It's hard to find a highway that has great conditions along the way. Wakapun toll roads, most highways, both roads and main roads in a state of disrepair, often interfere with driving comfort and accident-prone, especially when traveling at night.
Very many street users are complaining and nagging. There are even some people who can not wait for repairs and deliberately plant trees on paved hollow roads, in order to attract the attention of the government, in addition, of course to give warning to other road users:
So, before we assume or accuse others, it helps us to understand how to work pave the way, especially on how to strengthen the asphalt. This knowledge is also useful when we want to increase the asphalt around the environment with the help of ourselves.
There are several factors that affect the asphalt layer on the highway. So the wrong combination can speed up asphalt damage. How can we strengthen the asphalt so that it lasts longer?
 Source
Source
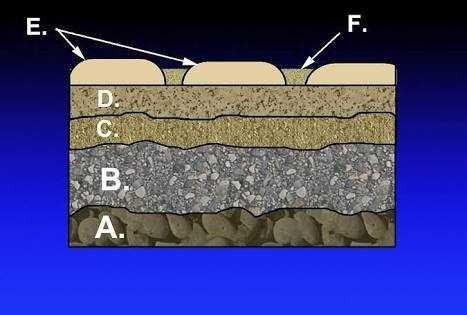
First, we must know the thickness of the asphalt layer in the work or planned.
- Surface coating (asphalt)
- Top foundation layer (A class aggregate)
- Middle foundation layer (Class B aggregate)
- Underclass layer (C class aggregate)
- Ground floor
If we look at asphalting work, we usually see the workers pouring the material several times. They sow sand, gravel, liquid asphalt or any other combination. This is actually done to create a layer that is thick enough to determine the asphalt's ability to withstand vehicle loads.
Bottom layer or Asphal Concrete-Base (AC-Base) is the first layer located above ground level. The minimum thickness of this layer is 6cm.
The next layer is the upper layer or Asphalt Concrete-Binder Course (AC-BC), often referred to as the last layer, intermediate surface layer, because it is in the middle of two or three other layers. The minimum thickness of this layer is 5cm.
The upper layer is called the Asphalt Concrete-Wearing Course or (AC-WC) layer. Another name is laston lapis wear, because this section is directly confronted with the tire pressure on the highway vehicle. The minimum thickness of this layer is 4 cm.
Thus, when summed, the minimum asphalt thickness that is either in accordance with the regulation is 6+5+4=15cm. the thicker the layer is used, the stronger and longer to use.
 Source
Source
Types of Asphalt Materials
One of the main keys of asphalt strength is to avoid water absorption, so the materials used must be waterproof. Materials commonly used for the bottom layer are colloidal clay, clay, silt, fine sand, coarse sand, gravel. Among these materials, the best used as a bottom layer is fine sand, coarse sand and gravel, because it does not absorb water, is stronger attached to the top layer, and can extend the life of the asphalt.
 Source
Source
Asphalt Loading
Simply put, the more often the highway through the vehicle, the higher the load and the possibility of damage to the asphalt layer. Highways that create heavy traffic and slow moving vehicles can also speed up damage. The easiest way to avoid this is by limiting the allowable load (tonnage). Some road signs indicate the limit of vehicle loads allowed in order to maintain the quality of the highway.
 Source
Source
The Slope Of The Road
Do you know why toll roads are not completely flat? This is one of the asphalt road construction techniques. Stagnant rainwater makes the asphalt easy, especially if passed by heavy and slow vehicles. The occurrence of holes in the asphalt layer, often occurs due to puddles that do not flow. Usually the road in the middle to each side of the road will have a slope to give way for rain water into the ditch channel.
 Source
Source
Water Disposal System (Drainage)
A strong asphalt layer requires a good drainage system. That is why the choice of material and the right kind of material, as mentioned above becomes an important consideration, because it determines the strength and endurance of asphalt ages. In addition, the ground floor to be coated is also very decisive. Many highways drown or descend partly, not because of asphalt layers or poor quality work, but the basics do not have a good drainage system.
That's the things we need to know about making paved roads. Hopefully the above information makes it easy for you to plan the asphalt road repair independently.
 Thank you, this is my writing for this time, if there are words that are not good, not polite, not clear. I can only apologize. Perfection belongs only to God, I am only human who can not escape from mistakes. So, greetings from me @youngky. For my friends in steemit and for all my faithful followers.
Thank you, this is my writing for this time, if there are words that are not good, not polite, not clear. I can only apologize. Perfection belongs only to God, I am only human who can not escape from mistakes. So, greetings from me @youngky. For my friends in steemit and for all my faithful followers.


About The Science I Have Written:
Science: | Science: | Science: | Science: | Science: | Science: | Science: | Science: | Science: | Science: | Science: | Science: | Science: | Science: | Science: | Science: | Science: | Science: |
Reference:
1, 2, 3, 4.









The water drainage, and the load passing through the asphalt road are the main issue. A road without a proper channel for water will cause potholes, same applies with loads, especially heavy duty trailers. They should have their designated route in my opinion