Methods of Relative (Indirect) Age Determination used in Archaeology : Part 3 - Final
Methods of Relative (Indirect) Age Determination used in Archaeology : Part 3 - Final
Geographical dating Methods as an aid in the determination of relative Chronology.
In prehistoric archaeology, geographical methods are of importance in the determination of the relative age of archaeological finds.
The Principle of Stratification
I have already pointed out the importance of stratification when deposits are found in the open veld, in caves and rock shelters, in rubbish heaps associated with ruins, etcetera. At these sites the lowest layers are usually the oldest, while the topmost layers are of more recent origin (we have already discussed the terraces of rivers, where the sequence is reversed).
Stratigraphy Revisted:
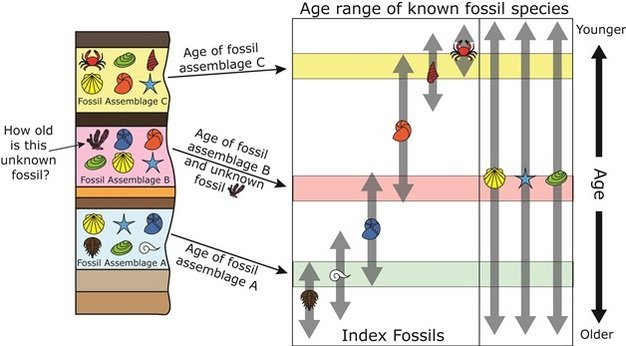
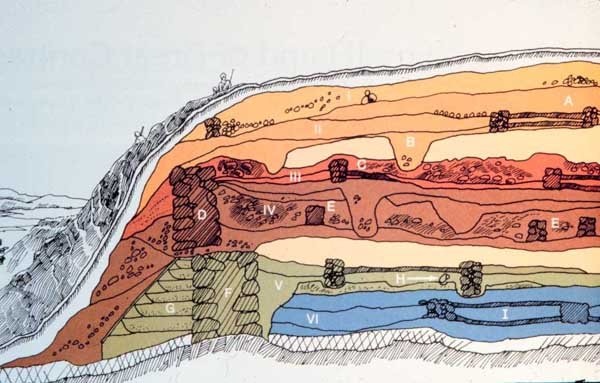
Stratigraphy refers to the description or study of the observable layers of sediments. Strati-graphic dating is a relative dating technique based on the knowledge that layers of sediments are normally laid on top of each other through time, in turn based on the geological law of superposition.
Usually the relative age of objects can be directly deduced from the strati-graphic conditions existing in a given number of strata. Stratification is the basis of every chronological investigation. The results which have been obtained by the above mentioned methods acquire the status of reasonable proof only when they are supported by the evidence of stratification elsewhere.
The Strati-graphic - Geomorphological dating Method
This method is applied in prehistoric geology in particular and is based on the principle that geological startification is associated with geomorphological phenomena,such as terraces in river beds and other sedimentation and erosion phenomena. The stratification of terraces, changes which take place in the shores of lakes, glacial deposits, etcetera. These local occurrences are then correlated with a more general chronology, and in this way the archaeological deposit itself is dated within the framework of this chronological sequence.
This correlation implies that the archaeological finds are also correlated with specific climatic conditions (which were among the factors that gave rise to the specific climatic'conditions (which were among the factors that gave rise to the specific geological occurrences) and, consequently, with ecological circumstances in general. Sites situated in the open can, generally speaking, be more easily dated than finds in caves. Although the stratification is usually very clear in caves, it is nevertheless sometimes difficult to correlate it with the geological stratification in the open, because the respective strata are formed in different ways.
Correlation with Glacial Deposits
This method is applied in areas where the glaciers have left their traces, especially in Europe and North America. The Ice Age (Pleistocene) consisted of a number of glaciations (in Europe there were four) with intermediate periods which were characterized by a warmer climate. The advance of the ice from its present bounds and its subsequent retreat brought about certain changes on the earth's surface through the action of glaciers and melting ice respectively, changes such as the formation of moraines and rivers. In addition, aeolian sand was deposited in fairly large quantities in the vicinity of glaciers - these are known as loess deposits. The relative chronology of the Ice Age - Pleistocene - is based on the interpretation of all these phenomena.
Archaeological deposits found in caves and in the open are correlated with these glacial deposits to establish their relative ages. Here the loess deposits play an important part. Apparently the climate on the edges of these glaciers permitted sufficient vegetation to support animal life. Consequently, a large number of camping sites occupied by prehistoric hunters have been found in these areas, both beneath and buried in various loess strata.
Other Geological Dating Methods
Various other geological methods are used in the determination of the age of archaelogical deposits These include the following:
~ correlation of archaeological deposits with alterations in the height of the shores of lakes or of the sea
~ determination of the rate at which deposits (both natural deposits and cultural deposits) were accumulated
~ a pedological investigation to determine the rate at which certain types of soil were built up (The climatic conditions which were responsible for their formation could then be deduced from a study of the soil. Archaeological deposits in, or underneath, such layers of soil are then correlated with the climatic chronological sequence.)
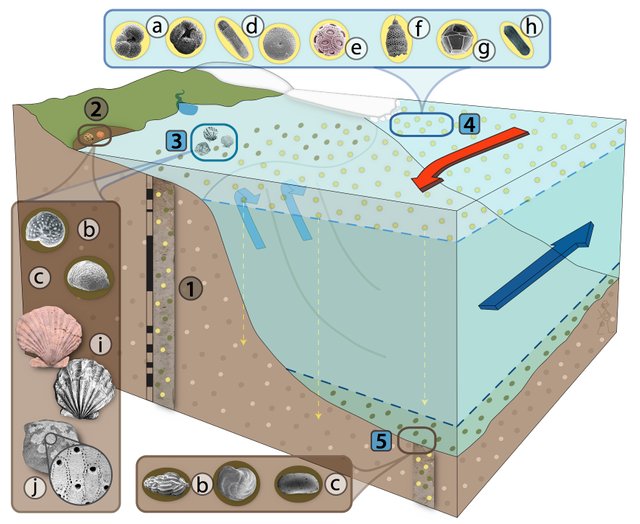
Oxygen isotope analysis of deep sea cores
As Fagan (1996/1997) points out, more and more emphasis is currently being placed a study of deep sea cores in an attempt to reconstruct the climate during the Pleistocene or Ice Age.
Deep sea cores, drawn from the floors of the oceans, contain the remains of a wide variety of marine organisms (of the Order of Foraminifera) that once lived near the surface of the sea. By measuring the ratio of the two stable isotopes of oxygen, 16 O and 18 O, found in the calcium carbonate of Foraminifera shells, the temperature of the seawater at the time of the formation of the shells can be determined. This is possible because the ratio will vary according to the temperature of the water. It also reflects the amount of seawater locked up in continental ice-sheets during the Pleistocene.
Isotope Analysis
Isotope analysis is the identification of an isotope signature, the distribution of certain stable isotopes and chemical elements within chemical compounds.
The above information has been used to compile a climatic sequence for the Pleistocene which consists of a number of warmer and cooler stages. These stages are referred to as oxygen isotope stages and their duration can be determined by directly or indirectly dating the deep sea cores, using techniques such as radiocarbon dating and potassium-argon dating (which I will discuss in my next series of posts).
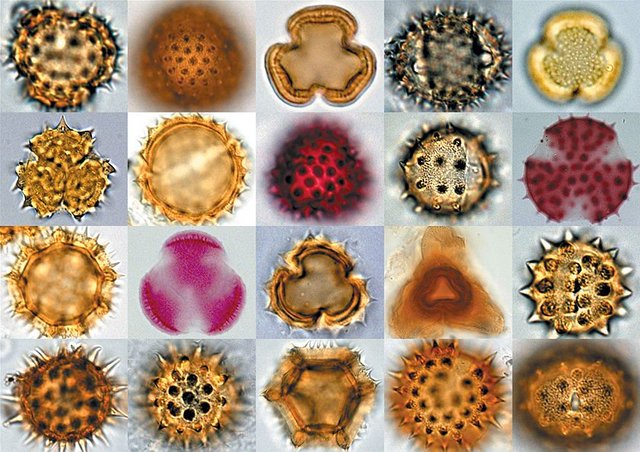
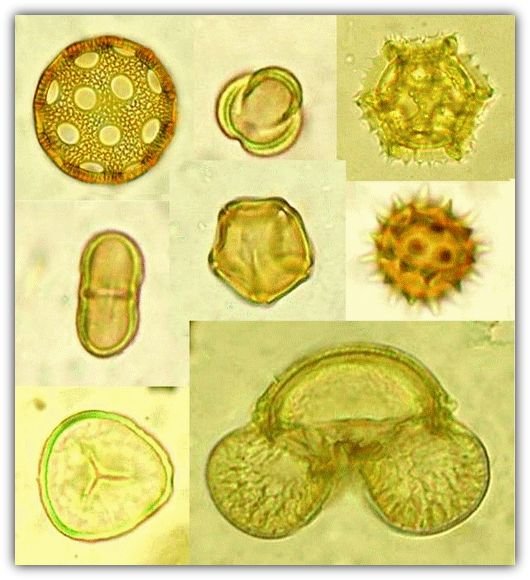
Pollen Analysis
In regions where the conditions are favorable for the preservation of pollen, pollen analysis plays an important part in the determination of climatic changes and ecological conditions.Archaeological deposits can be correlated with such changes.
Generally speaking, vegetation, being more sensitive to climatic changes than fauna, reflects these changes more accurately. Unfortunately, the preservation of pollen is dependent upon certain environmental conditions. It has been established that pollen grains are particularly well preserved in arid, water-logged or acidic deposits.
Most pollen analyses have been carried out on peat deposits. The lack of oxygen in water logged peat bogs as well as their acidic nature stifles the growth of bacteria, the main cause of pollen decay.
The Principles and application of pollen analysis
The pollen of trees and shrubs is blown about by the wind and deposited in their vicinity, for example in swamps. In the course of time these swamps often change into turf,in which pollen membranes may be found. The pollen of every plant has a characteristic form, pollen therefore serves as an indication of the trees and shrubs which must have grown in an area, even though these trees or shrubs now disappeared.
Very often various layers of growth are distinguishable in the turf itself, and sometimes each layer has a characteristic pollen formation of its own. These variations are indications of climatic change. When an entire series of deposits in a particular area has been studied, the findings can be correlated and the evolution of plant life and the history of the climatic changes can be determined. This historical sequence is usually portrayed by what are known as pollen diagrams. The pollen samples from archaeological sites may be compared with this standard pollen sequence in order to determine their relative age.
In addition, pollen analysis enables the archaeologist to obtain a fairly accurate picture of the conditions which existed in the natural environment of a particular industrial complex. In Central Europe, where a fairly extensive investigation was carried out over a wide area, the migration of groups has even been correlated with changes in the vegetation and climate. Pollen analysis is being used increasing in America.
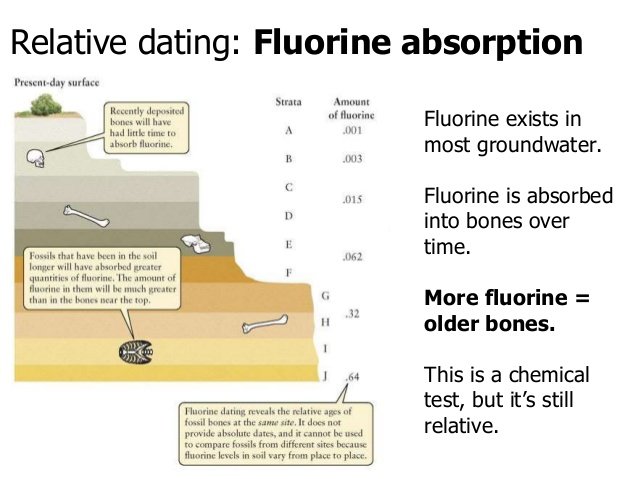
The Fluorine test
The main function of the fluorine test is to ascertain whether all the bones found in association in a particular stratum were actually deposited at the same time. When we discussed associated finds, we pointed out that they are of value as a method of dating only if found in situ. The question of contemporaneity becomes particularly important in the study of the remains of human skeletons.
Fluorine ions are usually present in subterranean water, These fluorines ions combine with hydro-oxydapatite which is present in bones to form flourine apatite. In the course of time the fluorine content of the bones increases gradually. If the fluorine content of a number of bones found in the same stratum is more or less the same,we can assume that all the bones were deposited at the same time. It is therefore clear that this test plays a very important part in the study of the remains of the human skeletons. In this study, it should always be remembered that the bones may have been buried, in other words that they may be of more recent origin than the stratum in which they were found (according to the principle of stratification).
Once the respective ages of certain animal bones have been established (by geological palaeontological calculations, for example), we can also relatively date the remains of human skeletons found in association, if authenticity is proved by the fluorine test.
Because the level of underground water and the quantity of fluorine present vary from place to place, this test cannot be used for the direct chronological classification of bones derived from sites situated far apart. When, however, the prevailing conditions are more or less the same, this test is used to calculate the relative age directly'on the basis of the fluorine content.
Fluorine Dating
Fluorine, uranium and nitrogen dating are relative dating techniques based on the premise that after the death of an animal, the relative amounts of fluorine and uranium in bone will increase and the amount of nitrogen will decrease.
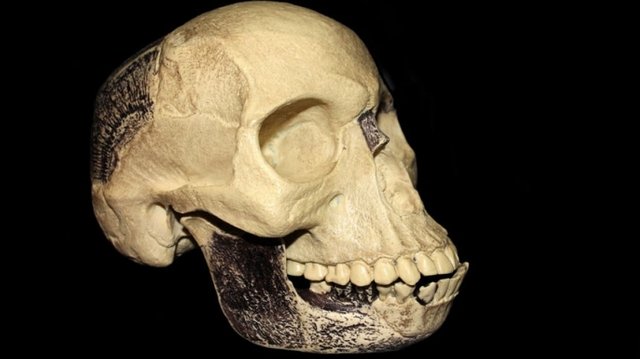
Piltdown Skull
In is only since 1950 that the fluorine test has been used more generally. It played an important part in the exposure of the fraud of the Piltdown skull. During the period 1908-1915 a fragmented skull, parts of a lower jaw and remains of extinct fauna were discovered at a site in Sussex in the south of England. The skull bones closely resembled those of Homo Sapiens and the mandible resembled that of an ape. It was therefore claimed that Piltdown man (or Eoanthropus as it was referred to) represented the missing link between humans and the apes. A fluorine analysis conducted by the British scientist, Kenneth Oakley, in 1953 revealed, however, that the jaw was younger than the skull.Further investigations brought to light that the remains had been tampered with to make them appear contemporary, and that the jaw belonged to a modern orangutan. Both the skull and the jaw bone had been treated with a pigment to make them look old and associated.
Thank you for reading.
Please Follow me for more on Archaeology and History.
Please check out my other posts:
Methods of Relative (Indirect) Age Determination used in Archaeology : Part 2
Methods of Relative (Indirect) Age Determination used in Archaeology : Part 1 - Introduction
The Preservation of an Archaeological Site : Part 2
The Preservation of an Archaeological Site : Part 1
Discovering your own Archaeological Site : Part 3
Discovering your own Archaeological Site : Part 2
Discovering your own Archaeological Site : Part 1
Archaeological Sealed Sites and River Deposits : Is it an Archaeological Site or Not? - Part 3
Caves, Rock Shelters and Larger Open-Air Sites : Is it an Archaeological Site or Not? - Part 2
Is it an Archaeological Site or Not? - Part 1
Understanding the Archaeological Record : The Aims and Subject Matter of Archaeology - Part 2
The Aims and Subject Matter of Archaeology - Part 1
Archaeology and the Natural Sciences
Introduction to Ethnographic Analogy and Ethnoarchaeology
The Nature and Scope of Archaeology
The Three - Age System : The Stone Age, The Bronze Age and The Iron Age
The Roots of Modern Archaeology
Significant 18th and 19th Centuries Discoveries in Archaeology
Archaeology as a Profession- Part 2
Archaeology as a Profession- Part 1
To Become or Not Become an Archaeologist? - Introduction to Archaeology Part 2
Please Upvote and Resteem.
Thank You!



Upvoted and Resteemed by xx-votesplus, the dropAhead curation team!
Do you want more earnings?
By doing things above you will give us more STEEM POWER (SP) to give you more earnings.
Keep up the good work!
Most recent post: It is official, WE are witnesses!
Hi @mandolincarls, I hope you are well. Thank you very much for accepting me as a memeber into xx-votesplusand for curating my post. I am truly appreciative.
Damned, I just read a teaser about the next posts ;)
Hi @lemouth!!!!!!!!!!!
Thank you for all the support and motivation. Being accepted into SteemSTEM is truly an honor for me, the community is a brilliant group of people and to be included and supported by all of you is an overwhelming feeling.
Hello @zest :) first of all great article and well written!
Could I have your opinion in this article? I'm a scientist and I've to say my brain dropped when I finished to read it.
https://steemit.com/steemiteducation/@beardedgentleman/the-human-species-is-way-older-than-we-are-taught-in-school
Hi @beardedgentleman, Thank you very much for the great comment and support. I will check out the post.
Thanks for this amazing feed! I'm gonna keep this one up again and brag to my issue.
Very interesting
Hi @steemitdigest. Thank you once again for the support, recognition and recommendation of my post. I think you have a great concept going.
yeah and some more in the future @zest i hope we'll be doing just fine here. I'll stay with you coz youre doing great
Just wanted to say I love this series of yours. It has been very informative & interesting :*
Hi @trumpman. Thank you sincerely for those amazingly kind and motivational words. I try to do my best and to know it's appreciated means the world to me.
you are welcome :*