Cell structure and function " Human Physiology "
As long as the human body is a permanent living marvel, and despite the tremendous progress we are witnessing, scientists have not yet discovered all its mysteries and mysteries. Perhaps this is because its creator wanted to be a continuous god to meet him. In our bodies there are many, many miracles. Or we notice anything that is going on within it, the body is an integrated and homogeneous system whose members work in perfect harmony and the more we examine the components of this body and the way we find the coin, we find many wonderful details that will remind us what the cell is a detailed form???
All organisms are formed in the basis of their composition from an infinite set of renewable cells. The cell is defined as the basic structural unit of man, animal and plant. The cell is also responsible for the functional and functional diversity of the different types of organisms, so that their forms, sizes and compositions vary. Or tissue that is responsible for achieving a specific goal of the body, the cells are vulnerable and damaged, but it is the growth and the formation of new cells to compensate for the damaged most of them, but may be unable to achieve this in some cases, causing a disease in one of the body , And a failure in the performance of his career goal.
The cell is characterized by its various types and sources of being accurate in size, impossible to see by the naked eye, scientists have developed over the years several types of devices that enable them to see the cell clearly, and identify the parts and components of finer size,
Microscope, cells are detected using a microscope in two main ways:
The slides are pressed after removal from the body between two slides, and are placed under a microscope. This method is used with dead cells. If used with living cells, this causes death and damage due to the pressure caused by the slides.
Laser This method is widely used with living cells to maintain and prevent damage by using laser tweezers to hold the cell, not moving it and touching it, using laser scissors to dissect it, and identifying its composition.
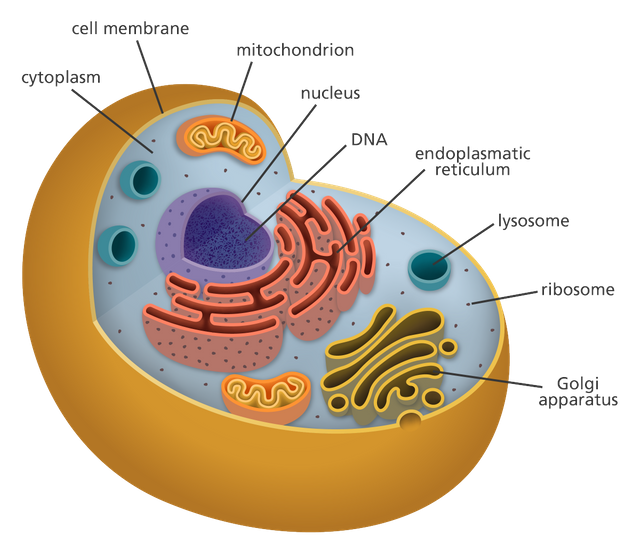
part One :
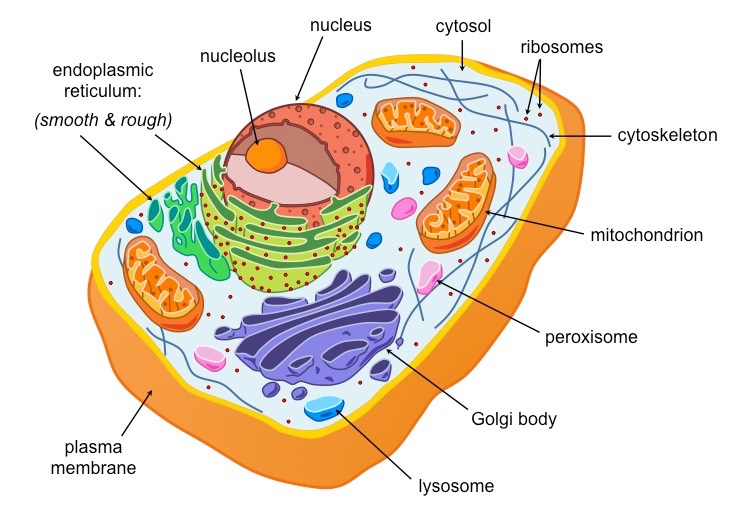
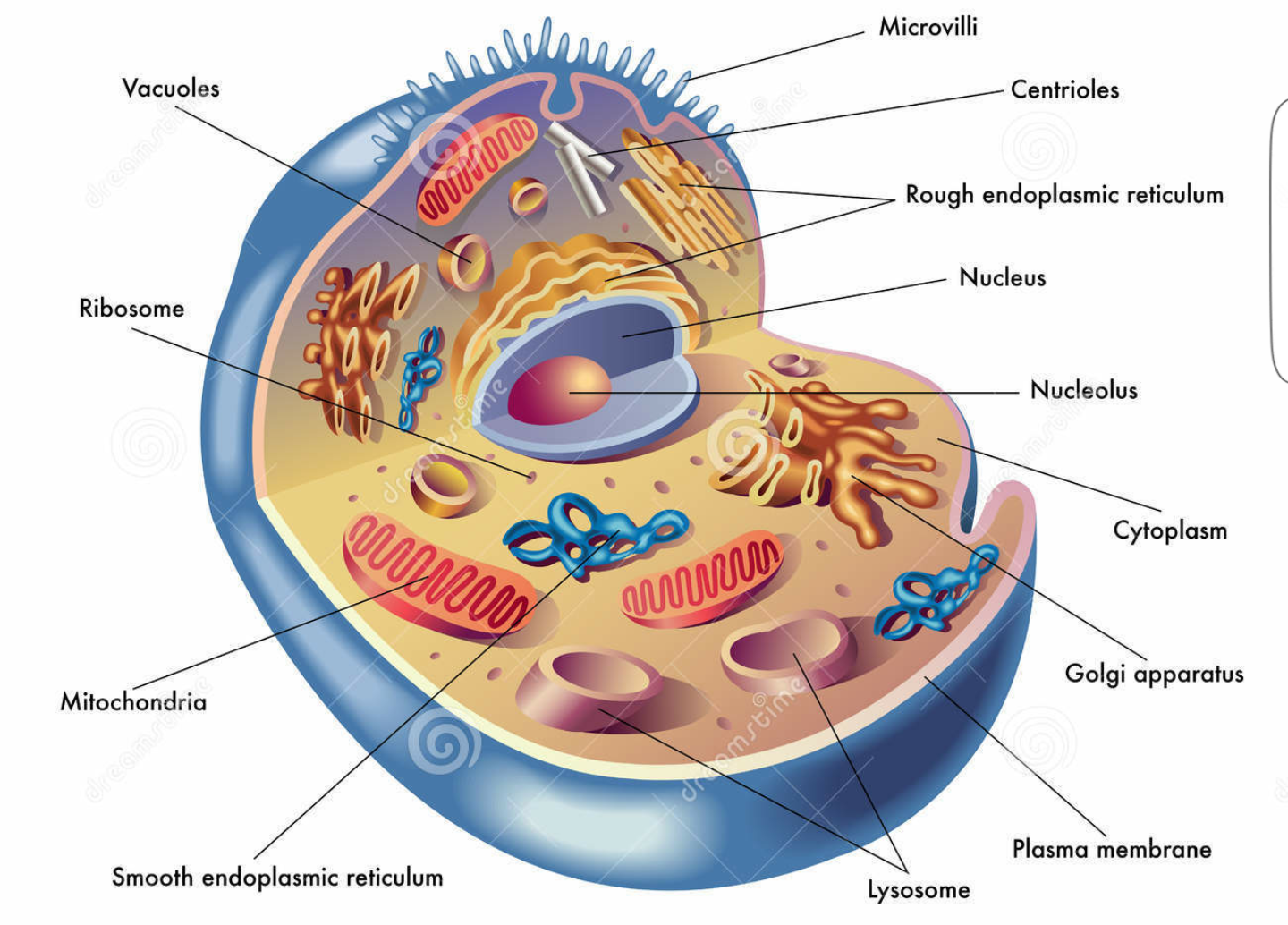
The eukaryotic cell generally consists of the following structures and organs:
- Plasma Membrane:
Membrane is a membrane surrounding the cell. It is characterized as a semi-outlet (optional permeability). It regulates the passage of food into the cells and the passage of waste outside.
- Nucleus:
All cell types contain one nucleus, one of the most important parts of the cell. It contains the genetic information (DNA) that regulates the growth and proliferation of the cell.
- Cytoplasm:
A gel material that surrounds the nucleus and contains all cell organelles.
- Centrioles:
Organelles work to assemble fine tubes and have a role in regulating cell division.
- Cilia and flagella:
Plaques that help the cell to move from place to place, and are found only in animal cells.
- Cytoskeleton:
A network of fibers that are distributed in the cytoplasm, gives the cell its specific form, regulates the movement of the organs within the cell, and plays a role in the movement of the cell itself.
- Golgi apparatus:
Contributes to the manufacture, storage and transfer of certain molecules produced by the cell.
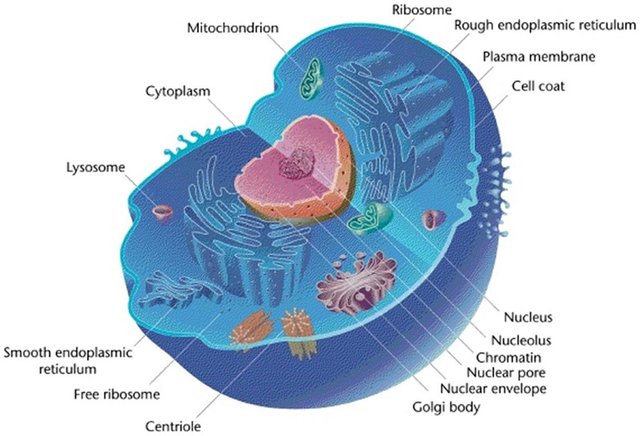
The second part :
- Endoplasmic Reticulum:
a network of membranes that are spread in the cytoplasm, and it has two types:
rough endoplasmic reticulum contain Raibusomat, and smooth endoplasmic reticulum does not contain Raibusomat, but they function similar to the function of the Golgi apparatus.
- Lysosome:
Organelles that digest and disassemble some cellular molecules that the cell no longer needs, and large cellular molecules such as nucleic acids.
- Microtubules:
Hollow rods have a role in supporting the cell, and contribute to giving the cell a specific shape.
- Mitochondria:
A cellular respiration that produces the necessary energy for the cell.
- Peroxisomes:
Organelles contain enzymes that help to break fat, and the formation of yellow acids.
- Ribosomes:
Organelles have a role in the synthesis of proteins, consisting of RNA, proteins, and proteins.
- Plastids:
Organelles are found only in plant cells, and have a role in storing the substances needed by the cell, and of the types, the green plastids in which photosynthesis occurs.
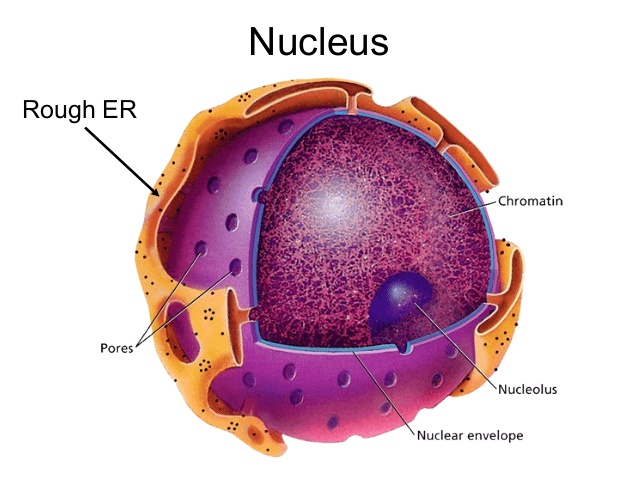
The nuclear membrane has no influence on large molecules. Nuclear pores are needed to regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the nuclear envelope. The nuclear pores pass through the two layers of the nuclear membrane and provide a channel through which small molecules and ions can pass freely, while the larger molecules need to carry proteins to carry them effectively. Some large molecules such as ribosome RNA and RNA proteins traverse smoothing as a condition for you to gene expression and maintain chromosomes. Although the interior of the nucleus does not contain interior chambers fitted with a membrane, its contents are not homogeneous. Where certain objects are made from certain proteins, molecules of ribosome RNA, and certain parts of the chromosomes. The most common of these is the nucleus, which is mainly involved in the synthesis of chromosomes, and ribosomes are produced in the nucleus and then released into the cytoplasm, where they translate the ribosome DNA.
The nucleus contains most of the genetic material in the cell, arranged in the form of long linear molecules of DNA-deficient ribosome DNA in a complex form as well as a large group of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes or chromosomes. Genes or genes that are based on these chromosomes or chromosomes together form the genome or genome, and these genes take this structure to enhance cell function. The nucleus maintains the existence of genes together and maintains their integrity, and also controls the activities of the cell through the organization of gene expression, so the nucleus is the center of control in the cell. The main structures that form the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double encrustation that encapsulates the nucleus and isolates its contents from cellular cytoplasm or cellular cytoplasm, as well as the nuclear matrix (which contains the nuclear plate), a network of fibers that give the nucleus mechanical support, such as the cellular structure that supports the cell as a whole.
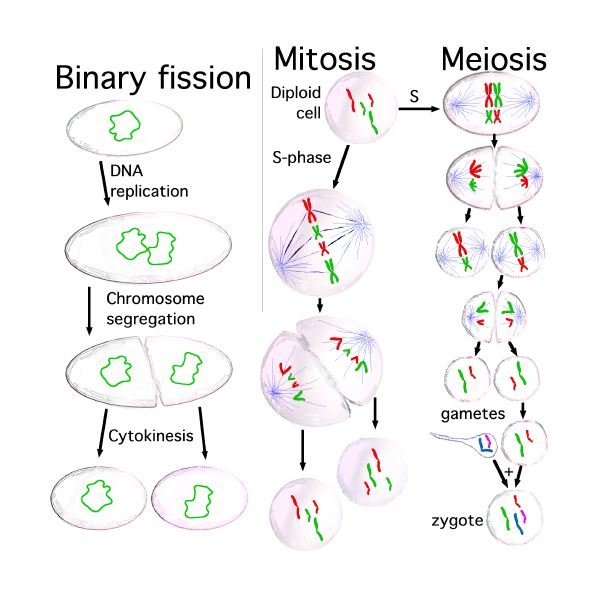
Cell division :
Cell division is the process by which the cell can grow, produce new cells, and there are two types of cellular division:
Metosis is the division that occurs in the body cells of the organism, and results in the division of each cell cell similar to the original cell, and passes the cell before the equal division of the interstitial in preparation for the beginning of division, and then the cell passes successive stages of equal division:
Primer, equatorial phase, dissociative phase, and final phase. Meiosis is the division that occurs in the sex cells to produce gametes, such as sperm and eggs. The division of the cell results in an equitable division of gametes in each half of the chromosomes found in the body cells. This is very important for maintaining the stability of the number Chromosomes in the organism; in humans, for example, the body cells contain 46 chromosomes, and the sperm produced by the equitable division contains 23 chromosomes, as well as the egg that also contains 23 chromosomes, and when fertilization we get back On cells containing 46 chromosomes.
The process of producing proteins in the cell cytoplasm, such as the proteins produced by the cell, enzymes that regulate chemical reactions in the cell, hormones, and many other proteins are very important for cell life. Since the genetic material governing the process of protein synthesis is inside The nucleus of the cell, so messenger RNA (RNA) acts on the transfer of instructions, or genetic code from DNA in the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
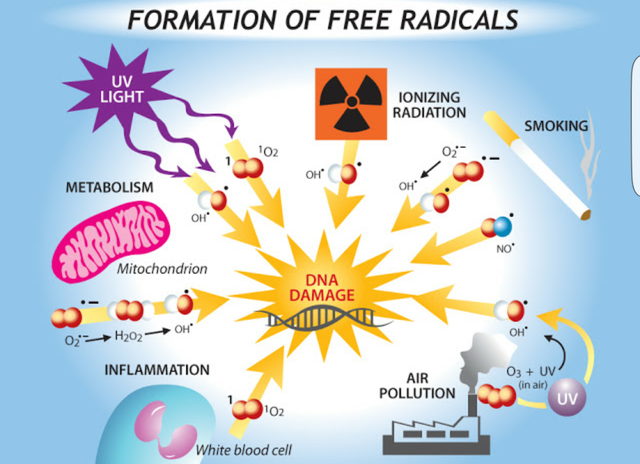
When the free radicals enter the nucleus, the DNA and the RNA dissolve. The abnormal cells that form the cancer cells also weaken the immune system.
Hence begins the spread of cancer cells thanks to continue the second part tomorrow .
You Like this post, do not forget to upvote or FOLLOW ME or resteem
Great information about how the cell functions in the human body.
I'M CELEBRATING 300 FOLLOWERS
Thank-you for YOUR awesome support!!!
Come Check Out Some of my Cool Posts:
A Cool Morning Gratitude Session
Apologies For Slow Up-Voting
FOLLOW * UPVOTE * RESTEEM * REPLY * WELOME!!
Source: Picture300
Thank you @igider for making a transfer to me for an upvote of 1.56% on this post! Half of your bid goes to @budgets which funds growth projects for Steem like our top 25 posts on Steem! The other half helps holders of Steem power earn about 60% APR on a delegation to me! For help, will you please visit https://jerrybanfield.com/contact/ because I check my discord server daily? To learn more about Steem, will you please use http://steem.guide/ because this URL forwards to my most recently updated complete Steem tutorial?