Life in the Abyssal Regions
The ocean, that great expanse of water that covers our beloved planet, is divided into several zones, depending on several characteristics. Today we want to talk about what is known as abyssal zone or abysspellic zone.
This area, located between 3,000 and 6,000 meters deep, is below what is known as the bathypelagic zone and over the hadopelagic zone. Due to the great depth to which it is, sunlight does not reach here, submerging all this area in absolute darkness.

This area occupies nothing more and nothing less than 70% of the total surface of the oceans, and is characterized by having a very cold environment, with a very high hydrostatic pressure and lack of nutrients, in addition to the already mentioned lack of resources natural light.
All these conditions mean that this place lacks vegetation that carries out photosynthesis. Therefore, in the absence of algae, the beings that inhabit the abyssal zone will only be able to feed on the detritus that fall from the surface.
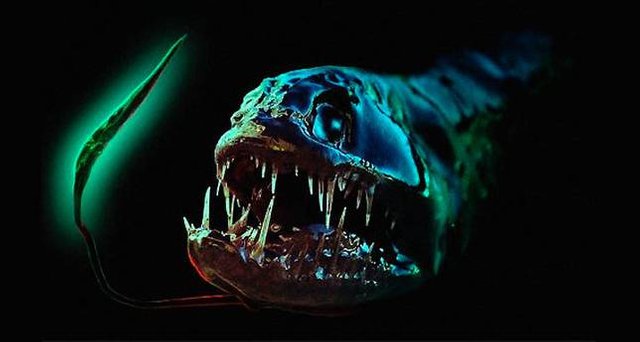
As for these abyssal beings, we can say that they are strange beings with a certain monstrous appearance. Most of them are bioluminescent, that is, they are capable of producing their own light, which on the one hand will help them to attract certain prey, identify with other specimens and escape from the dangers. This light, normally, is created thanks to a colony of bacteria that would inhabit inside the being.
The presence of abyssal gigantism is also common; and is that in this area you can find sea spiders up to 1.50 meters. In general, they are beings that have nothing to do with those that live on the surface, such as Caulophryne, Argyropelecus, Idiacanthus, Melanocetus, Saccopharynx or Chauliodus.
In marine biology, the term abyssipelagic fauna refers to the description of a particular type of environment or natural habitat, with certain species of marine animals swimming freely and living or feeding in open waters at such depths and never approaching the surface.
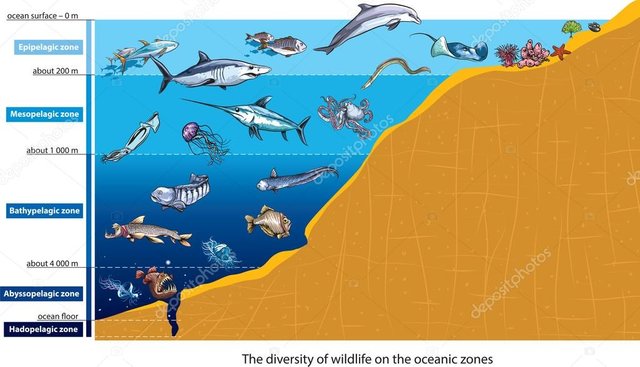
On the other hand, in marine biology there is also the term benthic abyssal fauna, which is the fauna that is linked to the bottom of the ocean, since it is very scarce and characteristic.
The abyssal fauna is formed by strange fish with monstrous aspect like:
Melanocetidae is a family of abyssal marine fish, with a single genus Melanocetus, which belongs to the list of species in the order of the Lophiiformes. The name of the family Melanocetidae comes from the Greek melanos, which means "black", and cetus which means "monster of the sea". In deep waters, the males end up living as parasites of the females.

Saccopharynx is the name of a species of abyssal fish similar to eels with large mouths, extendable stomachs, long bodies without scales and strange appearance. It is the only genus of the family Saccopharyngidae. The name comes from the Latin saccus, with the meaning of "saco", and from the Greek pharyngx, which is "pharynx". Like other saccopharyngiformes, fish of this genus are known as swallowers or enveloping eels.
Characteristics they are usually black and can reach 2 m in length. They have been found at depths of 1,800 m. Their tails end in a luminous organ shaped like a bulb. The exact purpose of this organ is unknown, although it is likely to be used as a decoy. 
Chauliodus is the name of a genus of abyssal fish belonging to the Stomiidae family that reach sizes between 30 and 60 cm in length. Like other deep-sea fish, fish of the genus Chauliodus use bioluminescent organs (photophores) to hunt and capture prey in the depths when sunlight does not penetrate the bottom. They have lights on their body, located on the belly and at the end of a fin to attract prey

Source
The phenomenon of bioluminescence
is mainly marine. In the deepest part of the ocean, the abyssal zone is the main source of light. We will not find it on the surface or in other marine areas (with rare exceptions). On land, this phenomenon is known as luminescence and differs in some of its characteristics.
Bioluminescence is the emission of light by a living organism. Its origin is in a series of chemical reactions that take place in this organism and that do not generate heat, only light. It is speculated that some of its functions are to protect against beings and also attract partners during the mating phase.

ormerly, this chemical phenomenon was attributed to sea monsters and other fabulous creatures, giving it a supernatural origin. But nowadays it is known that the bioluminescence is the result of the oxidation of the luciferin element by luciferase. This reaction is what produces the light source. There are two types of bioluminescence: the intrinsic one, or the one produced by the same living organism; and the bacterial luminescence. The latter is produced by the presence of bacteria, such as the photobacterium, vibrio or the alteromonas. Usually, the light generated by this bacteria is usually greenish blue.
https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_abisal
https://universomarino.com/2013/03/27/la-zona-abisal-de-los-oceanos/

It's nice to see when speculation gives way to actual data.
https://steemit.com/review/@plotbot2015/the-immense-journey-by-loren-eiseley-part-2