Math Patterns in Nature series: Why the Natural World Looks the Way it Does. #2 SYMMETRY
In this @beesteem series I'll introduce you to some fascinating patterns that you can find in nature and art. Those patterns may consist of symmetry, tree structures, spirals, meanders, waves, or stripes. Lot's of possibilities.
Today we will discuss SYMMETRY. Behind the beauty one can find an intriguing mathematical pattern!
What are examples of symmetry in nature? Do you recognize symmetry in these?


.
.
or this nice one:

The math behind symmetry
The two main types of symmetry are:
- reflective
- rotational.
Reflective symmetry - mathematics
Reflective symmetry is like standing in front of a mirror: A cut between two parts is showing the other part too. For example a Butterfly (wings) have a reflective symmetry:

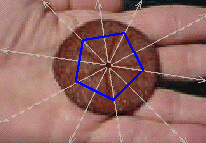
Rotational symmetry - mathematics
Rotational symmetry means that the object or image can be turned around a center point and match itself some number of times (as in a five-pointed star). For example, a snow flake:

There are also other rotational examples with different rotation angles found in nature::
Flowers shows rotational symmetry


Honeycomb show octahedral symmetry
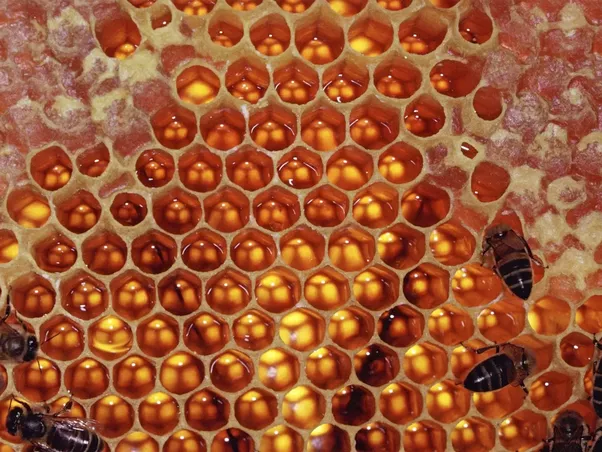
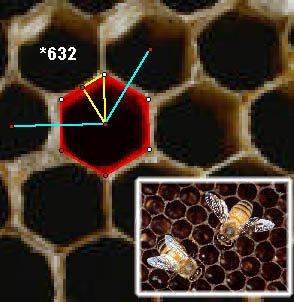

And also in the seas: jellyfish, seastar


Survival of the fittest? No survival of the one with most symmetry!
We are naturally attracted to symmetry. Research indicates that we consider a face beautiful when the features are symmetrically arranged. We are drawn to even proportions. Also animals choose mates on the basis of symmetry


Bee Safe!
@beesteem
Link to other math patterns posts :
I like the jellyfish part :-0