Wednesday-Educational Theme -A1C importance for Diabetics || 10% payout to steemit-pak
Hello Steemian
How are you all? I am good....after long time participating in steemit-pak.

I want to tell you some data on a1c it's a really good predictor of all sorts of diseases.
what is a1c?
it's simply a test that gives you feedback on your average blood sugars for two to three months in this measurement is called glycated hemoglobin now what is glucosamine and what does hemoglobin mean hemoglobin is the protein in red blood cells glycated or glycation is basically glucose sticking to the protein so when you expose this hemoglobin protein too much glucose becomes glycated and so the quantity of sugar and protein combining will raise your a1c.
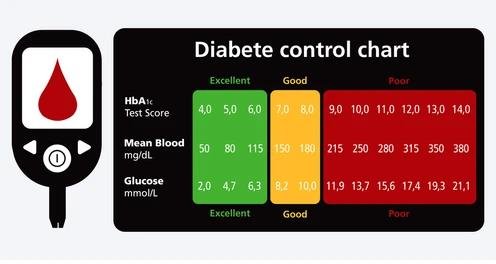

What is your level of A1C
so for example if you have an a1c of 4 your blood sugars are roughly about 68. if you have an a1c of 5 it's about 97 but typically if it's lower fives it could be like in the 80s so higher fives like 5.8 5.9 would be like 98. then you get 6 which is the blood sugar of 126 and if you get 7 you have a blood sugar of roughly about 152 and if it's an 8 it's 183 and it keeps going higher and higher and higher so a1c is a really good test to tell you what your average blood sugars are it's much better than a one-time glucose test because it tells you what's happening.


Diabetic patients If it too much sugar on weekends
over some time and so if you're doing good through the week yet on the weekends you go off your plan you eat a lot of sugar you're not going to probably have good a1c and so high a1c is a high carbohydrate diet now many disease processes occur when you have high a1c because the high sugar starts to create a lot of oxidation in problems with all sorts of tissues but there are four main issues that high glucose affects one is the combination of your brain and nervous system and so we have brain dysfunction and that can be anything from Alzheimer's to Parkinson's to dementia there's a whole series of descriptive problems with brain dysfunction then you have nerve issues you have peripheral neuropathies.


Brain Problem
which occur in the lower extremities like your feet and the bottom of your feet become numb painful burning the same thing with your fingertips right so what's happening you're getting oxidation Ina a circulatory system which is going to the nervous system and it's starving of the tiny nerves on the very end part, it's called the peripheral nerves but there are many other issues you can have you can have autonomic neuropathy which the autonomic nervous system is becoming dysfunctional.

Eyes Problem
That can affect your digestion your sleep cycles then we have the eye retinopathy the retina is the extension of the brain it's nervous tissue and that becomes majorly damaged when you expose it with a lot of glucose but when you have high glucose you also have cataracts have glaucoma you have many different issues with the lens of the eye and one big side effect of diabetes is you go blind then you're going to have problems with the arteries vessels the coronary artery
it's called endothelial dysfunction.


Heart problem
so you expose the inside of your artery to glucose you rust out the inside then you have inflammatory processes you get a clot you get plaquing you can get a stroke or a heart attack so your brain and nervous system the eye the artery and the kidney okay those are the four main tissues and with the kidney, the same thing happens if you expose the kidney to too much sugar you damage that inside filter because the kidney is a filter and so you then start leaking out all sorts of things so you have different stages of kidney the disease now there's a couple of things I want to mention as far as solving a1c
yes you need to cut your carbs down for sure and yes you need to reduce the frequency of eating that's called intermittent fasting both of those actions are going to greatly improve your a1c very very rapidly but there's something else you can do for the complications of all these diseases in other words there's something you can do to reduce th symptoms of exposing glucose to these tissues you can take b1 but you would want to take it in the form of a fat-soluble vitamin called benfotiamine.

If B1 depleted
you see what happens is this high level of glucose depletes vitamin b1 which is essential for the metabolism and breakdown of the sugar and so as you have high levels of sugar you deplete your b1 and you get a lot of complications including more glycation more oxidants more free radical damage so if you're a diabetic

if you're a pre-diabetic I would highly recommend in addition to reducing your carbs and doing intermittent fasting also take some ben photometry I would take probably four per day four pills per day and you're going to see amazing results with your symptoms you may even still, be a diabetic but you'll have a lot fewer symptoms you're going to notice your vision is going to be better fewer complications with peripheral neuropathy fewer issues with your kidney better focus and better cardiovascular function.
Picture Credit goes to Source

| 50 SP | 100 SP | 200 SP | 300 SP | 400 SP | 500 SP |
|---|
| 1000 SP | 1500 SP | 2000 SP | 3000 SP | 4000 SP | 5000 SP |
|---|