The ascend of today's Violence
Social Reality: Violence, Power, and Change
The ascend of today's Violence
Today we are going to talk about the Violence of everyday's life focused on the aspects of family environment and the violence on the mainstream media and finish by showing the therapeutic possibilities to treat Violence.1- Day-to-day Violence
1.1 - Family Violence
The family should be a refuge, warm a calm environment where the individual could feel he was protected and defended from the outside aggression of the world.
The family is based on affection but also on rejections that can feed aggressiveness, and structure the future approach to violence in adulthood.
Let's now analyze some types of family violence influencing the genesis of aggressive behavior.
1.1.1 - Parental aggression.
Parental aggression can have several forms of verbal and physical aggression, and other extreme behaviors like abandonment, undernourishment, burning, sexual abuse, and permanent harassment.
1.1.2 - Family conflicts.
Constant physical and verbal aggression or violence between the couple will influence the** aggressive models of behavior** in childhood and youth.
1.1.3 - Violence on old people in the family
In some families old people is subject to body harming violence, to be extracted from their assets and money or even abandonment.
1.2 - Aggressive parents profiling
Some studies have concluded that people that were beaten as children normally will beat their kids when they are parents and have a personality associated with, bad self-esteem and image, failed expectations in relation to children and excessive attention to be loved.
Childhood and youth aggression facilitate the process of becoming an "aggressor" in adult life.
This types of personality want to repair their infancy, by giving them what they didn't have, at the same time demanding from the kids the love and parenting they didn't have, but they finish by revenging the suffering of their childhood and youth.
1.3 - The influences on family violence
1.3.1 - Stress transfer
We see an increase in the conditions that generate stress in day-to-day social life.
Some studies have shown that accumulated tensions to day-to-day and life fatigue will be targeted to the children because it's easy and they have no defense, using them as a kind of drug to release tension.
1.3.2 - Cultural permissibility to spanking children
Some cultures and families still approve spanking children as a form of behavior "building", in the name of their responsibility to justify the right to beat children.
1.3.3 - Violence and theology
A theological conviction that spontaneous actions in children are bad as well as their tendency to find pleasure and is regarded as a sin.
So punishing children spontaneity is using suffering to correct what we ask and he/she doesn't do, using punishment to make children "good".
1.3.4 - Social conditions
Nuclear family disintegration and violence are connected to the growing violence today.
Unfortunately, many studies found out that the number of mistreated children is higher in low-income families and that mothers without conditions to sustain the children would spank and injure them.
The impotence of parents to solve the problem seems to influence brutality against children.
Some more results showed that violence in France was more on low-income classes, while in the United States violence was common to all classes.
1.4- Effects of parental violence
The first conclusion is that parental violence is like an epidemic that is passed from a generation to generation and is revealed in all phases of life.
Spanked children normally will turn in adult spankers and lots of studies have shown that the level of bad treatment in children development was correlated to the level of violence in crimes committed in adolescence.
Spanked people have a personal tendency to feel like a victim or to become violent, reproducing the cycle of victim/aggressor.
Other investigations in war, hostage situations, and terrorist attempts showed that the victims of this violence suffered from a disease called PTSD (Posttraumatic stress disorder),
Posttraumatic stress disorder was very well studied in the Vietnam War and showed that people that were exposed to war traumas, would have difficulty in controlling their own aggressive behavior, and had symptoms like hate, depression or social malfunctioning.
Some studies showed that violent crimes would increase after any war as a post-war contamination of social violence.
"Human nature is complex. Even if we do have inclinations toward violence, we also have the inclination to empathy, to cooperation, to self-control. - Steven Pinker"It is very difficult to change behaviors in children, being the best action anticipation and dissuasion of these actions.
2 - Media Violence
There are many controversies in studies about institutionalized violence present in any media outlet, and being watched by children interiorizing violence as a day-to-day reality.Watch the growing percentage of violent scenes in TV news and films.
The numbers showed that in 1977, any adolescent watching five hours a day of the TV at the age of sixteen have watched 20 000 violent assassinations on TV.
I do not even want to imagine this numbers in today's tv progs and movies because I don't even have a TV for 30 years now.
"Fifty years of research on the effect of TV violence on children leads to the inescapable conclusion that viewing media violence is related to increases in aggressive attitudes, values, and behaviors" - John Murray
2.1- Laboratory experiments
Singer and Singer in 1981 got results proofing that watching scenes of violence on TV do not awake aggression, but has the strange effect of the subject always choosing more films with more violence.
In children, until eight years watching violence have no immediate effects in aggression but can be the seeds of violence that can be seen when they are 18 years old.
2.2 -Reality experiments
Experiments in real life situation pointed that watching violent movies have a tendency to be "desensitized" about violence, creating attitudes that overestimate the place and importance of violence in reality and a bigger need for protection and repression.
Violent scenes on TV are not a direct cause of aggression but it can favor the violent responses of people that already are violent and facilitate the construction of aggressive models in childhood and early youth.
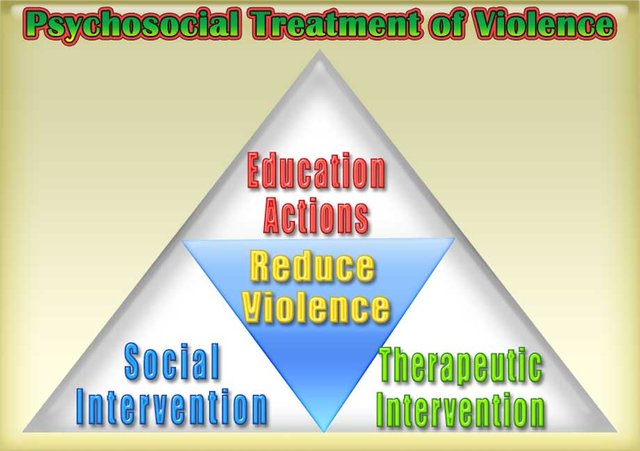
3- Therapies for violence
Violence in adults is the result of the story of the violence exercised in their early development, modeling the psychological structure of the use of aggressive pulsions.
Many studies have shown that violence in adulthood is the product of the violence suffered before since he was born.
Chiland in 1989 points out that the way of violence starts in the social environment of any children where that promotes aggressive discharges instead of investment of energy in psychic development, that generates structural personality malfunctions in the future.
So to find therapeutic models that could intervene in spheres of aggressiveness of the personality and the context where they happen.
The structure of any individual aggressive behavior in a social context, have an isomorphic( equal form) structure of the person's personality and the relations of his own story in equal circumstances.
Now let's see how to treat social violence using education, social change, and therapies.
3.1- Education Actions
These actions usually have three fronts for intervention, the education, preventive actions, and dissuasion.
Education starts with the family (socializing "behavior" till 3 years old) and later helped by the school (socialize "thought" till 12) and university (socialize "personality" till adulthood).
Education should create autonomous responsible adults constructed with children affection, positive sanctions, and tenderness, instead of punition that leads to bad self-concept, self-esteem, and self-depreciation based on frustration and suffering.
So education is about tenderness, teaching self-security and respect for other human beings.
Pierre Karli in 1987 saw education as the way to avoid imaturity and iresponsibilty states in the development and defines moral education as "reconaissance of of equal dignity of all human person and the ace'ptance of a true reciprocity in all human interactions".
He points a study by Zimmerman in 1983 showing that people administrating a degree of electric shocks to others depended on maturity and moral judgement.
75% of the subjects with maturity and moral judgement refuse to administrate shocks to other people.
13% (only) of the subjects with imature or week moral judgment refused to administrate shocks to other people.
Prevention is anticipating a behavior by education, the diagnosis of existing violence, and the measure of its consequences.
The other aspect of education is disuassion without repression, because violent people is totally immune to the power of the sanctions, what limits the level of dissuasion of violent behaviors.
3.2 - Social intervention
Social intervention is about acting upon social relationships and the socio-economical structure of the social context.
Pierre Karli pointed out prevention must focus first in the way of life and less populated urban spaces, second at the level of development of an "associative life" to spread change, and a third level to (re)stablish ways of communication and reduce damages.
Pierre Karli tought that organizing society was the first objective to diminishe and dissuade social violence.
In social psychology interventions, we can't focus only on people but also in social complex phenomena to change attitudes and culture.
3.3 - Therapeutic Interventions
Therapeutic Intervention is a way to change and dilute aggressiveness with personal conscious changes of attitudes and behaviors using two methods.
The first is a behavioral treatment to change one's personal social habits.
We know today that punishment only changes behaviors temporarily and its extinction is only possible by substituting it by a positive reinforcement of pro-social actions using a learned control of emotions by the person.
The second way to reduce aggressivenes is the use of the catharchic process to liberate aggressive pulsions.like using a boxing bag to exercize violence and discharge it.
But other studies found out that catharsis do not reduce aggressivenes but it is a good way to discharge violent pulsions, but with the danger of later recurrence to violence.
People watching football games have more tendency to show violent behavior after the end of it.
So catharsis is not a good, long lastig and safe solution.
In my point of view, the catharchic process generated in psychoanalyptical intervention can help everyone to turn on his/her conscious live history of violence and deflect it.
The best social therapy for humanity without violence is a more equitable distribution of wealth and greater participation of people in decisions about their future.
3 - Conclusions of the series about Violence
Violence can always be analyzed in itself adding the concepts of aggressiveness and aggression.Violence has various forms embedment in day-to-day reality, like bomb attacks, street violence, wars,"terrorism", nationalism hates, etc.
Violence can be seen as an inmate instinct inherent to human beings as a biological factor, necessary for survival.
Later some people proposed that this view is only of historical interest and that aggressive psychic conduct like Freud seeing it in the duality of Life/death pulsions exteriorized in the world.
Other analytical theories explained that behind aggressive expression there is always a frustration under a violent reaction,that may be dependent on environmental "triggers".
We have seen that early learning models in similar situations influence the emergence of violent behavior always looking at the culture, norms, and values of the social context and the socio-economical environmental.
We have finished by talking about day-to-day violence and some possible therapies that could attenuate or reduce social violence.
The next post starts the series about Power as another form of Social reality dynamics and some aspects of its connections to violence.
I finish here with a quote of Aldous Huxley about political power.
"If the problems of humanity could be thought about and acted upon within a frame of reference that has survival for the species, the well-being of individuals, and the actualization of man's desirable potentialities as its coordinates, these peripheral organizations would become central. The subordinate politics of survival, happiness, and personal fulfillment would take the place now occupied by the politics of power, ideology, nationalistic idolatry, and unrelieved misery. - The Politics of Ecology - Aldous Huxley (1894 - 1963)
Last posts in this series
Introduction:
Social Reality: Violence, Power and Change Violence:
An Introduction to ViolenceThe Concepts of Violence, Aggression, and Aggressiveness
The Theories on Violence
The influencers of Violence -Part One - Culture and Social Context
The influencers of Violence -Part Two - Social , Cognitive and Environmental Factors
The rise of Today's Violence- this post
Articles from the next series of posts about Social Reality, Violence, Power and Change:
Power:
What is Power?The Nature of Power
The Dynamics of Power
The Effects and Consequences of Power
Change:
Change and CultureThe Theories and conceptualization of Change
Factors determining Change
The ways of Change
Social Change
References consulted:
Les concepts fondamentaux de la psychologie sociale - Gustave-Nicolas FischerLa psychologie sociale - Gustave-Nicolas Fischer
The social-violence dynamics, power, change - Gustave-Nicolas Fischer Planeta / ISPA, 1980
Gustave-Nicolas Fischer is Professor of Psychology and Director of the Psychology Laboratory at the University of Metz.
French, J. R. P., & Raven, B.H. (1959). The bases of social power.
Castel, R. The metamorphoses of the social question. Voices, 1998.
Moscovici, S. (1976). Social influence and social change. London: Academic Press
Michel Foucault, Discipline and Punish: The Birth of the Prison
Festinger, L. (1954). A theory of social comparison processes.
French, J. R. P., Morrison, H. W., & Levinger, G. (1960). Coercive power and forces affecting conformity
Karli, Pierre, La notion d'agressivité, Point de vue d'un neurobiologist
Huesmann L. R., Moise-Titus, J., Podolski, C., & Eron, L. D., (2003).Early Exposure to TV Violence Predicts Aggression in Adulthood
Nickie Phillips, Violence, Media Effects, and Criminology
Violence is a menace that needs urgent attention!!!!
The effect of violence has crippled families and nations....
Thank you for this post...
SILENCE IS THE BEST ANSWER TO VIOLENCE
Fighting violence with violence only breeds more violence...
Kudos for the post!!!
Yes, instability and uncertainty of socio-economic environment stress the fight for survival and violence.
Imperialist governments just want to make business with guns and splash blood, civil deaths, and hate, because violence is their business.
We must stop spending money on war projects to build violence, and use it to stop famine and the social disruption on inocent civil communities that we have caused in the first place.
I would replace "Silence" by "non-violence". :)
God will help us....
Politicians are mostly the instigators of violence....
All because of power, they are ready to do anything not minding the outcome of their actions.
I'm not promoting violence neither I'm i promoting silence