Crypto Academy / Season 3 / Week 6 - Homework Post for [@stream4u] ||All About the Blockchain Technology


Thank you, Professor @stream4u, for your amazing lecture on Blockchain. I am here to submit my homework post.
Blockchain technology is a digital system of storing information. It has the property of being very secure and almost impossible to be hacked, damaged, or cheated upon. This is to say that the information stored or recorded on a blockchain can not be compromised by a third party.
The most available blockchain serves as distributed transactions ledger. Here, transaction records are generated and distributed across the network for all users to see. Thus, each transaction has records. Each of the new records is added in blocks with the previous and a quick look at it shows blocks of transactions, hence the name BLOCKCHAIN.
Blockchains are decentralized. Each of the decentralized ledgers of the transaction has a database managed by all participants. The database is called Distributed Ledger Technology(DLT). The image below shows a typical DLT in a blockchain.
In essence, blockchain is a type of DLT in which transactions are stored with an immutable cryptographic signature called HASH.
If a single block is changed, it will indicate immediately. Thus, for a blockchain to be hacked, the hackers have to change all the blocks, which is almost impossible.

There are four major types of blockchain, namely – Private Blockchain, Public blockchain, Hybrid blockchain, and Consortium blockchain. We will look at each in detail.
Private Blockchain
Private blockchains, as the name implies, are restricted to a few authorized users or participants. It is owned by an organization and deployed for voting, digital identity, asset ownership, supply chain management, among other private uses.
The security, permissions for usage, accessibility, and authorization are in the hands of the organization that owns it. Multichain and Hyperledger projects use this type of blockchain, for example Corda, Sawtooth, Fabric, among others.
Public Blockchain
This is a blockchain or distributed ledger system that does not need permission to use. In order words, they are no restrictions on who can use it. Thus, anyone can sign in and use it, provided they have internet access.
A user or node becomes part of the network immediately they sign into it. All records, both old and new are available for all users to access. On a public blockchain, any user can do mining, proof-of-work, confirm transactions, all without restriction.
Chief among the uses of public blockchains are the mining and exchange of cryptocurrency. The most popular public blockchains are Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin blockchains.
The security of the public blockchain depends on how sincerely the users follow the rules of the network. Violation of rules leads to losses to the users.
Consortium Blockchain
This is a semi-decentralized network, where more than one organization manages the database. Here, two or more organizations set up the blockchain and manage the nodes to share information or mining.
It is a direct contrast to the private blockchain, where only one organization controls the network. This type of blockchain can be used by the government, banks, or other corporate bodies. An example of a consortium blockchain is Energy Web Foundation and R3.
Hybrid Blockchain
Here, we have a combination of both private and public blockchains. Thus, it is possible to have a private, permission-based blockchain and a public blockchain, which is not permission-based, all in one.
The hybrid blockchain is simply a combination of the features of private and public blockchains. This means a selected amount of record or data is allowed to go public, while the remaining remains restricted.
This blockchain gives users the flexibility of joining a single private blockchain and multiple public blockchains within the same network. Transactions in the hybrid network can be verified both by private and public users. The provision of more nodes for verification on the public blockchain enhances the transparency of the hybrid network. An example of a Hybrid blockchain is Dragonchain.

Blockchain has a lot of benefits, especially in the crypto space. In this section, we will be looking at five major benefits of blockchain technology.
Transparency
Transparency is a major issue that can decide if users are to trust the network or not. The centralization of most systems deprives them of the benefit of being 100% transparent.
This is the solution that blockchain technology has brought. Now organizations can employ blockchain technology to ensure users trust their systems.
Blockchain technology is transparent because it contains peers, thus transactions are peer-to-peer without the interference of third parties.
Enhanced Security
Blockchain technology employs high-level security to records or information stored on it. It uses a consensus method that ensures that users agree to the usage of information before being used.
Transactions are recorded on nodes and they can not be lost. Thus, each transaction can be traced, no matter how old. This is further enhanced by the immutability of the dat6a stored in the network. No data can be erased or lost.
Low Cost of Operations
Since third parties are not needed in blockchain operations, the cost of paying for third-party activities is averted. Thus, organizations can cut costs by employing blockchain in their activities.
Easy Traceability
Every transaction on the blockchain can be traced from sender to receiver. In order systems, supplies can be difficult to trace, as such vendors or customers can deny receipt of products.
With the use of blockchain, everyone can trace who sent and who received.
Improved Speed and Efficiency
Transactions on the blockchain are fast and efficient, compared to what happens in traditional systems. The time-consuming activities of the analog systems are automated in the blockchain. This is possible even more because most blockchains run on smart contracts.

Blockchain is just one type of a distributed ledger technology (DLT). Instead of storing information on the centralized ledger, distributed ledger technology makes use of the decentralized system to store data on nodes. This transaction information is synchronized and sent to different electronic ledgers. Here several computers can serve as nodes to store the information as they are generated from each transaction.
Blockchain technology is closely related to DLT because it uses this technology in all its activities.

To look at this holistically, we need to first look at the meaning of double-spending.
The term Double Spending refers to a situation where an individual spends a balance of the same cryptocurrency more than once, thus creating a disparity between the record of spent funds and available funds. When this happens, there is confusion on how the funds were distributed.
This is impossible with fiat, as one cannot buy $40 groceries, pay the money and go to another store to spend the same money.
A blockchain like Bitcoin blockchain cannot solve this problem on its own. In a way to check this, different transaction records are sent to nodes in the network and adequate verification is done before confirmation.
In the case of the Bitcoin blockchain, when transactions are verified and confirmed, it becomes irreversible.
How Bitcoin Solved the Problem of Double Spending
Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency network that solved this problem of double-spending. This was done by employing the confirmation mechanism, as well as, maintaining a universal and common ledger system.
Through this, the bitcoin network keeps a record of all transactions that date back to the time of its launch in 2009.
For example, if Mr. A has 1BTC and he sent the same to two wallets, say wallets B and C. The first transaction will be verified and confirmed with a block. Thus when the second one comes it will be recognized as invalid.
Reference 5

In this section, I will be using my screenshots from here to explain.
Block Hashes
When you leave 1 on the space for block and 11316 under Nonce, any data you type in will generate a hash.
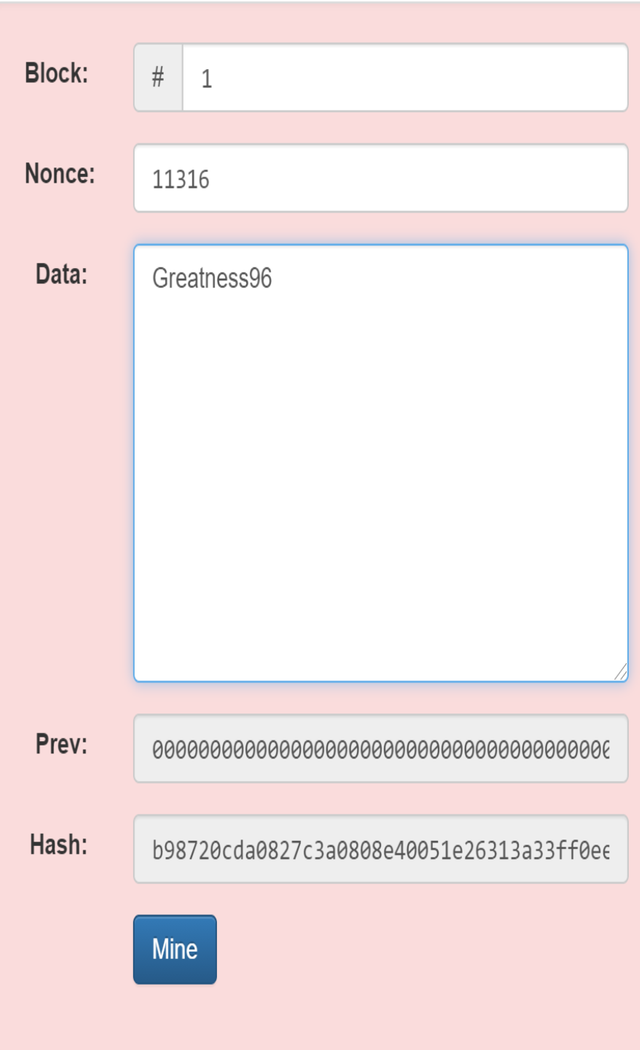
For the screenshot above, I used Greatness96 as data and the hash given is b98720cda0827c3a0808e40051e26313a33ff0eea6f57758bdaba444a25a1193.
The block is not valid because it did not start with zeros. When I clicked on mine I was able to get a hash starting with zeros as follows:
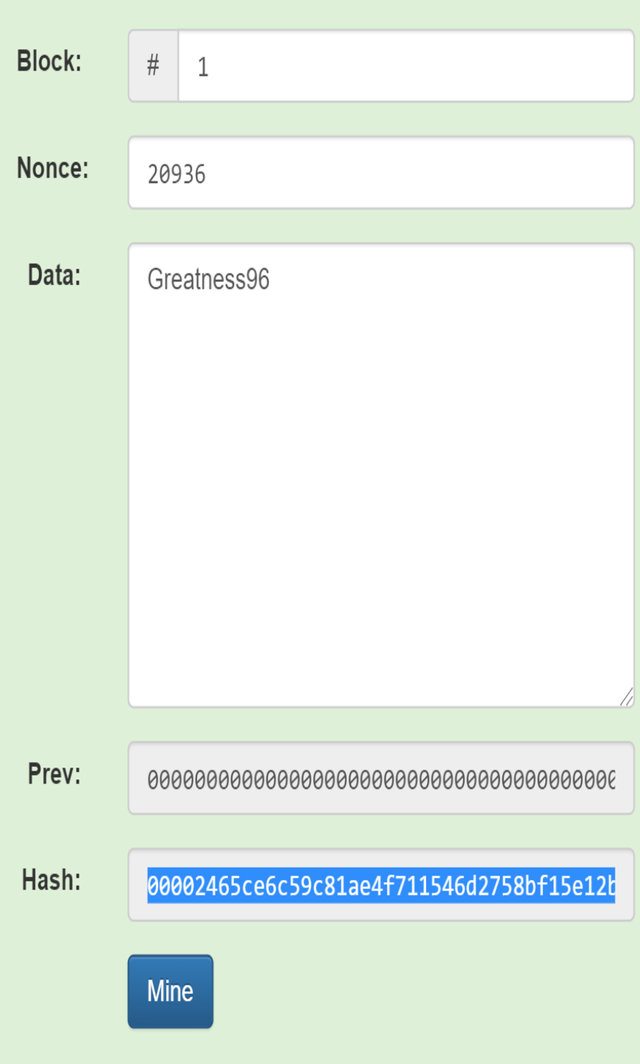
Hash:00002465ce6c59c81ae4f711546d2758bf15e12b38fdc303eaa618762be4d509.
If any of the middle blocks already created is changed, the entire data will be altered. This will indicate that something is wrong with the network and as such everyone will be alerted. This is why hackers cannot hack a blockchain easily because for a single transaction to be tampered with, all the blocks have to be removed.

This is a particular type of double-spending attack on the Bitcoin Blockchain. It utilizes a slight opportunity of the presence of a bug in the consensus network to run. Through this, the attacker causes losses to victims using malicious ways.
It could also be referred to as a confirmation attack as it allows the attacker to send double-spending transactions one block and use it to steal funds from the system. As explained earlier, each block should carry a single transaction. So, the presence of a bug in the blockchain makes it possible for the attacker to create two transactions in one.
This is usually done when a self-made block is sent to the network and the networks confirm it thinking it is valid. It was first described here.

Some of the limitations or disadvantages of blockchain technology are:
1.Poor scalability because of their consensus.
2.The speed could be reduced due to multiple users at a time.
3.High energy consumption, like in the case of Bitcoin mining.
4.The data are immutable, thus transactions cannot be reversed. If one makes a mistake, the funds are lost.
5.Users have to secure their funds, as the blockchain cannot protect what is in their wallets. If someone else gets access to another’s Bitcoin wallet, for instance, funds can be stolen and the blockchain cannot dictate if it is the owner doing the transactions or not.
6.High cost of setting up a blockchain does not allow just anyone to venture into it.
7.It is hard to integrate blockchain technology into a legal system.

Blockchain technology has come to stay. It is important to understand how it works. One of the major thing to know about blockchain is its decentralized consensus and as such, it is open for the public to use. One needs to follow the rules of the blockchain and be careful because the system permits usage by both fraudsters and genuine people.
If anything happens to your BTC, for example, you might not have anyone to run to. So, trade with caution.
Thank you for reading.
Hi @greatness96
Thank you for joining The Steemit Crypto Academy Courses and participated in the Homework Task.
Total | 6/10
Your Homework Task verification has been done by @Stream4u, hope you have enjoyed and learned something new.
Thank You.

@stream4u
Crypto Professors : Steemit Crypto Academy
#affable
Thank you for your review and corrections. I hope to do better in the next class.