EOSUnion Blockchain 101|The 4th class: What is the public chain, private chain and alliance chain?

In the first three classes, we introduced the definition of the blockchain, its three consensus mechanisms, and the two types of forks. In this class, we will help you make the three types of blockchains clear: Public, private and alliance chains.
Since the birth of blockchain technology, it has been calling for decentralization. However, due to the different development concepts and objectives of different enterprises, the blockchain, according to its application direction, has developed three different forms. The first one is the fully decentralized public chain, such as the Bitcoin and Ethereum. The second one is the partially decentralized private chain, such as the Ant Financial. And the third one is the partially decentralized alliance chain, such as the Hyperledger.

01 Public chain VS license chain
The public chain is recognized as a common blockchain that everyone can join in. For example, Bitcoin and Ethereum are open to everyone, which means everyone can participate, send a transaction and get a valid confirmation. In the public chain, program developers have no right to interfere with users, and they can protect users who use their programs. So in general, the public chain is considered to be "completely decentralized".
Conversely, the license chain is a blockchain that requires permission to join, and unlicensed nodes are not accessible to the blockchain system. Therefore, the license chain is considered to be “partially decentralized”.
The difference between the two is a bit like the knowledge planet with free and paid parts. Everyone can join Free planets, and participate in the discussion of topics, so does the public chain. The paid planets require users to buy an entry license, and users can join in with the license, so does the license chain.

02 Private Chain VS Alliance Chain
The license chain is divided into two types: private chain and alliance chain.
The private chain is a privately owned blockchain literally. It refers to the blockchain in which the write permission is completely in the hands of a person/organization, and all the nodes participating in the blockchain are strictly restricted. In some cases, some rules on the private chain can be modified, such as restoring transactions and other services. It is like QQ groups. The group owner has the highest authority, such as setting group rules, pulling people, muting people, etc., while other group members are limited by group rules.
The alliance chain is in between the public chain and the private chain, and it is also “partially decentralized”. Participants maintain the blockchain operation by applying to join the network and forming a stakeholder alliance. For example, if an alliance is established between 10 universities in Beijing to share courses between students, these courses can be only seen by the teachers and students of these 10 universities. If other teachers and students want to see them, their school have to submit an application to the alliance, and they will be able to join after the application is approved.
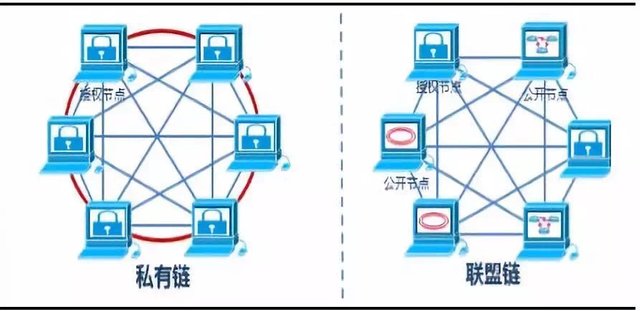
Let me explain the difference between the two with a more familiar life example. The alliance chain is like a QQ group with both group owners and multiple group administrators who participate in decision-making, voting, and jointly maintain the normal operation of the QQ group; while the private chain only has the group owner without administrators. To some extent, the alliance chain also belongs to the private chain, but the degree of privatization is different.

03 The advantages and disadvantages
The characteristics of the "fully decentralized" of the public chain determine that it has the advantages of low access threshold, transparent disclosure of all data, protection of users from developers, but also has bad features like low throughput and slow transaction speed. For example, the Bitcoin and Ethereum networks are often in a congested situation.
Since the private chain participation node is limited and controllable, it has a relatively short consensus time compared to the public chain, so it has faster transaction speed, better privacy protection, lower transaction cost, and is more difficult to be malicious attacked. However, since its authority is controlled by a few nodes, it cannot solve the problem of cheating fundamentally and is deviated from the original intention of decentralization.
The public chain and the private chain. The advantages and disadvantages are also due to fewer nodes and faster transaction processing. However, due to the small number of nodes, centralized power and security issues are prone to occur if the permissions are not well designed.
In general, the higher the decentralization, the higher the credibility and security, and the slower the transaction. In the three aspects of high efficiency, decentralization, and security, the blockchain can only meet two aspects. This is the paradox of the “impossible triangle” of the blockchain. Therefore, whether it is a public chain, a private chain, or an alliance chain, they have their own shortcomings. We should place the specific application at different blockchain types according to their features.
Finally, let’s review the main content of today:
Public chain: The public blockchain is open to everyone.
Private chain: The private blockchain is open to separate individuals or organizations.
Alliance chain: The blockchain formed by the interest alliance is open to nodes joining the alliance.
The former is more suitable for application scenarios with high requirements for credibility and security, but not for transaction speed; the latter two are more suitable for application scenarios with high requirements for privacy protection, transaction speed, and internal supervision.
Some other articles we wrote
EOSUnion Blockchain 101|What is the blockchain fork? After reading this article, I understand! https://steemit.com/eosamsterdam/@eosamsterdam/eos-amsterdam-eos-gov-telegram-channel-summary-august-10-august-12-2018-8-10-8-12
EOS Resource Renting VS EOS Force Voting Dividends https://steemit.com/eos/@eosunion/eos-resource-renting-vs-eos-force-voting-dividends
EOSUnion| Consensus Mechanism101 https://steemit.com/eos/@eosunion/eosunion-or-consensus-mechanism
What is Blockchain? This is the best answer I've ever seen. https://steemit.com/blockchain/@eosunion/what-is-blockchain-this-is-the-best-answer-i-ve-ever-seen
EOSUnion|After RAM, Here Comes the Time of CPU? https://steemit.com/eos/@eosunion/eosunion-or-after-ram-here-comes-the-time-of-cpu
The Global EOS Eco Summit held successfully! https://steemit.com/eos/@eosunion/the-global-eos-eco-summit-held-successfully
EOS Eco Development Weekly Reports| 07.28-08.03 https://steemit.com/eos/@eosunion/eos-eco-development-week-reports-or-07-28-08-03
Follow us
WeChat: eosunion
Steemit: https://steemit.com/@eosunion
Telegram Channel: https://t.me/EOSUnionChannel
Telegram Chat: https://t.me/EOS_Union
Email: [email protected]
Twitter: eos_UNION