How sharks' body shape influences their locomotion
«The function generates the form» is an assertion made by the American architect Luis Sullivan, though it applies not only to architecture, but also to nature in general, and to sharks in particular.
Today's post based on the online course «Sharks! Global Biodiversity, Biology, and Conservation» is about body shape and locomotion of sharks.
For a reason, each shark is characterized by individual anatomical features, some have a flatter body, others an elongate one. All this matters, considering where the shark inhabits and which way of life it leads.
TAIL
For example, if you consider the tails of sharks, you can see that they are quite different shapes. A white shark has a crescent-shaped tail for convenience of swimming vertically from the water surface and deep into the ocean, and also to overcome long distances during migration. A sand tiger shark’s tail resembles a point of a spit, which prevents it from gaining high speed and making long migrations.
BODY FORM
The different shape of lateral fins also gives advantages and disadvantages. So, the blue shark thanks to long breastpins can make sharp turns to catch a prey while hunt, but such fins are not suitable at all for life on the bottom, for example.
Now let us remember how a hammerhead shark look like.
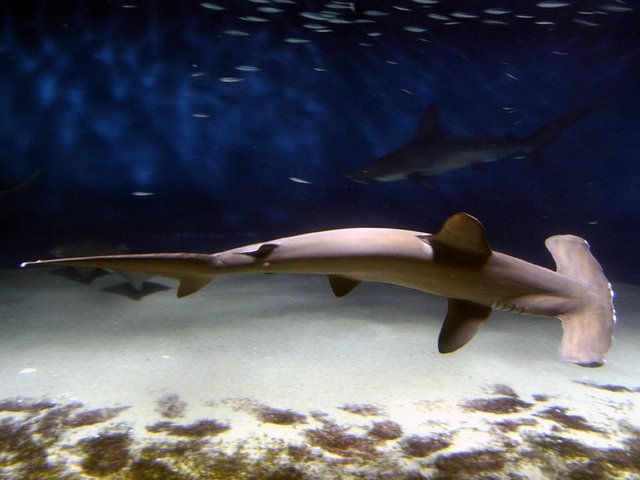

Its very unusual shape of the head immediately causes a bunch of «why»-questions. Professor Steve Kajiura suggests that since sharks have electroreceptors that capture electric fields that are located on the head, such receptors of hammerhead sharks are "allocated out on different sides". This helps to capture electrical impulses better and to analyze more quantity of water.
Moreover, there is a hypothesis that such a form of the head contributes to the increase of hydrodynamics: when the head is lifted, the shark becomes more maneuverable, accordingly, it is easier for it to hunt.
And one more thing: thanks to binocular vision the hammerhead more accurately calculates the distance from the prey.
MUSCULTURE
If you look at salmon (at already cleaned one), then you will observe distinct zigzag strips, these segments are called myomers. After cooking the fish, these parts are separated from each other very easily, since during thermal treatment of intermuscular septa contribute to separation of myomers.
It is the myomers that set the fish in motion, especially the tail from side to side.
There are 2 types of muscle fibers (in humans, by the way, they exist as well): red (slow) and white (fast). Red ones are located far from the spine and serve to balance when swimming, and white ones are next to the spine and are needed to increase speed.
Screenshot from the course
In fact, if the fish has more red muscle fibers, then it resembles a marathon runner — it migrates very far and is constantly on the move, if white fibers predominate, then the fish is comparable to a sprinter — a few quick movements to catch a prey and the rest of the time it is inactive .
The red color of the muscles is due to the fact that they have a large number of capillaries for regular supply of oxygen. Oxygen, in turn, is stored in myoglobin, which also has a red tint.
Sharks tendons consist of myosept (made up of collagen fibers), it looks not as a separate element like we might think, but rather as a connective tissue between the skin and muscles. By the way, the shark's skin functions like a tendon itself. Thanks to it, contractions of myomers are transmitted from the head to the tail.
METHODS OF SWIMMING
Each species of sharks has its own features of body shape, fins and tail. This affects the fact that they use their body differently when traveling underwater.
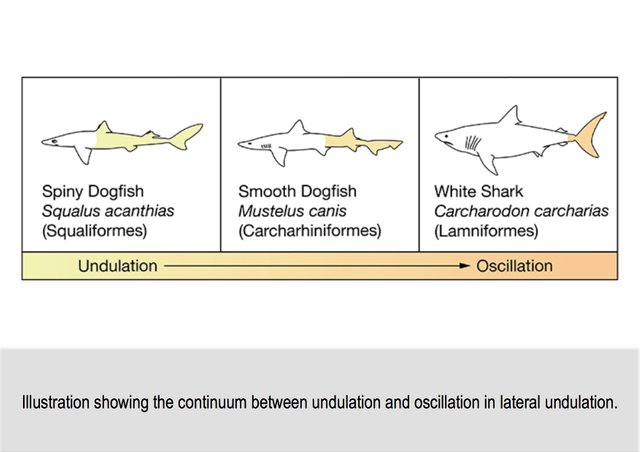
BIOMIMICRY
Scientists are always observing animals very attentively, as well as insects and fish, they are checking their shapes, properties, characteristics, and on this basis project inventions. This area of development is called biomimicry.
Engineers together with scientists from the universities of Virginia and Pringston developed a bot based on the manta ray. Technologists have tried to replicate mobility of the fish, because it turned out that they have a lot of other micromovements besides flapping of the fins, especially when it comes to sharp turns that would be useful for creating a bot. Moreover, the study of this manta ray made it possible to remove previously existing spinning propeller, which drove the robot into motion. Now underwater apparatus operates almost noiselessly and more nearly to the bottom.
DRAG
It is a known physics law: the larger a surface area drag the larger the drag itself. If an animal has a shape of a sphere it means its surface area drang is the smallest. Though sharks cannot have a spherical form because they need to cope with pressure drag. It is proportional to the animal’s length and its speed, for sure it increases if a fish swims faster.
While swimming slowly the water ovewhelms the body shape smoothly and evenly. In this case all the body parts are in contact with the boundary water layer. Scientists name such a flow as laminar. The opposite flow occurs when an animal swims fast creating vortexes in the water. For such a flow there is a term as turbulent.
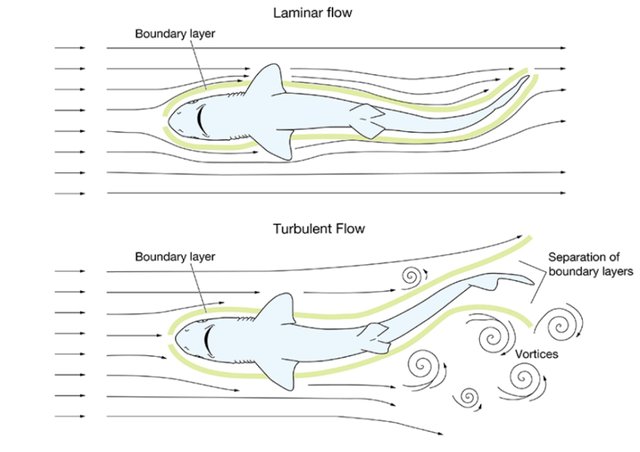
Screenshot from the course
The nature is very clever because it minimized pressure drag by giving sharks a fusiform body shape — narrower at the head and tail and wider at the shoulder.
One more thing greatly affecting fast swimming are scales. They are much flatter for those types who move fastly and more «open» who is slower in water.
BUOYANCE
Unlike bony fish sharks lack a swimbladder that allow to pump or decrease air inside it and provide a fish neutral bouyancy. Sharks have another system to control bouyancy: they concentrate low-density oil in the liver. Because oil is less dense than water the oily liver contributes into minimization of energy spending for keeping the shark in some water column. It means sharks do not possess a danger of barotrauma when gas-filled organs increase when under pressure underwater.
All pictures unless indicated otherwise are under license CC0.
Very interesting indeed! Thank you for sharing and for supporting @steemiteducation.

This post has received a 11.54 % upvote from thanks to: @crazy-daisy.
thanks to: @crazy-daisy.
For more information, click here!!!!
The Minnowhelper team is still looking for investors (Minimum 10 SP), if you are interested in this, read the conditions of how to invest click here!!!
Resteemed by @resteembot! Good Luck!
Curious?
The @resteembot's introduction post
Get more from @resteembot with the #resteembotsentme initiative
Check out the great posts I already resteemed.
@minnowpond1 has voted on behalf of @minnowpond.
If you would like to recieve upvotes from minnowponds team on all your posts, simply FOLLOW @minnowpond.