Create a RESTful API with Flask #1 : RESTfull Basic structure, Access the API as on the Client and Server, Create a Models
Repository
What Will I Learn?
- RESTfull Basic structure
- Access the API as on the Client and Server
Requirements
- Basic Python
- Install Python 3
- Install flask-restful
Resources
- Python - https://www.python.org/
- Flask - http://flask.pocoo.org/
- Peewee - http://docs.peewee-orm.com/en/latest/
Difficulty
Basic
Tutorial Content
Hi all, in this tutorial I will share how to create a RESTful API using FLASK. for those of you who don't know what API is. The API is a Application Programming Interface (API), So we will not create a website display. We will create a program that can be used by anyone. So later our program can be consumed or can be accessed from all platforms. When we use Gmail, before we use Gmail we must first log in. the authentication system is provided by Gmail so we can log on their side. this tutorial will demonstrate the RESTfull API system in detail using Flask. well, let's just start this tutorial.
RESTful basic structure in Flask
What we will learn first is the basic structure of the API in the flask. For those of you who don't have experience with API, I suggest you learn it first. In this tutorial I will not explain what is Flask ?, you can learn Flask in the curriculum section of this tutorial.
- Initialization
to make a RESTful API we need to use the flask-restful package. For those of you who haven't installed the flask, configure it in the flask. You can follow my previous tutorial. To use the flask-restful module we have to install it first like the following.
Install flask-restful
pip install flask-restful
After we have finished installing it, we can use the module in the Flask application as follows:
api.py
from flask import Flask
from flask_restful import Resource, Api
app = Flask(__name__)
api = Api(app)
class User(Resource):
def get(self):
return {'name' : 'Millea'}
api.add_resource(User, '/user')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug = True)
Use flask_resfull in Flask: We will use two functions contained in the flask_restful module, Resource and Fire
from flask_restful import Resource, Apiand use the Fire method in Flaskapi = Api(app).Class for API: I will create a class for the API, to make the API class on the flask, we have to pass the Resource parameter to that class like this
class User(Resource):.I will create a get method that we will use to test whether the API is running properly. We can define the
get()function for the get methoddef get(self):.API endpoint: Now I will make an endpoint URL for the API. I use the
add_resource()function. In this function there are two parameters. The first parameter is the function we will use and the second parameter is the URLapi.add_resource(User, '/user').To run the program that we created, we can run
python api.py
We have done to make access endpoints in the API. We can see what we return in the '/user' endpoint.
Access the API as on the Client and Server
Of course, in reality, the API will be created on the server-side and will be accessed on the Client-side. I will use Postman to consume the API that we created on the Server side. I will use two methods (get and put) that we will use to test the server side and client side on the API that we make.
api.py
from flask import Flask, request
from flask_restful import Resource, Api
app = Flask(__name__)
api = Api(app)
users = {}
class User(Resource):
def get(self, user_id):
return {'name' : users[user_id]}
def put(self, user_id):
users[user_id] = request.form['user']
return {'name' : users[user_id]}
api.add_resource(User, '/user/<string:user_id>')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug = True)
Import request function: Because we will consume the API on our client, we will use the request function in the module flask. to import it
from flask import Flask, requestGet method: In the get method I will pass the user_id parameter and then we will store the value in the
users = {}and simply pass the value from user_idreturn {'name' : users[user_id]}.Put method: In the put method we will input data and receive requests from the form frontend
users[user_id] = request.form['user'].
- Passing parameter: I will pass parameters to the API endpoint to be more dynamic like this
api.add_resource(User, '/user/<string:user_id>')We can determine what data type to pass on the endpoint, in this tutorial I pass the type string and the key is user_id.
We will test the two methods we use in the user class.
1. PUT Method
Endpoint : http://127.0.0.1:5000/user/1
http://127.0.0.1:5000/user/2
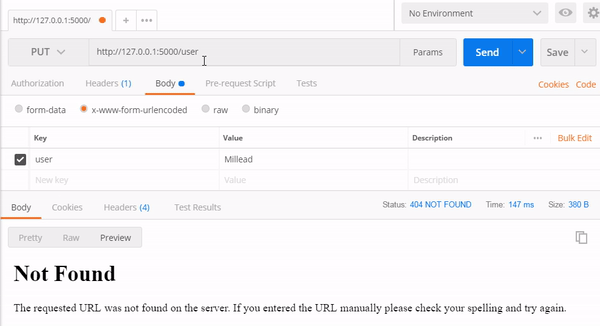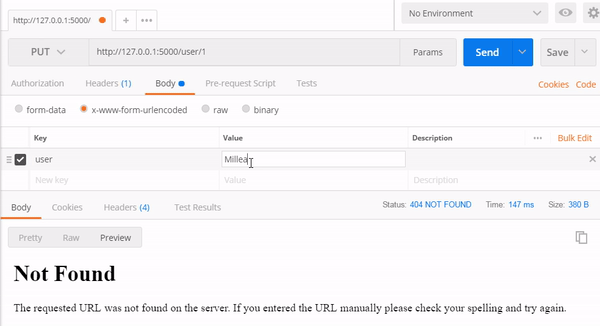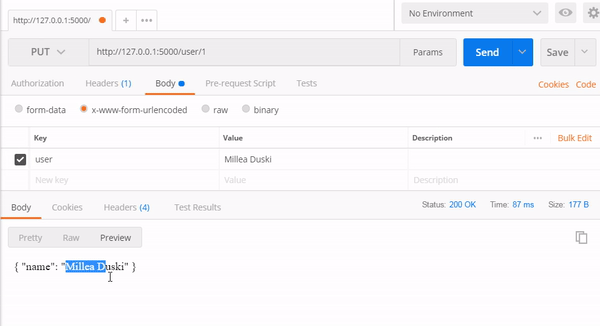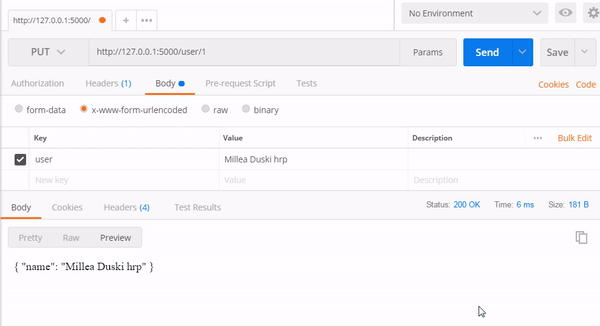
2.GET method
Endpoint : http://127.0.0.1:5000/user/1
http://127.0.0.1:5000/user/2
.gif)
As we saw in the picture above we have successfully run the GET and PUT methods. Next, we will discuss the database.
Make a model
Of course, to create an API is not as easy as we have done above, I will start to interact with the database. Models are an important part of database processing because the model is an abstraction from our database table. In python, I will use the peewee database. to install it we can do it like below:
pip install peewee
If you successfully install it there will be a message like a picture below:
After installing I will create a file with the names models.py for our models. The following is the code:
models.py
import datetime
from peewee import *
DATABASE = SqliteDatabase('coments.db')
class Message(Model):
context = TextField()
create_at = DateTimeField(default=datetime.datetime.now())
class meta:
database = DATABASE
Import peewee: Of course, we will import the peewee that we will use as a database, we can import all function in peewee like this
from peewee import *and we can enter the database by using theSqliteDatabase()function then select databaseSqliteDatabase('comments.db')Create a class in the model: We can take classes in the model with the required parameters, that is, a model like this
class Message(Model):. In the class message, I will create two columns in the database which is the first context and the second is created_at.Add the meta class: Then we will add the meta class to define the database that we will use, in this tutorial our database is defined in the DATABASE variable. So we can do like this
database = DATABASE.
Well to make models we only need to do the image above. we make models with the OOP concept so later we don't need to create a lot of new files for each model, we just need to create a new class to represent a database table. in the next section, I will migrate to the database. thank you for following this tutorial. hopefully, it is useful for you.
Curriculum
- Web development with flask
Web developement with python #1 : Flask initialization and Routing system
Web development with python #2 : Templating jinja2 and Method POST on routing system
Web development with python #3 : Get method, Query parameter and Navigate Routing
Web development with python #4: Store cookie and Get cookie in template
Web development with python #6 : Use flash message and combine it with framework boostrap
- File in python
File in python #1 : Read file and Write file and Modes file
File in python #2 : The interaction between user input, Read CSV file
File in python #3 : Write CSV file, Read and Write JSON file
- Class-based views
Tutorial Django - Class based view #2 : Use Class based view method and Get and Post method
Thank you for your contribution @duski.harahap.
After reviewing your tutorial, we suggest the following points:
There are already several online tutorials explaining the subject of your tutorial. Before doing a tutorial, please check if there is already much information about what you will write.
You have done some tutorials and you know that it is important for the code section to contain comments.
In the next tutorial try to bring something innovative to the open source community.
Your contribution has been evaluated according to Utopian policies and guidelines, as well as a predefined set of questions pertaining to the category.
To view those questions and the relevant answers related to your post, click here.
Need help? Chat with us on Discord.
[utopian-moderator]
Thank you for your review, @portugalcoin! Keep up the good work!
Congratulations @duski.harahap! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click here to view your Board
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPDo not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Hi @duski.harahap!
Your post was upvoted by @steem-ua, new Steem dApp, using UserAuthority for algorithmic post curation!
Your post is eligible for our upvote, thanks to our collaboration with @utopian-io!
Feel free to join our @steem-ua Discord server
Hey, @duski.harahap!
Thanks for contributing on Utopian.
We’re already looking forward to your next contribution!
Get higher incentives and support Utopian.io!
Simply set @utopian.pay as a 5% (or higher) payout beneficiary on your contribution post (via SteemPlus or Steeditor).
Want to chat? Join us on Discord https://discord.gg/h52nFrV.
Vote for Utopian Witness!