CALCIUM: Meet the biochemical and bioelectrical workaholic.

[credit: wikimedia creative commons author, Ragesoss]
Cells are the basic unit of life; every living thing possess countless number of cells which make up every bit of its biological complexity, cells are also relatively complex in that they perform virtually every action of a living system, this includes respiration and energy generation, reproduction, excretion of intracellularly generated wastes, breakdown of toxins (and the large molecules which serves as their source of nutrient) and ultimately, when these cells run out of life-sustaining signals and substances, they die.
Somatic death can be more conveniently explained in terms of cellular death, so also can other activities of a very developed system be explained in terms of the activities of their individual cells. Cellular activities can also be explained in a very smaller unit – molecular interaction. Molecular interaction involves the inter-reaction of non-living molecules which influences the concerned cell to react in a certain way, producing overall cellular action. These molecules include minerals, minerals are inorganic compounds which are in very little amount for certain vital function of the body, they are mostly metals and are needed for the everyday activities of the body.
))
[credit: wikimedia creative commons author, Jencom]
Micro-nutrient is a term introduced to include minerals and vitamins which are related in terms of acting as Cofactors in various body reactions. Essential minerals in the body includes iron (helps the erythrocytes to bind and transport oxygen), iodine (essential for the production of thyroid hormones which are needed for normal growth and development), zinc(helps in wound healing) and a host of others; when these minerals are deficient, these very important actions are impaired, this correctly spells out how much the body needs them.
Most of these minerals are specialized, perform a little number of action, ranging from singular to relatively few numbers of cellular action. Calcium is an exception to this as it is involved in many different activities of the body.
These actions are also unique on their own, this distinguishes calcium as one of the most versatile minerals in the body, it performs different actions in different parts of the body; calcium also exist in different forms as they perform these actions which are biochemical (chemical process taking place in a living body) or bioelectrical (biological processes which involve the movement of charged particles)
))
[credit: wikimedia author, Greg Robson]
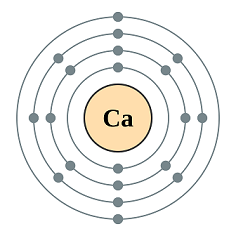
Calcium (Ça) is a chemical element with an atomic number of 20, it is the third most abundant element (after Aluminum and iron), it is found naturally in limestone, gypsum, and fluorite. It is divalent in its oxidized state (Ca2+) and thus is capable of donating two electrons in bond formation, it can. therefore, form compound with elements such as oxygen (CaO), Carbonate (CaCO3).
Existing inbound state; calcium in the form of calcium phosphate crystals are found in bones, teeth, and forms the cement which holds the teeth to their gums. Calcium in bones serves as very important means of regulating the intracellular and extracellular pool of calcium. The bone though having a rigid appearance is under constant remodeling, this involves breaking down the old bones and replacing the removed calcium with new ones, this process is of importance as it helps in maintaining a strong and healthy bone, it also provides free calcium for the body’s action. Bones are broken down to release calcium, new calcium is also used to replace the removed calcium, this creates a pathway for storing in excess supply from the diet.
Calcium also exists in free state as the divalent cation(Ca2+) this accounts for most actions of calcium in the body. This is seen in many activities of the body such as:
Fertilization:
))
[credit: wikimedia creative commons author, unknown]
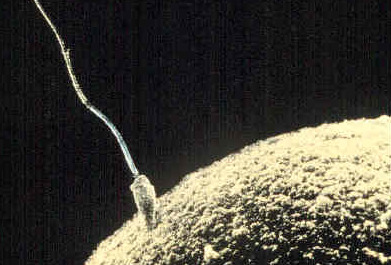
Fertilization is a stage in human reproduction, it is very vital as the production of offsprings are dependent on the efficiency of this process, arguably the most important stage in reproduction. It involves the fusion of male and female gametes (spermatozoa and ova respectively) to form a zygote, zygotes eventually undergoes several processes to grow and develop into a baby.
Fertilization occurs at the Ampulla of the Fallopian tube. The billions of sperm released during intercourse swim toward the ovum; however, only a very few percentages of this enormous number reaches the Fallopian tube.
When the spermatozoa reaches the ovum, it penetrates the outer covering (corona radiata) and reaches the zona Pellucida which it penetrates via the proteolytic action of the Acrosin in the Acrosome of the Spermatozoa, this causes the the maturation and fusion of these gametes. This fusion triggers the influx of Calcium. Calcium influx prevents the penetration of the other spermatozoa, thus only the sperm which swims fastest get to fertilize the ova. This prevents Polyploidy(double fertilization). However the mechanism of this action is still obscured, this action accounts for the infertility associated with calcium deficiency.
Blood:
The blood vessels maintain a constant flow of blood in the body; the distribution of the blood vessels includes areas prone to trauma. Trauma might arise as a result of injury, atherosclerosis and results in the rupture of the vessels, abnormal blood flow is also a cause of vessel injury. Most common source of injury to the blood vessels is of the external source; in case of external injuries resulting from mechanical or chemical agents, the ruptured blood vessel attempts to close the rupture through the coagulation pathway. This is very vital in maintaining the integrity of the blood vessels and a constant volume and mode of blood flow – a process known as Homeostasis.
Injury to the vessels cause ‘Tissue factor producing cells' to produce Tissue factor which forms a complex with coagulation factor VII (seven), this complex activates other coagulation factors which through a cascade of reactions converts Fibrinogen into a stable mesh of Fibrin which covers the ruptured surface.
Coagulation factors are specific plasma proteins which interact in a cascade of reactions to form fibrin; they exist as inactive zymogens and are activated in the process of coagulation. Calcium plays a vital role in the coagulation pathway as it acts as a co-factor in the tenase and prothrombinase complex which results I will the activation of factor X and II respectively. Phospholipids and the ‘accelerator’ coagulation factors (factors VIII and V) are also involved in this action.
Digestion and Blood sugar regulation:
Digestion includes all processes involved in the breakdown of the large molecules of the food we take into smaller molecules which can be easily accessed by the body cells, this involves many chemical and mechanical processes which help to reduce the food into the least obtainable form. Glucose is the most popular compound obtained from food as carbohydrates are the most consumed food worldwide. Glucose is the major sugar in the blood. However the body runs the risk of having an excessive pool of glucose after a carbohydrate-rich meal and a severe scarcity in case of severe starvation, these two conditions if not well handled results in hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia respectively.
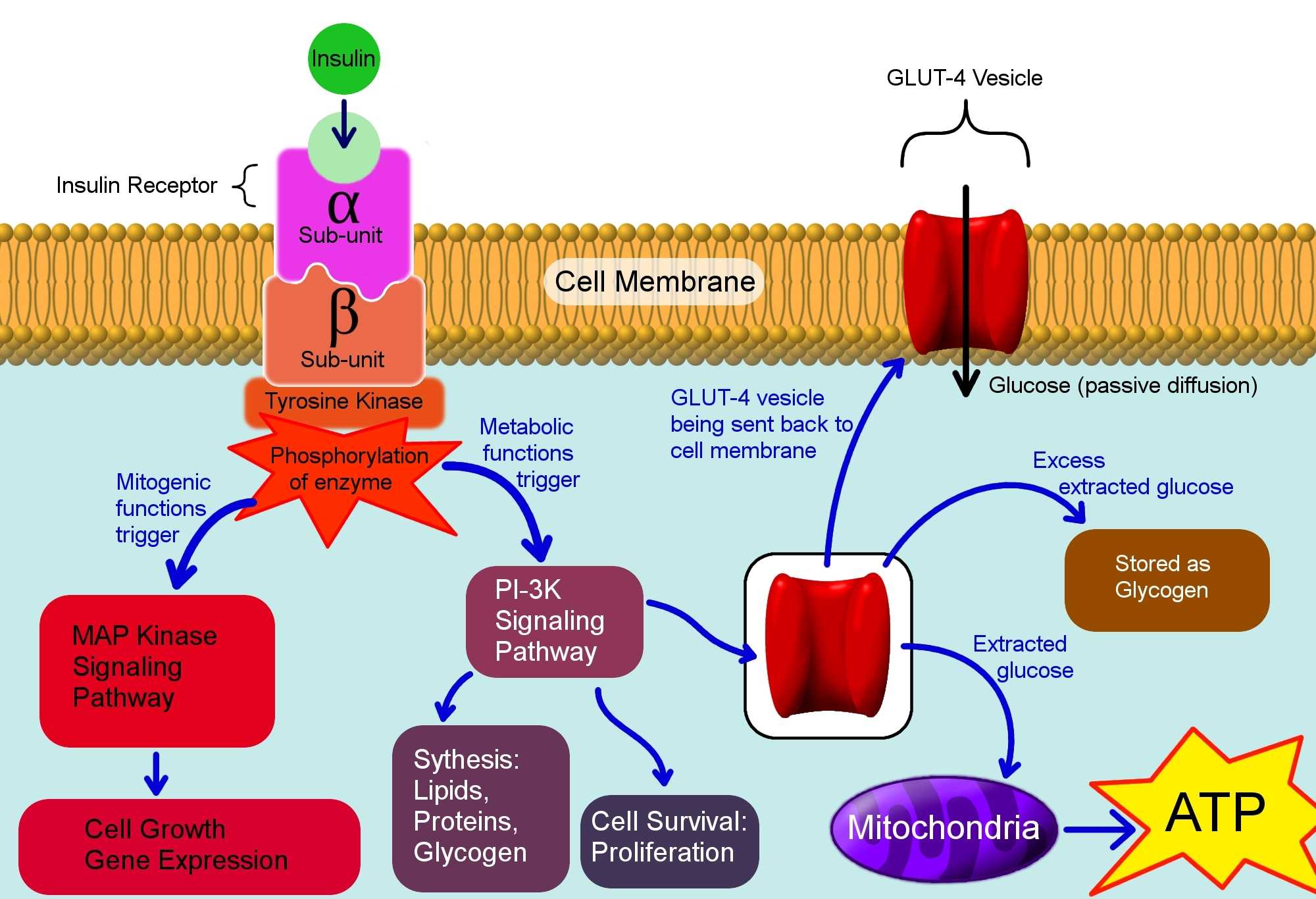
The endocrine system however produces hormones which helps in the regulation of the blood glucose levels, these hormones are know as Insulin and Glucagon. Insulin helps in glucose transport into cells thus reducing the blood glucose level. Glucagon acts in a reverse manner to increase the blood glucose, glucagon acts only on the liver as it’s rceptors are not found in the muscles, thus the glucose for the increase of blood sugar in the regulatory process Comes primarily from the liver.
[credit: wikipedia creative commons by BY-SA 3.0]
Calcium comes into play in this process as it aids the regulation of insulin secretion. After a meal, there is an increase in blood sugar from the carbohydrates in the meal, glucose migrates into the B-cells of the pancreas (the organ in charge of both insulin and glucagon production). The glucose which migrates gets digested in the B-cells to produce ATP and ADP which depolarizes the Beta cells causing a resultant calcium influx into the B-cells, this leads to the secretion of insulin through exocytosis. Calcium is thus indispensable to blood glucose regulation.
Calcium may be implicated in cases of delayed blood clotting and Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) due to an impairment of the above actions.
Calcium is also involved in many bioelectrical actions of the body system, this involves a regulated movement of charged particles into and out of the cell, creating electrical potential which enables the cell to function in a specified manner. This is seen in body actions such as:
Muscle contraction:
Beneath our skin is highly specialized tissues made up of cells which are capable of converting potential energy into kinetic energy, enabling the whole body to move voluntarily or involuntarily, these are known as muscles.
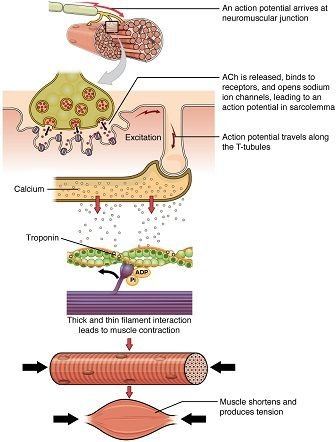))
[credit: wikimedia creative commons author OpenStax]
Muscles are an integral part of every moving system and organ in the body, the heart posses cardiac muscles which are conditioned to work involuntarily and at all times to ensure adequate pumping of blood, the muscles of our intestines and glands also possess the ability to stimulate involuntary movements. Most popular are the muscles attached to the bones of our skeletal system, they are a collection of fibers which work together to enable voluntary movements.
Voluntary movements are controlled by the nervous system (same as every other activity in the human body), however, we have a great control over these actions, thus one can stand only when he/she wishes, this is an example of a voluntary action. Our thoughts send signals known as Impulses to the brain via afferent neurons, the nervous system responds by sending efferent impulses to the effector organs which includes muscles, endocrine organs e.t.c
When an impulse moves through a junction of nerves and muscle fibers, there is a release of acetylcholine (image on the right), a neurotransmitter which enters the muscle cells and causes the influx of sodium ion (Na+), this causes a change in intracellular voltage in relation to the extracellular voltage. This causes the muscle organelles to release calcium into the muscle cells; a hundred fold increase in the Ca2+ concentration causes the muscles to contract, calcium thus regulates the contraction of muscles as a reduction in its concentration halts this action.
Neuronal transmission:
Impulses are also transmitted across the junction of neurons. A neuronal junction is a point where two or more neurons meet, it consists of a synapse and a synaptic cleft which is the distance a neurotransmitter must travel to reach the receptors on the other neuron, neurons terminate as synaptic knobs and they store neurotransmitter which is released on the process of impulse transmission. Calcium is essential if the transmission of impulses across neurons must take place efficiently.
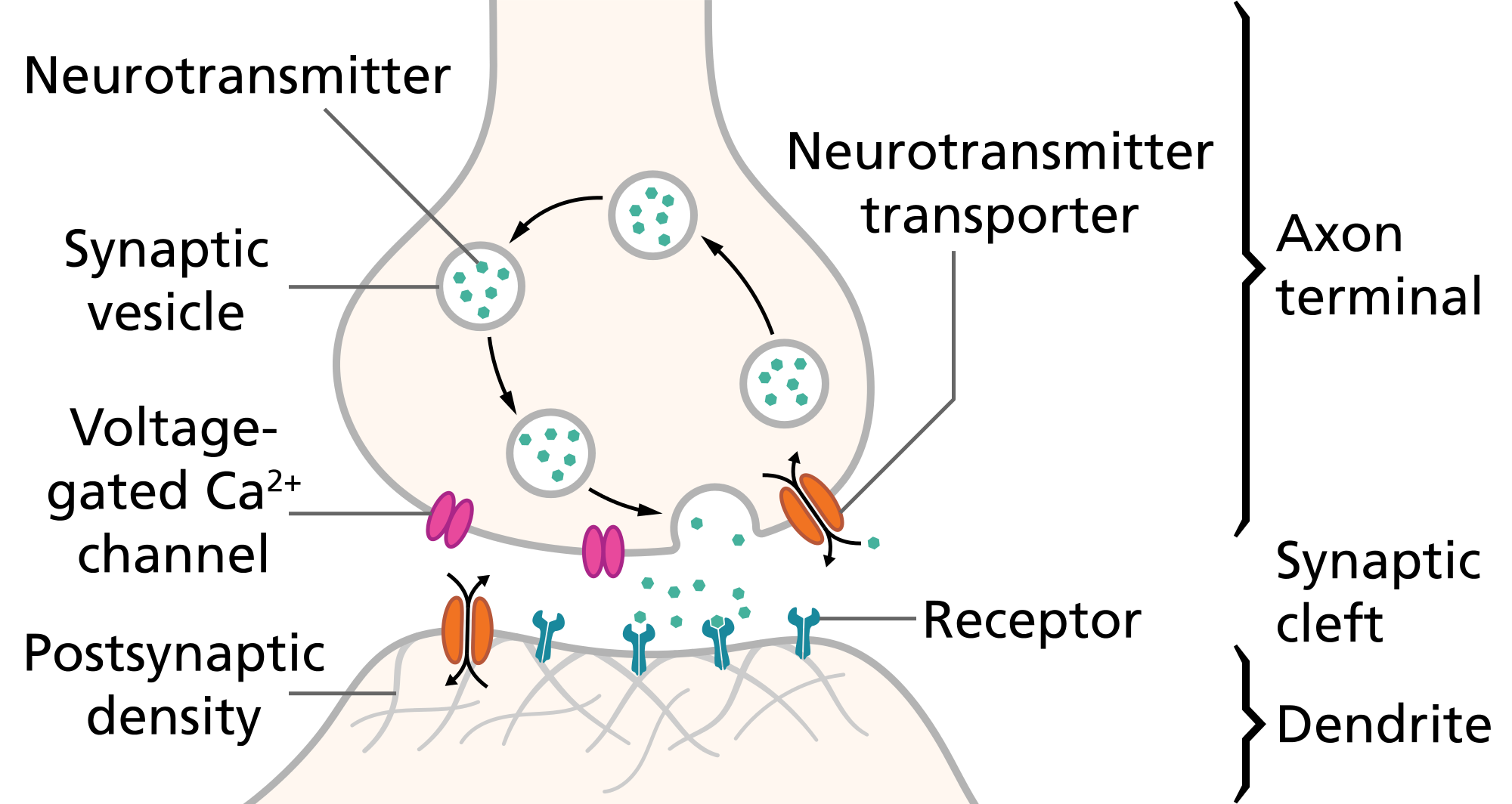
[credit: wikimedia creative commons. author Thomas Splettstoesser ]
The arrival of an impulse causes a change in permeability of the neuronal membrane to calcium, it permits the inflow of calcium into the neuron. Calcium influx causes the release of neurotransmitters which moves through synaptic cleft to attach to receptors located on the synapsing neuron. Calcium binds to Synaptotagmin which causes a conformational change in the protein complex that triggers the vessels containing neurotransmitters to fuse with the membrane of the neurons and release their contents into the synaptic cleft. Binding of the neurotransmitter and its receptor causes the onset of the action for which the impulse carries.
Calcium also functions in signal transduction of many hormones via the calcium-calmodulin system. The body needs to regulate it’s calcium pool to ensure the availability of calcium in an adequate concentration to enable these actions. The body regulates the calcium pool by a hormonal and metabolic mechanism. Hormonal regulation of calcium is by the interaction of vitamin D, Calcitonin, and Parathormone.
Vitamin D and Parathormone increases the calcium pool by generating calcium from bones through bone resorption and also inhibiting the renal excretion of calcium, Calcitonin, a 32 amino acid polypeptide hormone produced by the parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland in response to high concentration of calcium antagonizes the action of vitamin D and Parathormone to reduce the calcium concentration. There is a tight regulation of calcium within 3% of the mean value, this is to sustain these very vital actions which are regulated by calcium.
Calcium pathology
Calcium deficiency or failure of the regulatory processes results in severe malfunctioning of the activities which it is involved in. This can be seen in:
excess bone breakdown as a result of excess vitamin D production and Parathormone secretion or a decreased
Calcitonin secretion results in the excessive breakdown of bone, the bones lose their strength as a result of the excess uncontrolled removal of calcium, the bone, as a result, is prone to fractures. This can also be seen in women of menopausal age
• Excess calcium production may result in deposition of calcium on the surface of cells, this results in catastrophic calcification of the tissues, this may lead to cell death as calcium deposits act as a signal to the apoptosis mechanism. Dystrophic calcification is also seen in dead cells, this is however not associated with unregulated calcium secretion.
Conclusion
Calcium is an essential mineral, even though the bones have a large store if calcium, there is a need to external supply via nutrition as the body has mechanisms if excreting calcium, about 100mg of calcium is excreted per day through urine. If not replaced, the body runs the risk of calcium deficiency which results in the breakdown of bones to generate calcium, this is similar to the breakdown of muscles in protein malnutrition. Calcium can be supplied by nutrition via foods such as:
• Dairy products and green vegetables: Dairy products such as milk and cheese and green vegetables present the highest sources of calcium. Consumption of these substances replenishes the body’s calcium store.
The calcium store of these food items is as follows:
• Cheese – 222mg/oz
• Sardine – 108mg/ounce
• Yoghurt – 50mg/oz
• Milk – 285mg/Cup
Proper consumption of these foods is essential to a healthy calcium balance.
Reference
- https://draxe.com/top-10-calcium-rich-foods/
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calcium
- http://www.elixirindustry.com/Calcium-Information/calcium-bone-development.htm
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/m/pubmed/8408526/

))
))
Congratulations @joelagbo! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on any badge to view your own Board of Honor on SteemitBoard.
To support your work, I also upvoted your post!
For more information about SteemitBoard, click here
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPDo not miss the last announcement from @steemitboard!
You could have just edited the earlier post instead of posting the same post twice which is tantamount to spamming. Feel free to join the steemstem discord channel to interact with fellow scientists/science enthusiasts if you are not in there already. Here is the link https://discord.gg/KrWykYs
Many errors were pointed out, I felt it would be more explicit if i start from the scratch.
You need to format the earlier one to blank then. You can't have the same post running simultaneously.
I've done that, thanks
Ok, seen. Thank you.
Calcium are great nutrients for the body... Mum always insisted we use them for increased bone strength.. Don't know if they actually work. Lol
It really does work, guess you've got very healthy bones... Awesome Mum you've got. Lol
I hope so.
Lol, I thought it is only me..Each time, we were always asked to add it to our dose even if it's just a mere body pain
I am telling you o.. That thing always annoys me coupled with the fact that i hate drugs.
yh, quite annoying
Congratulations @joelagbo! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on any badge to view your own Board of Honor on SteemitBoard.
For more information about SteemitBoard, click here
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPDo not miss the last announcement from @steemitboard!