Deeper into anonymity: Proxy, VPN/SSH, and Tor
To make it easier, let's divide anonymity on the Internet into two areas:
- Social anonymity — when a person, consciously or unconsciously, tells about himself on the Web.
- Technical anonymity — when leakage of data is related to the technical means and applications used.
I've talked about social anonymity earlier, in my previous post, this time let's go deeper into technical anonymity.
Proxy-servers
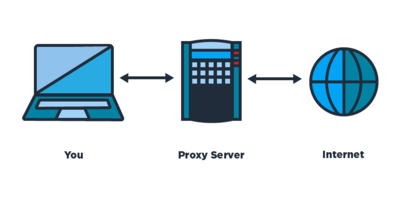
We can say this is the basic method to hide your IP address from the end resource. But their only advantage is that they are cheap (sometimes free) and easy-to-use. Proxy is useful to create some "multi-accounts" or visit a resource which blocked your IP address, but if you really care about anonymity it's too weak for protection.
At first, you have to trust your proxy provider since they will see all your outgoing traffic and since proxies don't support end-to-end encryption this may even hurt your privacy rather than help. Also, there is a risk of data leak since you'll need to configure every application to work with proxy separately.
VPN & SSH Tunnels
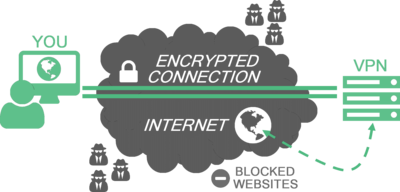
Historically VPN and SSH Tunnels were created for different proposes, however now they both can provide the same level of anonymity. Further, I will write only VPN meaning SSH Tunnel too.
Unlike proxies, VPN will encrypt all your traffic making it useless for your internet provider and others third-parties. Also, it's easier to setup VPN system-wide, so there is a lower risk of data leak by negligence.
The bad thing is that you still need to trust your VPN provider, so it's just a replacement of "big brother". You can reduce the risk by setting up a chain of VPN servers, from different providers. In this case, make sure not to give any identity data to the providers. Ideally, you will find a provider who accepts payments in cryptocurrency ;)
TOR
You can find enough information about Tor on the internet. I'll try to explain it simply, without delving into technical details. The issue of VPN is that it's hard to get it without compromising your identity, and even harder to get and manage multiple VPNs which we need to get a high-level anonymity.
The Tor network disguises your identity by moving your traffic across different Tor servers and encrypting that traffic so it isn't traced back to you. It's like a chain of multiple VPN servers (technically it differs) which you just need to connect to.
How does it work?
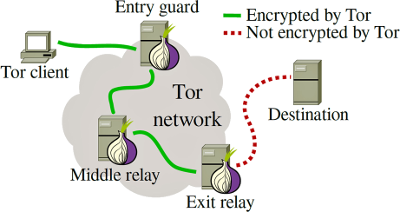
By default, Tor will map your traffic among 3 random nodes and will change them every 10 minutes. So, the first node (entry guard) knows who is sending the request, but doesn't know where it will just pass it to the second node. The last node (exit relay) will know which resource you're visiting, but it won't know who you are, because the request came from the previous node, but not from you.
The only disadvantage of Tor is slow internet traffic since your request will need to pass throw all nodes chain before reaching the destination. But I think this is an acceptable price for anonymity.
Resteemed by @resteembot! Good Luck!
Curious? Read @resteembot's introduction post
Check out the great posts I already resteemed.
ResteemBot's Maker is Looking for Work.
This post received a 0.210 SBD (4.51%) upvote from @upvotewhale thanks to @andhovesyan! For more information, check out my profile!