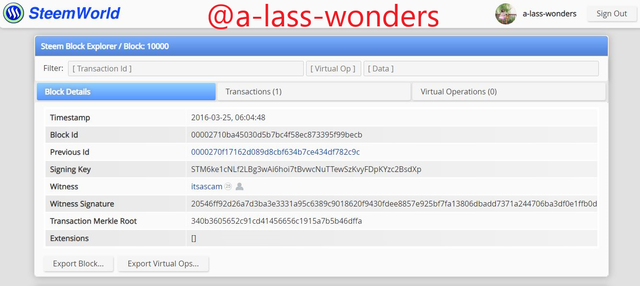
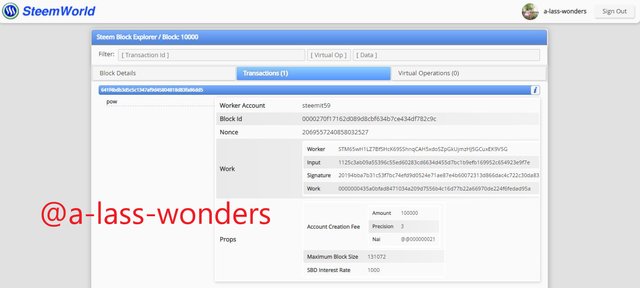
BLOCK-10000 OF STEEM We can see that producer of the Steem block-10000 is @itsascam.
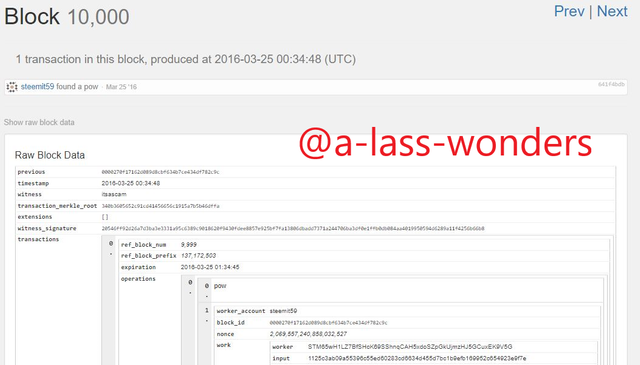
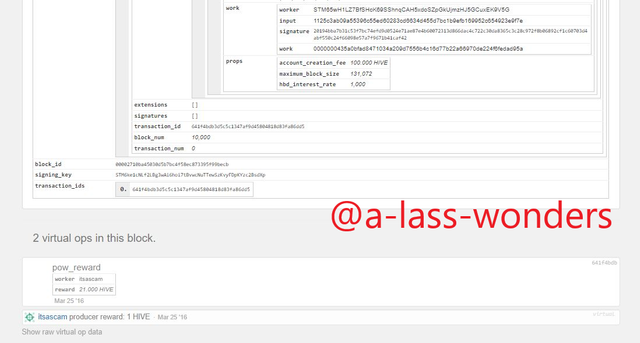
BLOCK-10000 OF HIVE We can see that producer of Hive block-10000 is also @itsascam.
CC: @awesononso
Thank you all for spending time to read my Homework post.
GOOD LUCK AND HAVE A NICE DAY!!
- My achievement 01 post: here.
- My achievement 02 post: here.
- My achievement 03 post: here.
- My achievement 04 post: here.