Euler's solution of the Basel problem

Leonhard Euler (1707-1783)
The Basel problem is the computation of the exact value of the series
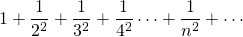
It is very easy to check that it converges, however to compute the exact value of its sum is a different matter.
This problem was stated by Pietro Mengoli in 1644 and the first to solve it was Leonhard Euler in 1734, when he was 28 years old.
Here I will present the solution given by Euler, at that time the proof was not rigorous, since it is based in the Weierstrass factorization theorem (proved in the middle of the XIX century). This theorem allows to express an entire function (a complex variable function which is analytic everywhere) as an infinite product which involves the zeroes of the function. It can be thought as a generalization of the fundamental theorem of algebra. That result was not rigorously proved at Euler's time, however it was supposed true in special cases.
Others rigorous computations of the sum of the series involves residues calculus or Fourier series. We are not going to present these proofs here. We shall show Euler's computation, which is very beautiful. These computations show that Euler was a master in doing computations.
Consider the Taylor series of sin z:
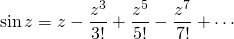
so
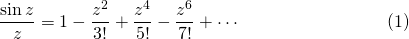
The roots or zeros of sin z are: (kπ)-1, with k an integer. The Weierstrass factorization theorem, allow us to decompose it as an infinite product. As I mentioned before at the time of Euler this result was not proved, however it was assumed it was true. Hence:
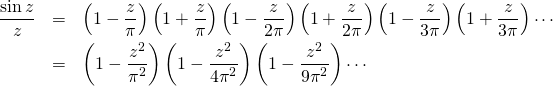
After doing formally this infinite multiplication, we have a power series. The term associated to the power z2 of this series is:
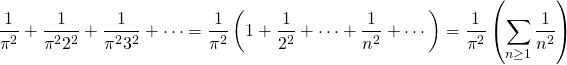
Since two power series are equal if and only if the terms associated to powers of the same degree are equal, for all degrees. After comparing this last expression with the term of z2 of the Taylor series (1) we get the desired equality
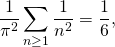
or equivalently:
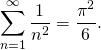
The problem is called after the city of Basel, because it was Euler home city as well the Bernoulli family. The Bernoulli family studied the series
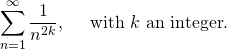
This series are associated with what we call today, Bernoulli numbers. However describe them is beyond the scope of the present post. This series is the value of Riemann zeta function on 2k, i.e. ζ(2k).
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Basel_problem
Henrici, P., "Applied and Computational Complex Analysis", Vol. 1, John Willey & Sons Inc. (1974).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Weierstrass_factorization_theorem
Source of the image: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leonhard_Euler
Excellent information @nenio. Thanks for sharing!. Voted!. I'm following you. Follow me!. I'm physicist.
I invite you to see my website http://www.cmc.org.ve/tsweb where I have published drafts of the texts that I am writing.
I am participating in the Cervantes Photography Contest: 4th Delivery. I invite you to see, comment and vote my photos: https://steemit.com/spanish/@tsoldovieri/concurso-de-fotografia-cervantes-4a-entrega
I invite you to see also: https://steemit.com/spanish/@tsoldovieri/la-planta-de-lechoza-o-papaya-d
Regards!.