CLASSIFICATIONS OF ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATION
Have you ever sat by the phone waiting for it to ring? Well, I guess we don't sit by the phone anymore since we carry it with us wherever we go. If we care to know what caused the difference, then we have to study the classifications of electronic communication.
Electronic communications are classified according to whether they are one-way transmission also known as simplex or two-way transmission called full duplex or half duplex. Also, electronic communication either simplex or duplex can also be classified based on the type of signal involved, which can be either analog or digital signals.
Let's explain classifications of electronic communication
Electronic Communication Classifications
The simplest way in which electronic communication is conducted is one-way communications, normally referred to as simplex communication. Example of such communication class is shown in the image below.
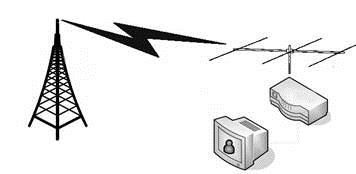
The most common forms of simplex communication are radio and TV broadcasting. Another example of one-way communication is transmitted to a remotely controlled vehicle like a toy car or an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV or drone). Also, simplex channel is applicable in fiber optic communication. It consists of a pair of fiber strands often combined to one cable, it is two in one cable. A single strand is used for transmitting signals and the other is for receiving signals. The importance of simplex mode is that its entire bandwidth can be used during the transmission.
Full Duplex

The bulk of electronic communication is two-way, or duplex communication. Typical duplex applications are shown when people communicating with one another over the telephone can talk and listen simultaneously because there are two communication paths between them. Thus, using the full duplex mode can greatly increase the efficiency of communication. Full-duplex is illustrated by the image to the right. It consists of a pair of simplex links that allows bidirectional simultaneous transmission.
Half Duplex
Half duplex communication is a form of two-way communication in which only one party transmits at a time while the other party receives the transmitted signal at that instance. The image to the left illustrates a half duplex communication.
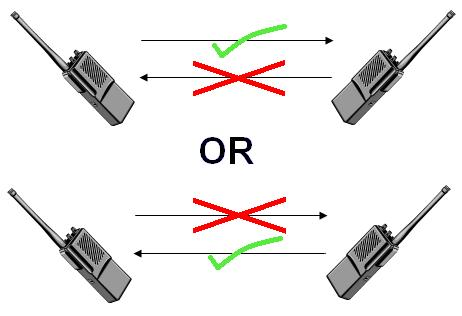
At a particuler point, half duplex can be considered as a simplex channel whose transmission direction can be switched. A Walkie-talkie is a typical example of a half-duplex device. Walkie-talkie contains a “push-to-talk” button which is capable to turn on the transmitter while the receiver is off. It functions such that once the push the button, the receiver component of the device is off, thereby causing you not to hear the person you are talking to but your partner can hear you. An advantage of half-duplex over full-duplex is that half-duplex makes use of a single track which is cheaper than the double tracks.
The communication is two-way, but the direction alternates: the communicating parties take turns transmitting and receiving. Most radio transmissions, such as those used in the military, fire, police, aircraft, marine, and other services, are half duplex communication. Citizens band (CB), Family Radio, and amateur radio communication are also half duplex.
Analog Signals
An analog signal is a smoothly and continuously varying voltage or current. Some typical analog signals are shown to the left.
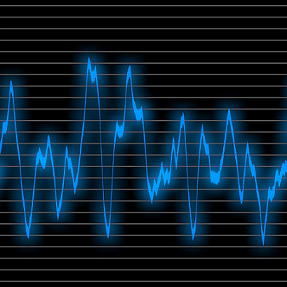
An analog signal is a continuous wave denoted by a sine wave and may vary in signal strength (amplitude) or frequency (time). The sine wave's amplitude value can be seen as the higher and lower points of the wave, while the frequency (time) value is measured in the sine wave's physical length.
There are many examples of analog signals around us. The sound from a human voice is analog because sound waves are continuous, it has various shapes and colors in a continuous manner due to light waves. A wall clock having its hands moving continuously can be considered as an analog signal.
A sine wave is a single-frequency analog signal. Voice and video voltages are analog signals that vary in accordance with the sound or light variations that are analogous to the information being transmitted.
Digital Signals
In contrast to analog signals, digital form of signal transmission do not vary continuously but change in steps or in discrete increments. Most digital signals use binary or two-state codes. The earliest forms of both wire and radio communication used a type of on/off digital code. The telegraph used Morse code, with its system of short and long signals (dots and dashes) to designate letters and numbers. In radiotelegraphy, also known as continuous-wave (CW) transmission, a sine wave signal is turned off and on for short or long durations to represent the dots and dashes.
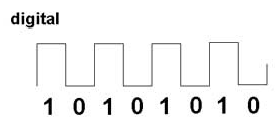
Data used in computers is also digital. Binary codes representing numbers, letters, and special symbols are transmitted serially by wire, radio, or optical medium. The most commonly used digital code in communications is the American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII). Many transmissions are of signals that originate in digital form, e.g., telegraphy messages or computer data, but that must be converted to analog form to match the transmission medium. An example is the transmission of digital data over the telephone network, which was designed to handle analog voice signals only.
If the digital data is converted to analog signals, such as tones in the audio frequency range, it can be transmitted over the telephone network. Analog signals can also be transmitted digitally. It is very common today to take voice or video analog signals and digitize them with an analog-to-digital (A /D) converter. The data can then be transmitted efficiently in digital form and processed by computers and other digital circuits.
Image Credit
References
https://medium.com/@fiberstoreorenda/introduction-to-simplex-half-duplex-and-full-duplex-fbda8d591e3a
https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/s/simptran.htm
https://www.diffen.com/difference/Analog_vs_Digital
http://www.chegg.com/homework-help/definitions/analog-signal-4
https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-are-digital-and-analog-signals-definition-lesson-quiz.html
Learn more about communication in the video below
Being A SteemStem Member