Monitoring Diabetes Just Got A Little Bit Easier With Nanotechnology
As far as science and technology go, there certainly is no limit to what we can achieve; if we persist.
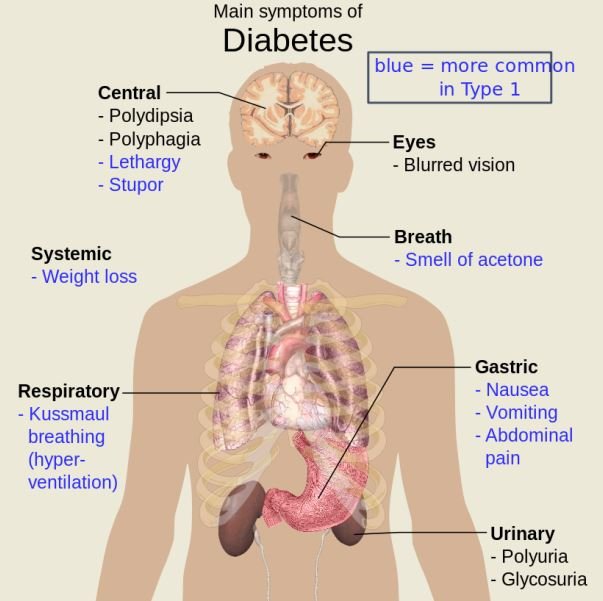
Diabetes is simply a condition in which the body has high blood sugar level over a long time. This is often due to a situation where the pancreas becomes deficient in producing adequate insulin or when the cells of the body are not responding properly to the insulin produced.
The name itself, "diabetes" was first used by the Greek Apollonius of Memphis in 230 BCE. The two popular forms of diabetes mellitus are the Type 1 diabetes (associated with youth) and Type 2 diabetes (being overweight). In 400 - 500 CE both types of diabetes were classified as separate conditions by Indian physicians Sushruta and Charaka.
Statistically;
- 422 million people are living with diabetes, as of 2016
- 1.5 – 5.0 million died per year from 2012 to 2015, due to diabetes related illnesses
- World economic cost of dealing with diabetes in 2014 was estimated to be US$612 billion
- In 2012, diabetes cost the United States $245 billion
The disease which is a function of too much sugar or high blood glucose in the blood, has always been very tasking to monitor.
But with nanotechnology comes an improved tool for monitoring a person’s glucose levels. Traditional means of monitoring a person's blood sugar levels often involves analysing their sweat, tears and blood.
However, researchers have developed a flexible ultra-thin sensor capable of carrying out real-time glucose tracking in the blood.
The Nanotech wearable Glucose Sensor
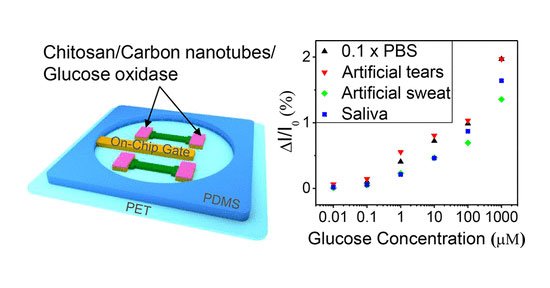
The new Nano-device can be integrated into the back of wristwatches or into contact lenses to aid glucose-level monitoring. The biosensor is fitted with on-chip gates and then attached to either the wristwatches of contact lenses so that they can monitor glucose levels from the resulting body fluids - sweat, tears, and even saliva.
As part of our modern digitalization, wearable sensors have become very common, with regards too health issues.
The sensors used in fields of medicine today often assess a person’s physical activities by studying heart rate, pulses, etc. The limitations of studying health challenges using traditional health markers have been noticeable. But despite this , their significance can be life-changing.
The process of analysing certain health conditions, involves analysing blood samples from the affected individuals; for instance - the pricking of fingers in order to draw blood samples. The act of prinking the skin for blood sample also tends to deter people from being very cautious and from carrying out regular checks.
Limitations of other glucose sensing devices include the fact that some of them cannot detect low levels of glucose, or they can’t work if they are bent.
But the wearable glucose sensing device promises more. It’s still an innovative idea and is still being tweaked by the researchers, Moh Amer, Chongwu Zhou and colleagues.
The Development
The biosensor which is developed for the purpose of studying the presence of high glucose (sugar) level in the body was created using;
- nanoribbons of indium oxide
- natural chitosan film
- a glucose oxidase enzyme
- a single-walled carbon
In a case where there is presence of glucose in the test sample, the glucose goes on to react with the enzyme, which releases a set of brief chain reactions leading to an electrical spark.
Upon testing, it was discovered that the glucose sensor, was capable of detecting a 10 Nanomolar to 1 millimolar in glucose concentration, which is highly sensitive enough to veil the levels of glucose in saliva, tears and sweat.
It was also noted that bending the film repeatedly up to a hundred times, did not affect thee film of the sensor. Also, the performance of the sensor experienced know performance issues.
Conclusion
The new technological breakthrough hinges on the capability of the glucose biosensor to read and monitor the level of glucose and sugar in the body through the body fluids.
Apart from the innovative function of the new ultra-thin glucose sensor, researchers have suggested that the sensor can also be used in monitoring the food sector as well as the environmental sector, in no distant time.
Certainly, it is safe to assume that the new development is another plus for science and technology
Reference: rf1, rf2, rf3, rf4, rf5, rf6
Thank you for your time and for reading my post.
If you found this post interesting, then kindly UPVOTE, RESTEEM and FOLLOW @rickie, for more quality posts.
You Can Check Out My Other Posts Below:
- The Future of Space Food for Astronauts Could be Human Excrement (Faeces)
- A Bacteria Has Been Found To Produce Gold By Consuming Metals
- The future of Oil-Spill Cleanup could be Oil-absorbing Cellulose
- Can We Afford To Lose Bats, Given Their Importance?
- New Blood Test Can Predict Early Signs of Alzheimer's Disease
- What is Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) and How does it Work?

This is so interesting to know.... Thanks to you. Lovely post
Fantastic technology
This small Board with a large number of needles is another nanotechnology that can change the life of diabetics for the better.

Each micro game has its own sensor, which is invisible to the naked eye.
This technology allows to collect and analyze blood. Research is conducted by British scientists.
The length of the needle is about one millimeter, and the diameter is about fifteen microns.
This ensures the patient is painless to use. These needles are attached to the patient's hand. A blood sample is taken with a microneedles sensor. These sensors are mounted in the needle with the help of the nanowires.
This technology allows you to painlessly monitor blood glucose levels.
Scientists are now finalizing a transmitter that will send SMS messages to the hospital or relatives of the patient if he or she is at risk of a hypoglycemic attack.
Yea, this is really a great plus from science to health.
The nanotechnology can
Great work!
Thank you
The best and most beautiful things in the world cannot be seen or even touched - they must be felt with the heart.