SLC21/WK6: Electricity bill and Electrical Cable, Circuit Breaker size Calculation
Hi guys, it's week 6 in the Steemit engagement challenge and I'm delighted to share my entry in this topic today which talks about Electricity bill and Electrical Cable, Circuit Breaker size Calculation. It was a wonderful lecture filled with many information and the tasks are also beautiful.
After going through the course I feel it will be great to share my entry in the contest and that is why I have decided to attempt the questions given in the course below. Without further ado let's get started. I'm going to be using my knowledge from the class and a little research I carried out to perform this task.
A.
| Write three key differences between XLPE and PVC cables. |
|---|
To clearly discuss the key differences between the XLPE and the PVC cables I will like to share it in a tabular format below. So let's consider the below table for a clear information.
| Difference | XLPE | PVC |
|---|---|---|
| Composition & Insulation | It is composed of a crossed-linked Polyethylene which enable the cable to have both thermal and mechanical features and this enable the cable to perform better when carrying electricity | It is composed of thermoplastic polymer and also has very low thermal resistance which made it always degradate when the temperature of the electricity is high. |
| Resistance to Temperature | When there is a continuous operation, this cable can withstand upto 90°C operating temperature also about 250°C for short circuits | The thermal capacity here is low hence the operating temperatures it can withstand is 70°C and also about 160°C for short-circuit. |
| Durability and Flexibility | This cable has a strong resistance to environmental factors such as radiation and moisture and for that reason it is mostly used for underground or high voltage connection | This cable here can not withstand environmental factors such as much radiation or moisture as it can easily wear out hence it is best used for indoor connection and for low voltage. |
| Write three key differences between single-core, two-core, and three-core cables. |
|---|
To clearly discuss the key differences between the single-core, two-core, and three-core cables I will like to share it in a tabular format below. So let's consider the below table for a clear information.
| Difference | Single-Core | Two-Core | Three-Core |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Conductors | As the name implies single core, it contains only one conductor which is used to transmit signal (doesn't have neutral & earth) | Has two conductor which one of the conductor act as neutral and the other act as live to transmit signal (doesn't have earth) | Has three conductor which represent live neutral and earth for transmitting signal to appliances that needs earthing |
| Usage | Mostly used in transmission of high voltage | Mostly used for double insulated appliances at home | Mostly used for appliances that required earthing especially appliances in factory and industries |
| Complexity and Cost | Not complex in its design and it is mostly cheap | A little complex in its design and a bit costly than the single core | Due to the additional conductor which is the earth, it is mostly complex in design and very expensive |
| Write about peak and off-peak hours in your country. |
|---|
When we talk about Peak and off-peak hours in electricity here in my country Nigeria, we are referring to periods of higher demands and periods of lower demands. So below let's look at it in a broader view.
| Factor | Peak Hours | Off-Peak |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Periods where the demand for electricity is in its highest demand we call that period peak hours | Periods when the demand for electricity is low is called the off-peak hour |
| Time | Morning (6:00 AM – 10:00 AM) & Evening between (6:00 PM – 10:00 PM) because these are period where people are very stable at home | Afternoon(10:00 AM – 4:00 PM) & Night (10:00 PM – 6:00 AM) as there no people at home and when people will be sleeping respectively |
| Characteristics | Rates of electricity increase because of the demand | Low electricity rate due to little or no usage of the electricity |
| B. Calculate your house load and prepare the electricity bill for November 2024 by following Example 1. |
|---|
Using the sample provided in example one, I will start by highlighting the things that consume electricity in my house below and also the bill per unit in Steem. So consider my house appliances below.
In my house, five lights of 30 watts are on for 6 hours per day, two fans of 70 watts are on for 4 hours per day, and a hot plate of 70 watts is on for 5 hours per day. Our electricity company's electricity bill per unit is 0.19 Steem. How much will my electricity bill be in November 2024?
Solution:
Formula to calculate electricity consumption: Watts * Number of loads * Hours
Electricity consumption of the lamp per day:
= Watts * Number of loads * Hours
= 30 *5 * 6
= 900 WH
= 0.9 KWH [1 KW = 1000 Watt]
Electricity consumption of the Fans per day:
= Watts * Number of loads * Hours
= 70 * 2 * 4
= 560 WH
= 0.56 KWH [1 KW = 1000 Watt]
Electricity consumption of the hot plate per day:
= Watts * Number of loads * Hours
= 70 * 1 * 5
= 350 WH
= 0.35 KWH [1 KW = 1000 Watt]
Total electricity consumption in a day:
= Lamps + Fans + Hot Plate
= (0.9 + 0.56 + 0.35) KWH
= 1.81 KWH
= 1.81 Unit[ 1 KWH = 1 Unit]
Total electricity consumption for November 2024:
= Total electricity consumption in a day * 30 [November Month= 30 Days]
= 1.81 * 30
= 54.3 KWH
= 54.3 Units
Electricity Bill Per unit = 0.19 Steem
Total electricity bill for November 2024:
= Total electricity consumption for November 2024 * Per Unit cost
= 54.3 * 0.19
= 10.317 Steem(Ans.)
| C. Calculate the total electricity bill with the HT meter values given in Example 2 and design an electricity bill in Excel. |
|---|
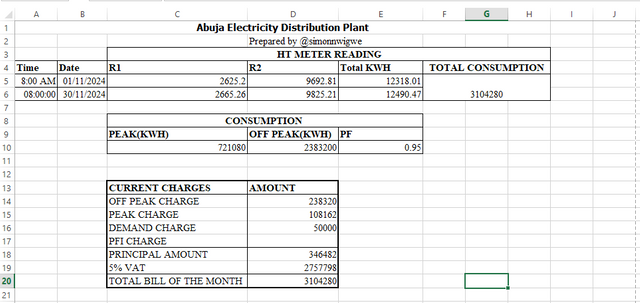
HT Meter Reading:
| Date | R1(Peak) | R2(Off Peak) | Total KWH |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01-11-2024 | 2625.20 KWH | 9692.81 KWH | 12318.01 |
| 30-11-2024 | 2665.26 KWH | 9825.21 KWH | 12490.47 |
| Peak Rate | 1.5 Steem |
|---|---|
| Off-Peak Rate | 1.0 Steem |
Formula:
R1(Peak)=(2665.26-2625.20)KWH * 18000= 721080
R2(Off Peak)=(9825.21-9692.81)KWH * 18000= 2383200
Total KWH = R1 +R2 = 721080 + 2383200 = 3104280
Aæ
Total KWH = (12490.47-12318.01)KWH = R1 + R2
Total Electricity Bill = R1(Peak) * 0.15 = 721080 * 0.15
Total Electricity Bill R1(Peak) = 108162 [Per Unit cost = 0.15 Steem(Peak)]
Total Electricity Bill = R2(Off Peak) * 0.10 = 2383200 * 0.10
Total Electricity Bill R2(Off Peak) = 238320 [Per Unit cost = 0.10 Steem(Off-Peak)]
1 KWH = 1 unit
My Electrical Bill Design
| D. Figure out the cable and circuit breaker sizes you need to setup a 20 ampere, 220 volts, and power factor (PF) 0.9 washing machine at home. |
|---|
To determine the Cable Size and Circuit Breaker we may consider using the formula provided in the task which is given below.
Power, P= V * I * PF
Where;
P = Power = ?
V = Voltage = 220 volts
I = Current = 20 Amp.
PF = Power factor = 0.9
= 220 * 20 * 0.9
= 3960 Watt
To determine the cable size and circuit breaker from the above divide the total power by three.
P = 3960/3 = 1320 Watt
A 1320-watt load would require a 2.00 RM cable and C10 (10 Amp) circuit breaker for the washing machine at home.
Finally, u wish to invite @josepha, @dove11 and @waterjoe to also share their entry in this contest if they haven't done that already.



Upvoted! Thank you for supporting witness @jswit.
I have read all your post your post is very well written yours was equal to 10 I have given your post provo but I request you to vote on my post sometimes to encourage me. Granted, I will be grateful to you.