The Dynamics of Power - Part 5 - Decision-making and Leadership
Social Reality: Violence, Power, and Change
The Dynamics of Power - Part 5 - Decision-making and Leadership
On this series on the Dynamics of Power in Part 1, we talked about the Legitimacy of Authority, in Part 2 the Models of Leadership, in Part 3 the Characteristics of Leadership, Part 4 was about the Interrelationship in Leadership, and this post is the last post about the cycle Leadership talking about Decision-making and Leadership.
The next post will be about the cycle of Power by studying its effects on society and people.
One of the important parts of Leadership can be seen in the process of decision-making of the Leader.
A Leadership style refers to a leader's characteristic behaviors and how he makes decisions, when directing, motivating, orienting, and managing a group of people.
We are going to present some theories on Decision-making and Leadership: the Participative Model, the Rational Decision model, and the Transformational Model.
1- The Participation Model
In 1973, Vroom and Yetton introduced the Participation Model that can help us to find the best decision-making approach and the leadership style to assume related to the situation in which it occurs.

The following codes represent the five possible decision-making processes, using the following three models, where the first two are subdivided:
1.1 - The Autocratic Model (A) that can show two subgroups:
1.1.1 - Autocratic (A1):
Is expressed in the using the pre-information they already have to make decisions, without requiring any further input from the team.
1.1.2 - Autocratic (A2):
Consult the team to obtain specific information needed, and then he/she makes the final decision.
1.2 - The Consultative (C) Model that has 2 subdivisions too:
1.2.1 - Consultative (C1):
Inform the team of the situation and ask for opinions individually, but they don't meet the group together for the discussion. They make the final decision.
1.2.2 - Consultative (C2):
Joins the team together for the group discussion about the issue, asks suggestions, but they still do the final decision.
1.3 - The Collaborative Model (G):
Work with the team to attain a group consensus. The main role of the leader is almost facilitative, and support the team members to reach a final decision agreed by the group.
he Collaborative and Consultative style approach is a better solution when there is need of information from the group to solve problems, defining difficult problems and where self-motivation is a must or we have time to get a group decision.
The Autocratic Style is suitable when, the leader's knowledge is bigger then the people, he/she have self-confidence and is sure about the acceptance of their decisions or if there is not enough time available.
1.4 - Leadership: Influence versus Imposition
The Influence of a Leader can be positive if the led bring their own motivation, and it is negative when there is an imposition.
In Leadership it is possible to impose certain actions on a subordinate, using the Power to achieve it, but it is impossible to impose the motivation to each one in the practice of the action.
It is the motivation that the Leadership has to improve, and it is not enough to achieve the objectives of the organization, unless that the actions developed by the subordinates are executed by their free will and determination.
2 - The Rational Decisional Model
In the Robert Tannenbaum and Warren H. Schmidt model, the Leadership Style is defined as a continuum of seven forms of decision-making, ranging from a maximum of a full centralization of authority in the leader to the total delegation of authority to the group of subordinates.
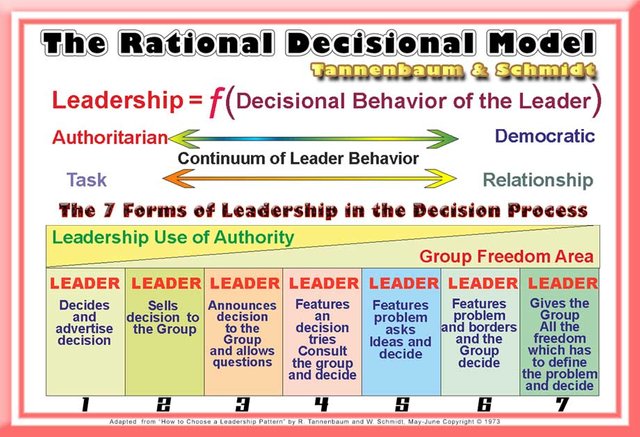
This theory allows us to quickly identify the type of leadership that is being pursued, just by looking at each Leader's decision-making process.
"Teamwork is a strategic decision." - Patrick LencioniRobert Tannenbaum and Warren H. Schmidt studied the forces influencing Leadership Style and concluded that in choosing the type of leadership, the leader must take into account three types of forces, namely:
2.1 Forces that constrain Leader:
The system of values, personal growth, and beliefs
Trust in your employees
Personal inclinations on how to lead
The feeling of safety in situations uncertainty
2.2 - Forces that Operate in Employees:
-Need for freedom or higher guidance
-Disposition to take on responsibilities
-Security uncertainty
-Interest in problems or work
-Knowledge and experience to solve problems
-Expectations of participation in decision making
2.3 - The Forces that Operate in the Situation:
-Type of organization, values, beliefs and policies
-Performance of the subordinate group
-Time Constraints
-Complexity of functions and knowledge required
"Information is a source of learning. But unless it is organized, processed, and available to the right people in a format for decision making, it is a burden, not a benefit." - William Pollard
3 - Transformational Leadership
Transactional leaders guide or motivate their followers in the direction of established objectives and goals, identifies the roles and task requirements or in some cases corrects fails and errors.
Transformational Leaders provide individualised attention and intellectual stimulation, and possess charisma.
Howell & Hall-Merenda in 1999 studied the effect of Transformational Leadership under close or remote situations.
Strangely they found out that Transformational Leaders have higher performances with followers in close rather than a remote situations.
Passive leaders have less performance with proximity rather than at a remote situation.
Burns in 1978 defined that the Transformational Leadership is conceived a generation process capable of using the Power to transform into social systems.
For him, Transactional Leadership is a process of influence that acts on the level of motivation of the followers to achieve their own goals. Unlike transactional leadership, transactional does not produce social change.
I'm going to mention an interesting study about the gender differences in Men vs Women.
Payne and Cangemi in 1997 discovered that after a proper training for a task, men and women perform the same behaviors and that before or in the absence of training, men and women perform stereotypical gendered behaviors.
Watson and Hoffman in 1996 saw that women show less confidence and low satisfaction with their performance than men, even though they didn’t differ in the accomplishment.
4 - The Boss and the Leader
The Boss | The Leader |
| The Boss says "I", "Me" and "Myself" | The Leader says ‘We", "Us", and "Ourselves" |
| The Boss drives and dominate people | The Leader coaches and empowers people |
| The Boss depends on authority and coercion | The Leader sustains on influencing and motivating people |
| The Boss inspires fear and imposition | The Leader inspires enthusiasm and goodwill |
| The Boss fixes problems blaming someone | The Leader finds solutions for the problems |
| The Boss knows how things are done | The Leader shows how to do things |
| The Boss accepts the system | The leader challenges the system |
| The Boss thinks on the short term | The Leader sees on the long term |
| The Boss has only a Mission | The Leader has a Vision to fulfill the Mission |
| The Boss maintain | The Leader develop |
Last posts in this series on Social Reality: Violence, Power and Change
Introduction:
Social Reality: Violence, Power and ChangeA - Violence:
An Introduction to ViolenceThe Concepts of Violence, Aggression, and Aggressiveness
The Theories on Violence
The influencers of Violence -Part One - Culture and Social Context
The influencers of Violence -Part Two - Social , Cognitive and Environmental Factors
The ascend of Today's Violence
B -Power:
What is Power? - IntroductionThe Nature of PowerThe Dynamics of Power:
- Part 1 - The Legitimacy of Authority
- Part 2 - The Models of Leadership
- Part 3 - Characteristics of Leadership
- Part 4 - The Relation in Leadership
- Part 5 - Decision-making and Leadership - this post
Articles from the next series of posts about Social Reality, Violence, Power and Change:
The Effects and Consequences of PowerC - Change:
Change and CultureThe Theories and conceptualization of Change
Factors determining Change
The ways of Change
Social Change
Very wonderful article
Energy and power are important things in modern life
I very much like the chart at the end!
"I" and "We" is something that I noticed and experienced especially at school or University back then. So-called "group work" always ended up with one or two acting bossy and always talking in first person. They even stole ideas from others, and only because the teacher is acting bossy and "I" as well, they had the guts to market the ideas of others as their own because they knew that the teacher would praise them and not the creator of the idea. Bossiness led by ego always comes at the cost cooperativeness. AUTHENTIC cooperativeness.
But I can only reiterate over and over, those who cry loudest have the biggest fear to become cried at themselves ;)
We are in an Era that people must understand that to follow leaders in decentralized systems is not a good strategy for self-autonomy and freedom, because sooner or later they will impose their "belly buttons" to the people following them.It's a time to understand the total delusion of collectivist power.
What we need is "Agents of Change", because they try to change themselves with the same principles they want to act.
They are guided by what they think is the best solution for all the members of a community and have the "moto" of facilitating an environment for the spread of autonomy, self-awareness, and free speech, as the keys for personal freedom that the Agent believe in the first place.
Leadership is very important for a nation but it be a true leadership either people suffer. And now what we can see, true leadership build a country peaceful and greedy leaders announce civil war.
Leaders of mechanistic culture who want to survive in the new Age of Globalization need to start thinking as agents of change and break with outdated conceptions of centralized organizational culture.
The role of the new agents of change for decentralization is to assist decentralized communities, to explore their common goals, to overcome obstacles, to create new values, attitudes and behaviors through the processes of identification and internalization of community members.