[Sansanmycin Uridylpeptide]: The New compound from Soil Bacteria to eradicate Tuberculosis
The scourge of Tuberculosis could soon be a thing of the past, if the discovery of a certain compound in soil bacteria by scientists, is anything to go by.
Tuberculosis is an unenviable and rather popular disease caused by a bacteria known as Mycobacterium tuberculosis. TB as it is also known, commonly affects the lungs, although it can affect any organ in the body.
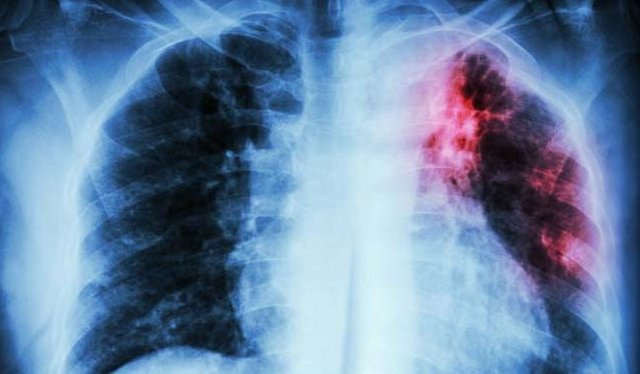
The treatment of the dreaded disease has experienced increasing and troubling resistance in recent years; as most drugs in current use, which have existed for over 40 years, have gradually become ineffective in dealing with the bacteria-causing disease.
Tuberculosis: A Global Top-10 Killer
Worldwide, and according to the World Health Organization (WHO), Tuberculosis is one of the top causes of death in the world – especially within low to middle income or developing nations. Most cases of the disease infection are curable, but a lack of proper treatment can lead to death.
It is statistically known that one-fourth of the world’s population is currently plagued with Tuberculosis. And TB is the top killer of people living with HIV infection. In 2014, it is reported that about 1.5 million deaths were recorded from Tuberculosis related cases, and 1.8 million people reportedly died from the disease in 2015.
In 2016, 1.7 million deaths were recorded worldwide from about 10.4 million people infected the same year.
In the United States, about 9,272 TB cases were reported in 2016, at a rate of 2.9 cases for every 100,000 persons.
Despite the sad and awful statistics, the WHO reports that huge progress was made in the fight against the disease as no fewer than 49 million lives were saved between year 2000 and 2015, through proper, early and effective diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
Scientists waging the war against Tuberculosis
The recent discovery of a compound
“sansanmycin uridylpeptide” in soil bacteria capable of obliterating Tuberculosis is the work of a team of international researchers from the United States, United Kingdom and Canada, led by the University of Sydney, Australia.The scientists developed synthetic and potent forms of the natural compound, showing its ability to kill the tuberculosis bacterium in the laboratory.
Drug Resistant Tuberculosis (TB)
There are two known forms of drug-resistant TB, and they are;
- Multidrug-resistant (MDR-TB), and the much rarer;
- Extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR-TB)
The drug-resistant TB has become the worrisome trend of late; as some forms of the disease have become quite unbothered by the current drugs and treatment procedures used against them.
- In TB cases of 2015, about 480,000 were MDR-TB
- About 250,000 deaths were estimated to have been due to drug-resistant TB
- Nearly half of the world’s MDR-TB cases are accounted for by China, India, and Russia. Source
Of the two first-line drugs - isoniazid and rifampin - used to treat TB; the MDR-TB and XDR-TB are both resistant to the drugs. The rarer XDR-TB is also resistant to any fluoroquinolone, and one of ‘amikacin’, ‘kanamycin’, or ‘capreomycin’ (all known as second-line drugs). This then leaves patients with very limited treatment options.
Treating the drug-susceptible TB in the U.S., costs on average about $18,000. While the treatment of the XDR-TB costs in the region of $494,000.
Sansanmycin Uridylpeptide: The New compound to eradicate Tuberculosis?
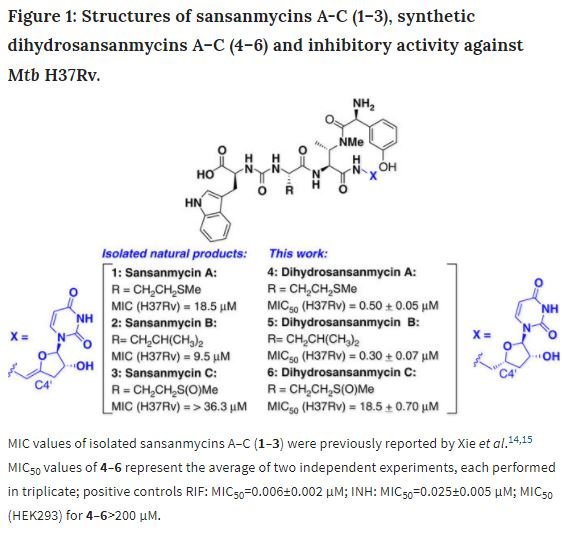
The study by the team of scientists centers around “sansanmycin uridylpeptide”, which is a compound produced by a bacteria, and has the ability to stop other bacteria from growing around them.
The researchers showed via laboratory tests, that the sansanmycin compound analogs which were created for the study via synthetic chemistry, effectively killed the M. tuberculosis which causes TB. The team was able to also produce more potent variations of the natural compounds.
The sansanmycin compound analogs works by targeting an enzyme which aids the building of the cell wall of the tuberculosis bacterium known as “Mtb phospho-MurNAc-pentapeptide translocase”, or MraY.
A lead author of the study, Richard Payne, who is a professor in Sydney’s School of Chemistry, said that the new analogs killed the TB bacteria inside the host cells (macrophages) that the TB bacteria inhabits once inside the lungs. Prof. Payne said;
“Without a cell wall, the bacterium dies. This wall-building protein is not targeted by currently available drugs.”
“Attacking this “Achilles heel” of the bacterium prevents it from being able to build a cell wall.”
Conclusion
The discovery of the new compound analogs by the consortium of scientists; as echoed by Prof. Payne is that their discovery would highlight and herald a new era of development of potent TB drugs to fight the disease.
According to authors of the research, further tests and advanced safety research have already been planned; as further studies seek to demystify the mechanism by which the sansanmycin compound selects their target for extermination.
PS: World Tuberculosis Day is marked every year on March 24th. It is a day to create awareness about the dangerous TB epidemic and highlight measures to avoid and eliminate the disease. Ahead of the World TB Day 2018; live safe, Stay healthy and remain TB-free.
Reference: r1, r2, r3, r4, r5, r5, r7
Thank you for your time and for reading my post.
If you found this post interesting, then kindly UPVOTE, RESTEEM and FOLLOW @rickie, for more quality posts.
You Can Check Out My Other Blog Posts Below:
- Monitoring Diabetes Just Got A Little Bit Easier With Nanotechnology
- The Future of Space Food for Astronauts Could be Human Excrement (Faeces)
- A Bacteria Has Been Found To Produce Gold By Consuming Metals
- The future of Oil-Spill Cleanup could be Oil-absorbing Cellulose
- Can We Afford To Lose Bats, Given Their Importance?
- New Blood Test Can Predict Early Signs of Alzheimer's Disease

I've followed your blog quite a long time ago. Nice share. Can I resteem this?