Crypto Academy / Season 3 / Week 6 - Homework submitted to @stream4u | Let's Open the Blockchain
Introduction
It's another wonderful time again to attend the academy, it's already the week 6 of the season 3 and I am glad to have been part of it this far. The new week has begun and our dear professors have prepared different lectures to impact students with crypto knowledge. For this session, I have attended the lecture presented by professor @stream4u as he took us on a ride about the Blockchain, it was really a great lecture and I will be working on the task given by the professor using this article.
Design made in Canva using a free image- Image source
1. What is the Blockchain?
The name blockchain has been around for quite some time and this is the technology behind Bitcoin and many other cryptocurrencies. The blockchain is referred to as a system that records data/transactions in a decentralized way such that it's impossible the alter or change or hack the information stored on it. Going further, the blockchain comprises of blocks that stores the data of each transactions and linked it with other validated blocks in a chain format thereby completing the blockchain.
Blockchain can also be seen as a digital ledger that stores data in a secure way and the data are distributed across the nodes of the blockchain bringing about full transparency. Let's see three components of the blockchain, namely; Blocks, Nodes and Miners. Lets discuss each of these in the section below.
Blocks
In blockchain technology, a block is a unit of transactions or data recorded. The block stores the information about a recent transaction on the blockchain and it is required to pass through the process of validation before it can be added to the chain of existing chains in the blockchain. The features of the block are; Data of the block, Nonces and Hash (it's a fixed length alphanumeric numbers that stores the information of the block in a more flexible way).
Nodes
Nodes in the blockchain technology is known to be a set of computers that are connected together for swift running of the blockchain. Nodes share the data of new blocks with other nodes in the system using a P2P (Peer-to-peer protocol) in the quest to validate the transaction before adding a block to the chain.
Miners
Miners are the set of people that are involved in the validation of new blocks on the network before it can be added to the chain. The work of the miners includes validation and securing the network in question. The process of mining differs from one network to another, for example, Bitcoin uses the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus algorithm which requires setting up high energy consuming equipments to solve computational equations in the quest to validate transactions on the network and miners get block rewards for the work done.
Types of Blockchain
According to research, we have four types of blockchain as at the moment of compiling this article and they are; Public blockchains, Private blockchains, Consortium blocchains and Hybrid blockchains. The aforementioned blockchains above are further classified into two parts; Permissioned and Permissionless blockchains. Let's take a look at the discussion of each of the 4 blockchains below.
Public blockchains
Public blockchains can be seen to be the earliest blockchain technology which is used by Bitcoin. The public blockchain utilizes the Distributed ledger technology whereby all the data are not confined in one place rather it is distributed across the entire network using the Peer-to-peer protocol.
This blockchain type eliminates centralization and improve transparency since its data is distributed to all nodes through peer-peer. Notably, It's permissionless and open source which allows the participation of anyone to serve as a node in the network for transaction validations or propose change in the network. As stated earlier, notably, this blockchain type is the technology behind the Bitcoin.
Merits of Public blockchains
Demerits of Public blockchains
Private blockchains
Contrary to the Public blockchains, Private blockchains are permissioned that requires some level of permissions grant from the governing body before anyone can be allowed to access certain data on the network. Private blockchains also utilizes decentralization and peer-peer protocol to distribute data on the network but certain access are restricted and can only be granted to a set of nodes as permissioned by the governing body.
For emphasis, Private blockchains typically run on a small scale with their data kept private and a miner that wishes to join the computing power of this type of blockchain must take permission from the body that runs the blockchain. Let's take a look at some of the merits and demerits of this blockchain type below.
Merits of Private blockchains
Demerits of Private blockchains
Consortium blockchains
Consortium blockchain is not known as Federated blockchain and it exhibits the features of both Private and Public blockchains. Consortium blockchain is the type whereby different organizations come together to run the same blockchain with the parties involved having the access to the ledger, with this it looks like Public blockchain because it is not controlled by single body and it is a permissioned blockchain meaning only members of the organizations involved can access it which makes it more like a Private blockchain.
The Consortium blockchain runs on decentralization utilizing the P2P protocol for exchanging data between the organizations involved, yet, access to certain information are restricted by the bodies involved as they can choose who can have access to certain data. For example, a consortium blockchain run by 8 organizations, a certain data may be restricted to altering by other nodes and opened to only the General managers of all the 8 organizations, that's how consortium blockchain works. Let's take a look at the merits and demerits below.
Merits of Consortium blockchains
Demerits of Consortium blockchains
Hybrid blockchains
Hybrid blockchains can be seen as the interpolation of both public blockchain (permissionless) and private blockchain (permissioned) to give a birth to a new blockchain. Hybrid blockchain is the type set up by an organization such that the governing body can set who can access the data on the blockchain and restrict others from accessing it.
The records on this type of blockchain are not revealed to the public but can be verified through the interaction with smart contracts such that the governing body can't alter the data stored on the hybrid blockchain. Nodes that joined the network can have access to all data stored on the hybrid blockchain but their identity is hidden from other nodes unless they had a transaction together. Let's see the merits and demerits of hybrid blockchains below.
Merits of Hybrid blockchains
Demerits of Hybrid blockchains

2. What are the Benefits of the Blockchain?
The blockchain technology has brought many innovations as such it has so many benefits. Some of the benefits of the blockchain would be discussed in this section.
Transparency
One of the benefits of the blockchain is transparency as data stored on it is visible to all and verifiable. The transactions made on the blockchain are recorded on the digital ledger which reveals the information of the transaction, information like; timestamp, the involved addresses (both the funding and receiving addresses), the transaction type, the amount involved and many more.
The information is stored in a fixed length alphanumeric combinations known as Hash and the details of the transaction can be easily verified on the blockchain explorer as such, keeps the transaction open to everyone to see, this is seen 100% in the public blockchain type.
Immutability
Another great benefit of the blockchain is immutability, the data stored on the blockchain is permanent which makes it impossible to change. Know that, we discussed earlier that each transaction on the blockchain is recorded in the Hash which has the details in a confined environment such that it is impossible to alter it for any reason.
This is a great benefit of the blockchain which is better than the database system used by the earliest financial systems whereby data can easily be faslely modified at any time of choice, blockchain eliminates such occurrence as such, data stored on the blockchain remains intact and hard to hack or change it.
Decentralization
The existing conventional system operates under a centralized system awaits approval from a central authority before a transaction can be completed on a network. In this case, blockchain technology has brought in decentralization whereby different nodes of the network can work independently without taking order from a central server.
Blockchain enable users to carry out desired transaction with the elimination of intermediaries. For instance, making a request about a certain transaction from a bank that runs on the conventional financial system comes with going through some procedures that takes time and even awaits approval from the central authority, in the case of blockchain, all data is available to the users at ease without being through much stress. All blockchain types has this feature although slightly restricted in some, yet, it's general.
Traceability
Traceability is another benefit of the blockchain whereby all transactions that takes place on the network can easily be traced. In a transaction, the addresses that sends and receives, the amount of funds that was moved, and many others can easily be traced from the origination to the destination. Traceability of transactions can be easily done on the blockchain as all the processes involved in the transaction are recorded on the blockchain and available to everyone that wishes to see it. This kind of traceability cannot be accessed by a mere person in the conventional financial system unless a great dispute happened, all thanks to the blockchain for this innovation.
Enhanced Speed
Data storage on the blockchain is quite time-effective and contained efficiently, with the Hash effectively storing the unchanging data. Let's talk about the speed of transactions, in blockchain technology, transactions are swiftly done as there has been the elimination of third parties that tend to slow down the speed of transactions. The enhanced speed can also be related to the decentralization innovation of the blockchain whereby users are not expected to wait for a central authority to grant an approval on a transaction and that results in an enhanced speed of transactions.
Aforementioned points are some of the benefits of the blockchain and they are of great innovations to the world.

3. Blockchain Distributed Ledger
Blockchain distributed ledger is a digital ledger that is used to store data on the blockchain. The process of storing data in the blockchain distributed ledger utilizes decentralization whereby many computers are connected from any part of the world to effectively share data related to transactions with other computers in the network and update the data as new one comes in. The computers that makes up the network are called nodes.
The data stored in the distributed pattern in this blockchain distributed ledger are shared with other nodes of the network utilizing the P2P protocol. It is impossible to alter the data stored in the blockchain distributed ledger, once it is stored, it remains intact and hard to change. This is an improved innovation as compared to the conventional database that can be edited anytime the governing body wishes to. The basic features of blochchain distributed ledger are Security: It is highly secured, Transparency: data is distributed in such a way that it can be easily seen and verified by anyone, Resistance to modification: It becomes hard to alter the data stored in the distributed ledger, Decentralization: Each nodes of the distributed ledger is capable of running on its own without being affected by other faulty nodes and so on. Let's see an image below.
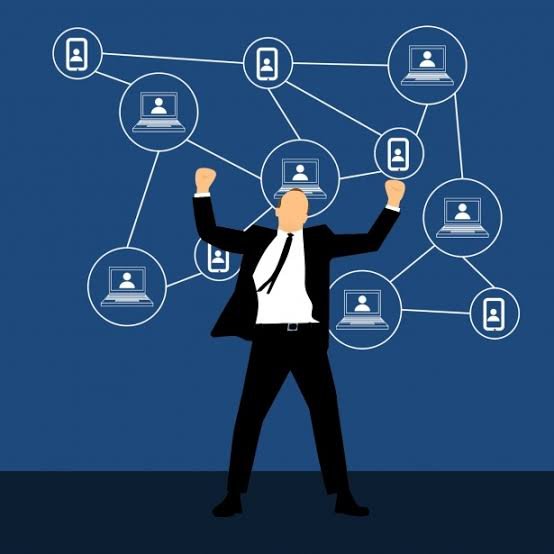.jpeg)
Blockchain Technology- Image source
Carefully inspecting the image above, all that can be seen are devices (nodes) connected together with no sight of a central device. That is just the way blockchain distributed ledger works, sharing data amongst nodes without a central authority, in addition, if one of the nodes isn't functioning, it does not affect other nodes and the network progresses. Another thing is consensus, if the required consensus has been reached between the required number of nodes, the transaction involved is validated with the faulty node having no effect on the process.

4. What Is Blockchain Double Spending and how Bitcoin handles this problem?
Blockchain double spending is such a disastrous occurrence whereby a digital asset is falsely spent more than once. How? This is quite technical but it exists, an hacker in the crypto ecosystem can send an asset once and falsify another identical transaction that looks real but it is not.
This problem is very particular with Bitcoin which has 10 mins blocks validation such that an hacker can send a worth of the digital asset to an address and in the process of waiting for confirmation, the hacker creates another transaction by manipulating the blocks in such way that the first asset sent looks unspent and in that process, send the same asset many times to his own benefit. This is seen in attacks such as Race attack, Finney attack and Vector76 attack, and mostly achievable during the 51% attack when the hackers have control over the computing power.
Let's get technical about it, a user that initially sent 2 BTC to an address, while waiting for the transaction's validation, he manipulated the block by mining another block to render the first transaction unspent and in the process, ended up spending 2 BTC twice or more, to have 4 BTC or more. That's the act of double spending.
In other ways, an initiated transaction can be reversed by an hacker after he has gotten the service, since the transaction is still awaiting the block validation time, he can reverse the process and have his funds back thereby ending up with twice the amount he had initially.
How Bitcoin handles the Double spending problem?
The problem of double spending is handle by Bitcoin in two ways, namely; Confirmations on the blockchain and deactivation of partially spending of UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output).
i. Confirmations on the blockchain
This is one of the ways Bitcoin handles the problem of double spending whereby all transactions submitted to the network undergoes confirmations and the first to get confirmation pull through to the destination wallet while the ones that failed in confirmation would be pull out of the network.
Take for instance, a user with 0.5 BTC submitted a transaction of the total wallet balance to an address and in the process of trying to cheat the system, sent another 0.5 BTC to another address with the intention to perform a double spending, the first transaction to get a minimum of 6 confirmations pull through and is put on the blockchain such that it cant be altered while the second transaction is pulled out of the network as it is considered invalid.
ii. UTXO- Complete spending
Another way that Bitcoin uses to take care of the problem of double spending is through Complete spending whereby a user can not partially spend the UTXO (Unspent transaction output). This method is effectively used in Electrum Bitcoin wallet, in this case, you can't partially spend the funds in the Bitcoin wallet rather it is automatically sent completely to create two outputs, after confirmation, the actual withdrawal goes to the destination wallet and the remaining is routed back to your wallet through a Change address.
Take for instance, I have a total 0.5 BTC in my wallet and I sent 0.25 BTC to an address, in that process, two outputs would be created, 0.25 BTC to the desired address and 0.25 BTC to be routed back to my wallet through the change addresses. Note that, this example is cited while I neglected the transaction fee. Let's see how it works below.
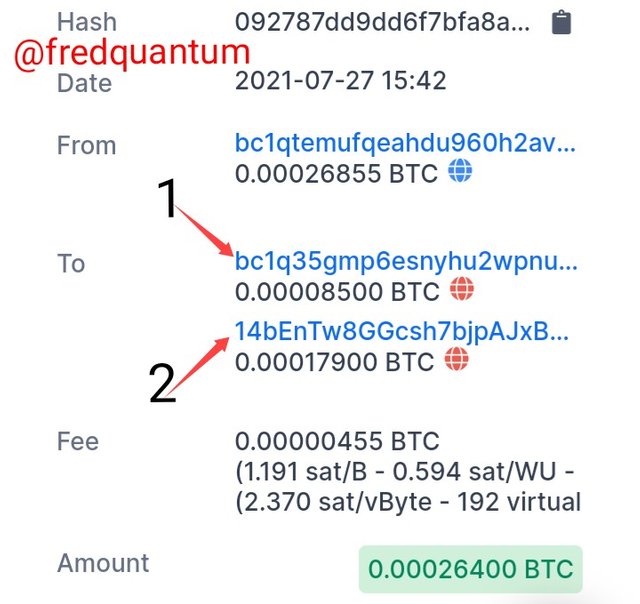
Bitcoin Complete Spending- Image link
The screenshot above is the transaction I made around a week ago, from a total of 0.00026400 BTC, I sent 0.00017900 BTC to the address tagged 2 and 0.00008500 BTC was routed back to my wallet through a Change address tagged 1 after confirmation. This is a typical example of how Bitcoin handles double spending through Complete spending of UTXO.

5. How Blocks' Hashes work in Blockchain
Let's open a basis to this study, as stated earlier, Hash is a fixed length of alphanumeric combinations that stores the data of each blocks on the blockchain. The process of making up a Hash starts from Input which is passed through the Hash function and finally gives the Hashing Output which is the Hash value.
First of all, let's explore the blockchain demo website created by Anders Brownworth and in this part we will be considering the Hash section of the website here!
The landing page- Image source
Let's input our data and see what the output Hash looks like.
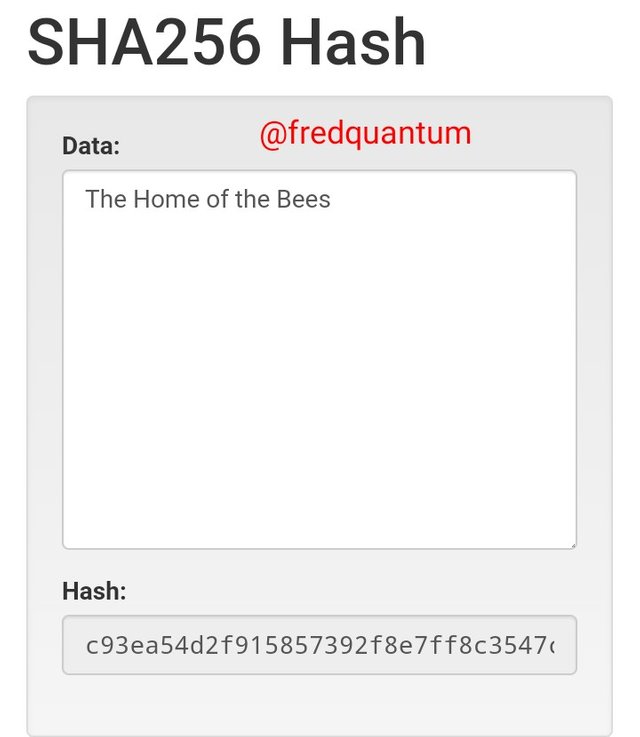
The Hashing output- Image source
The resulting Hash for the input "The Home of the Bees" is; c93ea54d2f915857392f8e7ff8c3547c2bfdc2f5ed07dee05e84d98cb8e73fd1. Now let's see what bigger input brings, will it still be fixed length as smaller inputs?
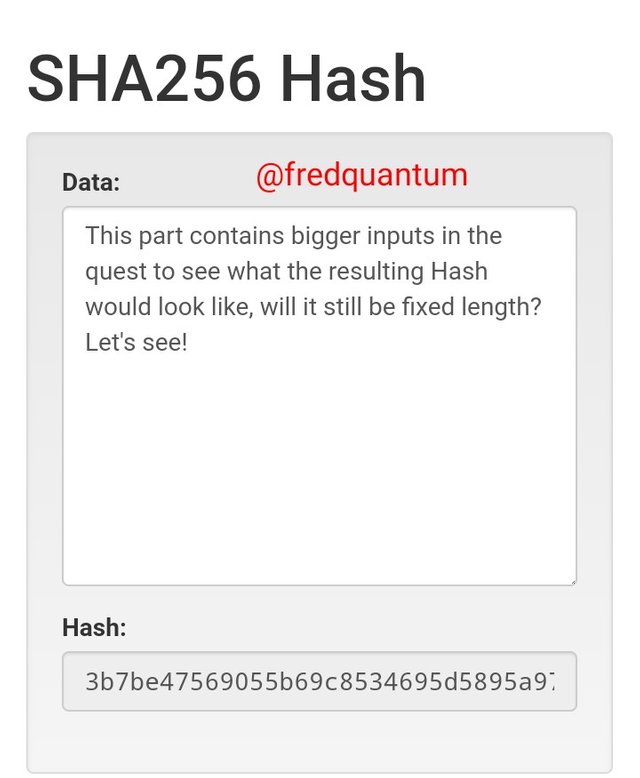
The Hashing output for bigger input- Image source
For this part, I inputted "This part contains bigger inputs in the quest to see what the resulting Hash would look like, will it still be fixed length? Let's see!" and the resulting Hash has remains fixed length, the Hash; 3b7be47569055b69c8534695d5895a979083c8d636902ad7b6dc4e510086599a.
Now, let's navigate to the blockchain section of the website Anders Brownworth Blockchain Demo, we can learn a few things while we explore the practical side of the blocks' hashing process.
Landing page of Anders Brownworth- Image source
From the above, I clicked the blockchain button. Now I am at the blockchain section. See the screenshot below.
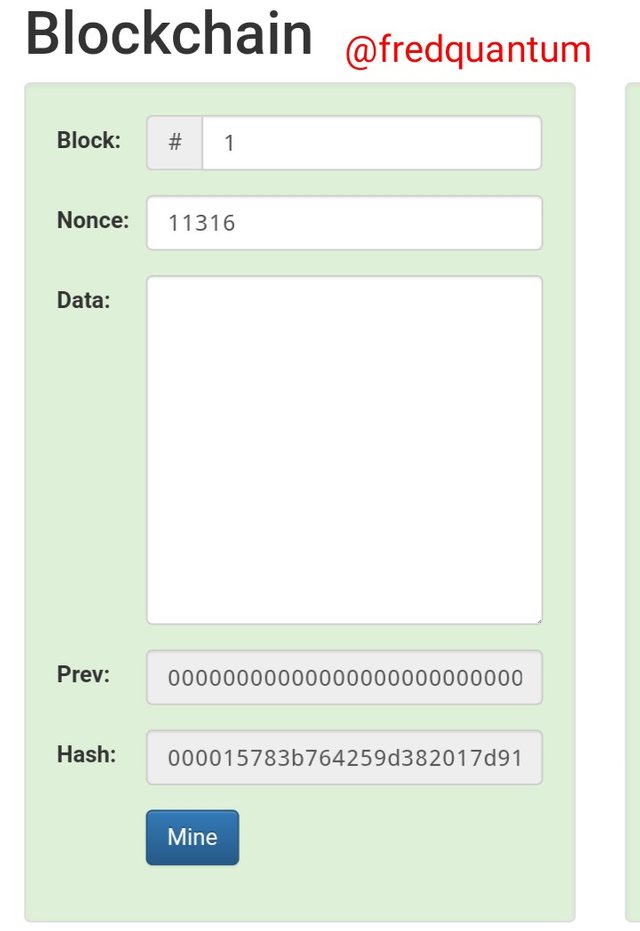
Blockchain Demo page- Image source
To have a valid block ready to be added to the chain, the Hash must start with a few zeros and from the image uploaded above, the Hash starts with a few zeros and that makes it a valid block. The Hashing output above is; 000015783b764259d382017d91a36d206d0600e2cbb3567748f46a33fe9297cf.
It's time for me to add my input and see how it's been treated by the hashing function. Let's see if it gives a valid block through the Hash.
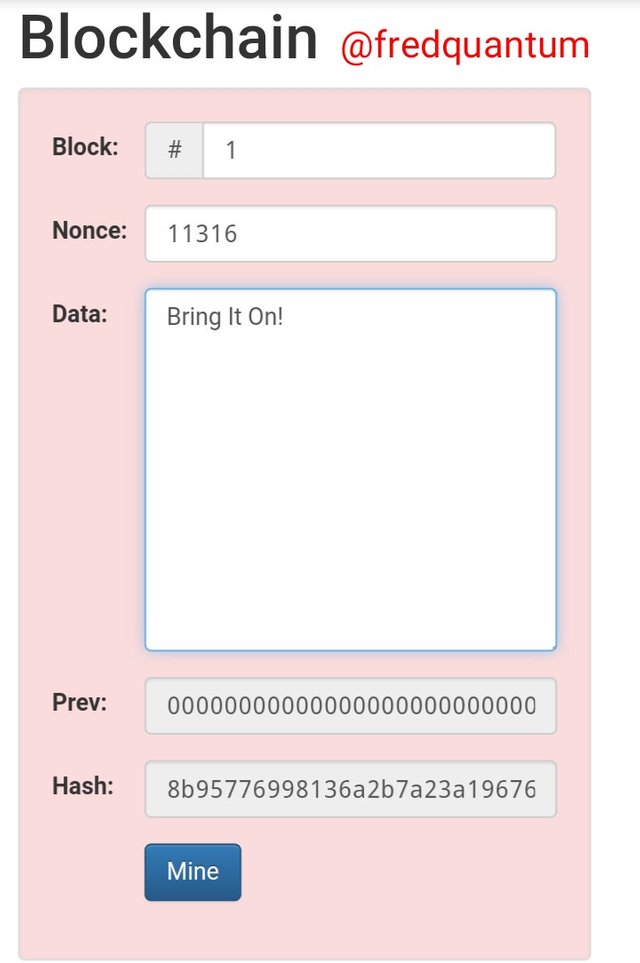
Output in Hash- Image source
So from the above, I put Bring It On! as my input and the resulting Hash is ; 8b95776998136a2b7a23a196762761319ecad06a8426b9b038601de8894affa8. From the Hash, this is an invalid block as the Hash didn't start with zeros such that I have to tweak the Nonce (Number Only Used Once until a valid block is achieved.
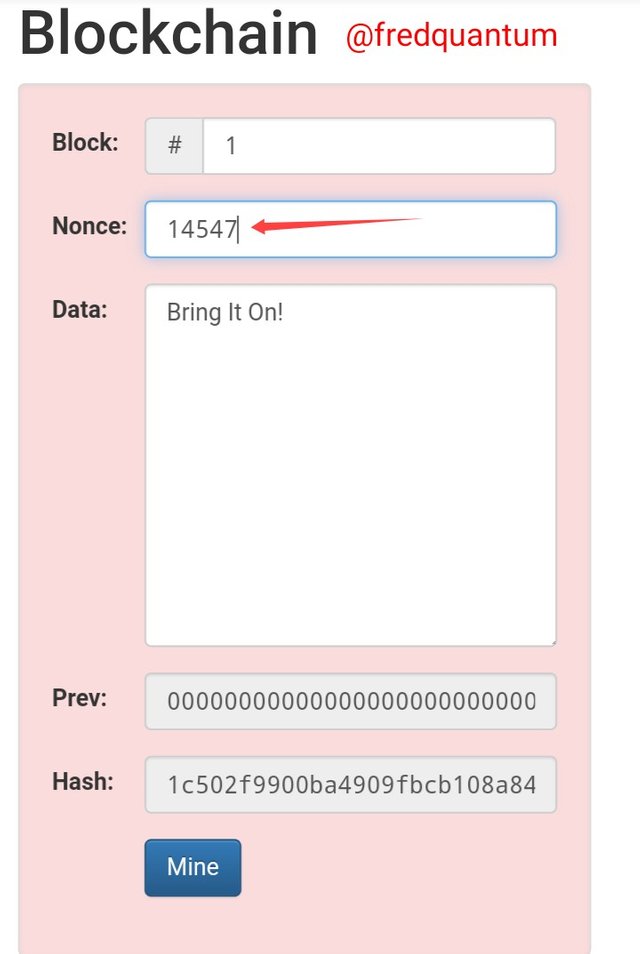
Output in Hash- Image source
In the quest to get a valid Hash, I changed the Nonce to 14547 and the Hash produced is still invalid because it doesn't start with zeros, thus it's not valid and the block cannot be added yet, the Hash is; 1c502f9900ba4909fbcb108a846746137a15f0461a45a30f01be63d485340719. Let me proceed.
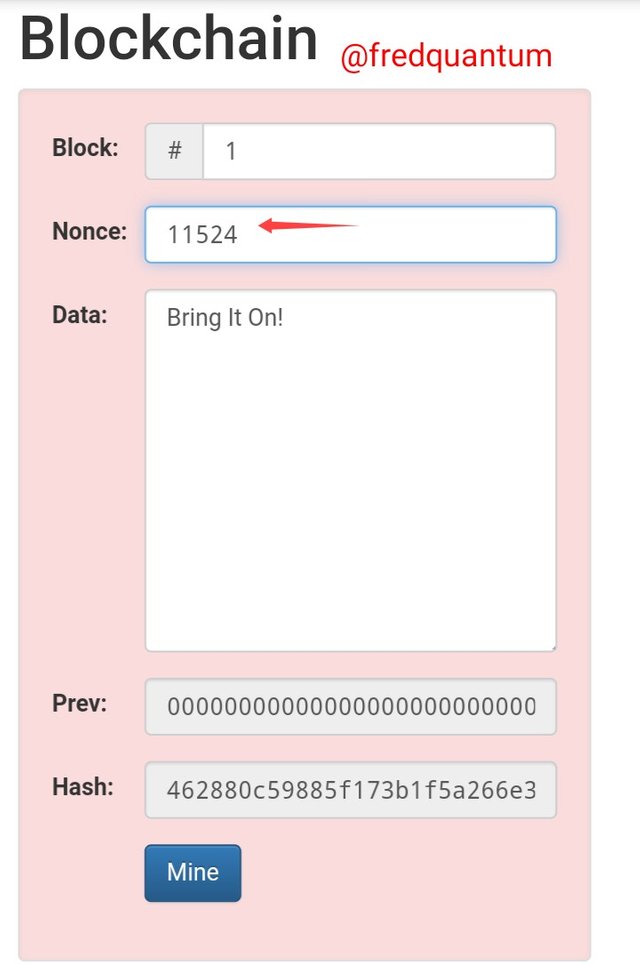
Output in Hash- Image source
Again, I tweaked the Nonce to 11524 and the Hash gotten is invalid as seen from the screenshot above which means the block is not valid yet and can't be added to the chain. The Hash gotten from the above is; 462880c59885f173b1f5a266e34504c19aa1f5aaefb457d1993694eb4f79ff1b.
Take for instance, I am a miner on a network competing for block rewards within limited time, I have wasted a lot of time without being able to solve the block, although, there case is different as they have machines that does the job. In this case, to avoid wasting more time, I clicked on Mine, and let's see what that gives me.
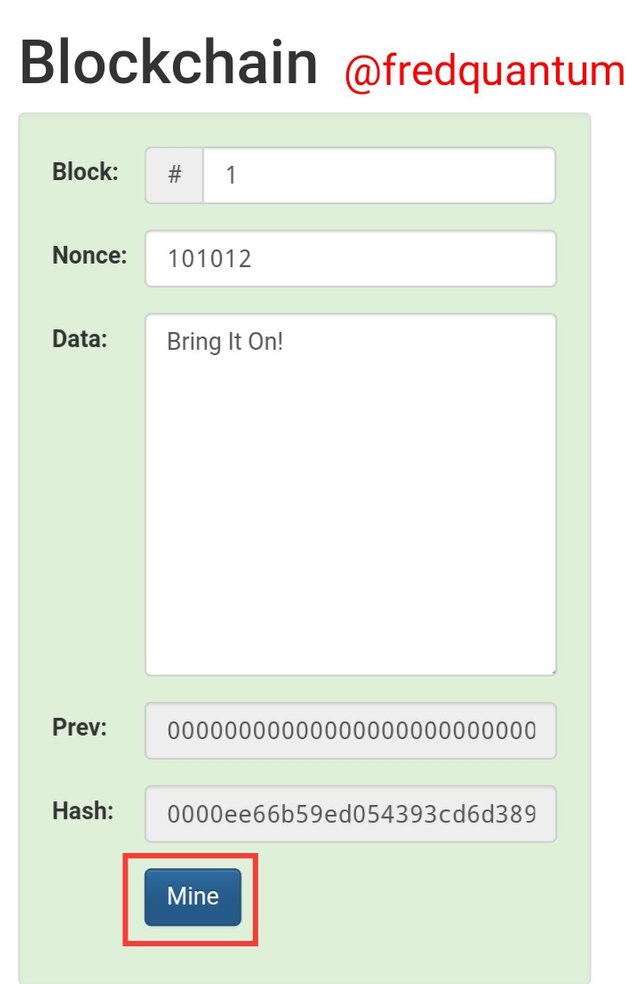
Valid Hash- Image source
Finally, I was able to provide a valid Hash for the input "Bring It On!" with the Nonce 101012 and that makes this block a valid one. In real life, If I am able to successfully provide a valid block like this, it'd be added to the chain. The valid Hash above starts with a few zeros and the value is; 0000ee66b59ed054393cd6d3894f0e117495ab5216405301907a6083412ec2a9.

6. What Is Race Attack in blockchain?
Race attack in blockchain can be related to double spending as it's one of the attacks used for the purpose of double spending. Race attack in blockchain can occur in trades between buyers and sellers, and it involves the creation of two conflicting transactions with the aim to frivolously spend the same fund twice.
The buyer in this case creates two transactions on a network, the first of the transaction is sent to the trade partner (seller) who sends the products involved to the buyer without making a confirmation of the funds claimed to be sent by the buyer. The buyer then broadcast the second transaction to the network which is routed back to his wallet and get his funds back
This is another means to dubiously use an asset to gain another asset without spending a dime. An illustration of this is when two traders agrees on 0.1 BTC for a digital asset, the buyer creates two conflicting transactions ,the first one worth 0.1 BTC sent to the seller whereby the seller didn't wait to confirm the transaction then send the digital asset, the second transaction worth 0.1 BTC created by the buyer is now broadcasted to the network and routed back to his wallet.
It is important to be careful of an attack like this in the crypto ecosystem, if you are involved in a trade with someone, wait for the confirmation before releasing the asset to the other party.

7. Disadvantages of Blockchain
As much as the innovations brought by the blockchain technology is, likewise, it has its demerits too. Some of these disadvantages will be discussed in this part of the task.
Modification Issues
When I was discussing the benefits of blockchain earlier, I added a few things about immutability whereby it is hard to alter the data stored on the blockchain. Though, it sounds nice that data stands the way they are stored but one way or the other, there might be reasons to alter the data stored earlier which now becomes hard because of blockchain's immutability and this is a great disadvantage of blockchain.
51% Attack
This is a great threat to blockchain, the 51% attack is with no doubt a great disadvantage of the blockchain when hackers gain more than 50% control of the total computing power as such, that puts them in charge of mining and can easily manipulate mining and rake assets to their own purse. The effect of 51% attack can be so disastrous and this is another worrisome disadvantage of the blockchain.
Cost of Operation
This can be seen in the case of blockchain network that utilizes the Proof of Work consensus mechanism which requires that miners set up a high energy consuming machines. Not everyone can afford the cost involved in this case and it limits the involvement of some people in the mining process which is another great disadvantage of blockchain.
Crime
Another disadvantage of the blockchain is crime, this is mostly common in decentralization brought by blockchain whereby users can easily transact without verifications like KYC (Know Your Customer) as such the blockchain can be used for illegal money movement.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the blockchain technology has brought many innovations to the world having a few of them to be immutability with effective storage of data, decentralization which eliminates the presence of third parties in transactions and many other benefits.
Hash is the fixed length alphanumeric combinations which stores data on the blockchain in a very flexible way that can't be altered but can be verified. The process of getting to the Hash starts from inputs which is passed through the Hashing function and then gives the Output in Hash to build valid blocks, and added to the blockchain.
Although, innovations of the blockchain are numerous, yet, users in the space should be aware of the attacks (51% attack, Race attack, Finney attack and many others) that are threats to the blockchain as such it is important to practice safety precautions to prevent the ones that can be done via our patience and carefulness while transacting. Thanks to professor @stream4u for this great lecture.

Cc: @stream4u

Written by;
@fredquantum
Hi @fredquantum
Thank you for joining The Steemit Crypto Academy Courses and participated in the Homework Task.
Total | 8/10
Your Homework Task verification has been done by @Stream4u, hope you have enjoyed and learned something new.
Thank You.

@stream4u
Crypto Professors : Steemit Crypto Academy
#affable
Thanks for the review professor @stream4u. My bad, I excluded a part of the task. Thanks for the review once again.