What is Blockchain? This is the best answer I've ever seen.
Since Nakamoto Satoshi first proposed the concept of blockchain in the paper "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System" he published in 2008, the concept of blockchain was hot once again, becoming the first " windy spot" of 2018.
During the past 10 years, books and articles about the blockchain have emerged in an endless stream, but few people can explain it right in an understandable way. They either simply equate the blockchain with Bitcoin, talking about BTC books and mining, or use some incomprehensible concept of technology, making users confused, which is a very unfriendly experience for newcomers who want to get started or who just started to learn the blockchain.
EOSUnion team also experienced this experience when we first started to enter the blockchain world several years before, so we really want to do something to help. After we have enough understanding through the blockchain world, EOSUnion team hopes to give a series of "blockchain lectures" to everyone to share the blockchain knowledge, and hopefully, we can make progress together in this industry and share the blockchain development dividend.
Let’s follow the EOSUnion to the first class of the Blockchain Lecture, which mainly talking about the basic composition of blockchain and its three layers of mystery.
01 Basic Composition
Most of the explanations we have seen on the blockchain about the Internet are: "The blockchain is essentially a decentralized distributed ledger database." However, in fact, this term applies only to bitcoin-related blockchain applications, as blockchain technology itself may not include "books."
So how should we understand and define the blockchain? We explain in two parts in a step-by-step manner:
First, let's look at the composition of the blockchain: it is a series of data blocks that are concatenated in the order of occurrence, each of the blocks contains information for multiple transaction confirmations.
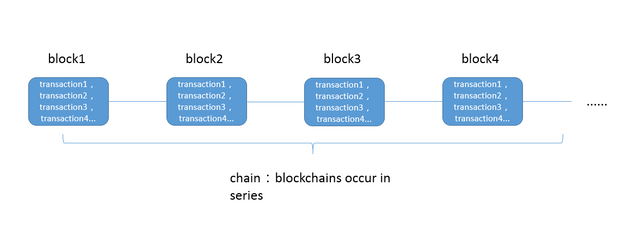
This sentence contains three key concepts of blockchain: Transaction, Data Block/ Block, and Chain.
Transaction: Each of our operations results in a change in transaction information and status results, such as adding a record;
Block: Records the transaction and status results that occur over a period of time, that is, each block contains several pieces of transaction information (it is a consensus on the current state, and the consensus will be discussed in detail later) ;
Chain: A series of blocks that are connected in series in order of occurrence, which is a log record of the entire state change.
After understanding the simple composition of the blockchain, we can further open up the mystery of the blockchain.
The first layer of mystery:
The blockchain is a decentralized database (system)
Before we understand decentralization, let's take a look at a centralization process, an example from our daily lives. Suppose we want to buy something on Taobao, the transaction process is: 1. We transfer the money to Alipay 2. After the payment, Alipay tells the seller to deliver goods 3. Seller makes the delivery 4. We confirm the goods received 5. Alipay transfer the money to the seller.
In this process, our transactions with the sellers are all around Alipay, in which Alipay acts as an authoritative centralization agent. But if we assume the extreme situation, e.g., Alipay bankrupts and run away or Alipay received your money but does not admit your transaction (which a large number of P2P online loan platform had done before), then we are tragic.
The decentralized approach is much simpler. We only need to hand over the money with the seller, and then both parties claim to complete the transaction, and then the transaction will be packaged and recorded in the system, simple and fast. And thus eliminate the risk of being controlled by the centralized agent.
But the above example has a big potential problem: how to ensure the accuracy and validity of each transaction without an authoritative centralization agent? This leads to another two layers of mystery in the blockchain – the consensus and not being tampered with.
The second layer of mystery:
Blockchain uses consensus system to reach a consensus on new data
The process of transaction data records (ie, block addition) is: the person who has the right to package the transaction(i.e., nodes or BPs) places the packaged transaction (block) on the existing database (blockchain) and then broadcast to the whole network. Once the other nodes receive the information and verify that the block is correct, the new packaged transaction will be synchronized. Each packaged transaction is called a block, and the blocks are continuously superimposed and extended to form a blockchain.
However, since each person (node) is spontaneously recording or synchronizing transactions, there is a high network delay in the case of peer-to-peer communication, so the order in which the data is received by each node is inconsistent. In this case, how to ensure the consistency of each node data?
Since the blockchain does not have a centralized agent to command and coordinate, the blockchain needs a system to ensure the consistency of data of each node. This system needs to solve two basic problems:
Who has the right to record data in so many people (nodes) - only one person can record at a time;
How other people (nodes) synchronize data – because data consistency is maintained.
Thus, the consensus system came into being. However, due to different application scenarios, the designed targets are different. Different blockchain systems adopt different consensus system. At present, there are mainly three types, namely PoW, PoS, and DpoS, which realize the formation of a correct and consistent consensus data in the whole network. (About how these three types of consensus system solve the two basic issues mentioned above, we will elaborate in the next class).
The third layer of mystery:
Blockchain uses cryptography to ensure that existing data cannot be tampered with.
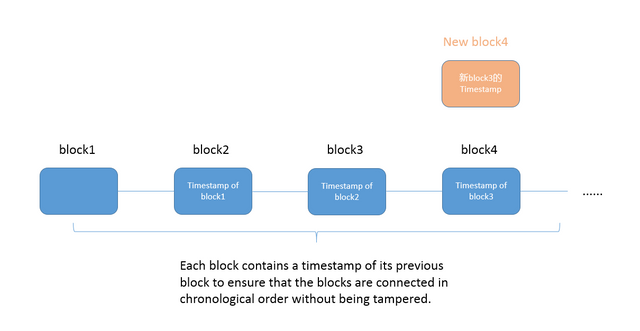
As we mentioned earlier, a transaction that each person (node) packaged is called a block, they will cover the time stamp of the previous block in this block, and each newly generated block will generate in strict chronological order. An irreversible chain will be formed, in which each block contains a timestamp of the previous block to ensure that the block is linked in chronological order without being tampered with.
If we want to tamper with the transaction data of block 4 to make a fake transaction, then we must tamper with the data of block 3, because the timestamp of the new block 4 does not match the block 3, and so on, we must also tamper with Block 2 and block 1 data.
The longer the chain, the more data you have to tamper with, and the harder it is, so we generally say that the blockchain can ensure that the existing data is not tampered with (unless you persuaded more than 51% of miners in the whole network to change a certain account, otherwise your tampering is invalid).
In fact, we can understand the timestamp of the block in this way: like DNA, our DNA is inherited from the DNA of our father, and the DNA of our father is inherited from the DNA of our grandfather... So if we want to change our own progeny DNA, then it is necessary to change the DNA of our father, and then change the DNA of our grandfather... The difficulties can be imagined.
Finally, let's summarize what we learned today:
- The basic composition of the blockchain consists of three parts: transaction, block, and chain. Several transaction information is packaged into blocks, and the blocks are connected in series in the order of occurrence and extended into blockchains.
- The blockchain is a decentralized database (system);
- The blockchain uses a consensus system to reach a consensus on new data;
- The blockchain uses cryptographic methods to ensure that existing data cannot be tampered with.
Follow us
WeChat: eosunion
Steemit: https://steemit.com/@eosunion
Telegram Channel: https://t.me/EOSUnionChannel
Telegram Chat: https://t.me/EOS_Union
Email: [email protected]
Twitter: eos_UNION

@eosunion