Sidechains – Crypto Academy / S4W8 – Homework Post for @pelon53
This is my homework post for Steemit Crypto Academy Season 4 Week 8 of Professor @pelon53’s class Sidechains.

Note : I performed this task on Windows 10 PC, Google Chrome.
Task 1 - Sidechains with the use of ZK-Rollups
1.1. Sidechains
Sidechains are separate blockchains that work in parallel with a main blockchain (or main chain). Sidechains are becoming one of the most popular solutions today to the scalability and high cost problem of blockchain (especially the earlier generations), without compromising its security properties.
Sidechains are blockchains that are separate and distinct from the main chain, with their own rules, their own consensus algorithms, their own Byzantine Fault Tolerances. But even so, a sidechain works in parallel with the main chain.
Sidechains can help its main chain with scalability and cost issues by recording most transactions off-chain, not on the main chain (or on-chain). In sidechains, a mechanism that accommodate the flow of assets between sidechains and their main chains are important, because the transaction will basically be done on the sidechains.
Examples of Sidechains are:
- xDai Chain or simply xDai. xDai Chain is a stable payment Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) blockchain which was designed for fast and cheaper transactions. xDai Chain has its native stable token named xDai, with ticker XDAI. xDai stable token is used for transactions, payments, and fees. It is stable to USD. xDai also has a governance token named xDai Stake, with ticker STAKE. This governance STAKE token is used to support the underlying POSDAO Proof-of-Stake consensus. STAKE is currently trading at USD 13.53 (according to CoinGecko).

- POA Network or POA Core. It is an autonomous network. The autonomous network is secured by a group of validators which are all United States notaries. These validators allow the network to work fast and provide inexpensive transactions. POA Network has its own native token named POA Network with ticker POA, and is currently trading at USD 0.01892722 (according to CoinGecko).
1.2. ZK-Rollups
ZK-Rollups are one of the currently available and used rollups. Rollups is a solution produced to speed up transactions by executing them outside the main chain, while keeping the transaction data in the main chain. So, basically, rollups are secured by layer 1.
Rollups work at Layer-2 and are effective at: 1) cutting costs, 2) facilitating participation, and 3) accelerating transactions. So, unlike sidechains which are separate blockchains, rollups are part of the “main chain” itself.
There are two types of rollups currently available: 1) Optimistic Rollups, and 2) Zero Knowledge Rollups (or ZK-Rollups). These two rollups differ in terms of security models. If Optimistic Rollups considers all transactions valid by default and computations are executed with fraud-proof technique, then ZK-Rollups performs offchain computations and sends validity proof to layer 1.
Examples of a blockchain using ZK-Rollups technology:

- ZCash. ZCash is a blockchain that has a native token named ZCash with ticker ZEC. ZCash token is a privacy coin, which is a token that prioritizes the anonymity of its users. The ZCash token is based on Bitcoin's codebase and has several similarities to Bitcoin including a fixed total supply of 21 million units of tokens. At the time of writing, ZEC is trading at USD 158.61, based on data from CoinMarketCap.
- Loopring. Loopring is Ethereum-based software aims to incentivize users around the globe for operating a platform which enables the creation of new types of crypto asset exchanges. Loopring was founded by a software engineer named Daniel Wang who works for internet-based companies including Google and JD.com. Loopring was basically createdfor trading and payment. The ICO was conducted in 2017 and raised 120,000 ETH (equivalent to USD 45 million). Loopring has a native token named Looring which has a ticker LRC. At time of writing, according to CoinGecko, LRC is trading at USD 0.516.
1.3. Sidechains and ZK-Rollups
Sidechains and ZK-Rollups are two of three currently popular solutions for blockchain scalability and cost issue. The third one is Optimistic Rollups.
They work pretty much the same way: do most of the logging off the main chain. In the Bitcoin ecosystem, this kind of working system is found at Lightning Network technology. The differences between Sidechains and Rollups are:
- Sidechains are separate blockchains while rollups are a layer-2 solution of a blockchain.
- Because Sidechains are blockchains that are separate from the main chain, a mechanism that facilitates the flow of assets from the main chain to the sidechain, and vice versa, is needed. While in the rollups system, it’s only the transactions are executed at layer-2 while the records are sent to the top of the blockchain, no flow of assets takes place.

Task 2 - Liquid Network Sidechain

Liquid Network is a sidechain protocol built on top of the Bitcoin ecosystem. Liquid Network was developed by Blockstream which declared itself as "the global leader in Bitcoin and blockchain technology".
As a sidechain to Bitcoin, the Liquid Network offers conveniences and advantages that the Bitcoin blockchain does not have:
- Fast. Liquid Network's blocktime is 10 times shorter than Bitcoin's. If Bitcoin takes about 10 minutes to add a block, then Liquid Network adds one block every minute precisely. It only takes two confirmations to validate a transaction.
- Multiple assets. On the Liquid Network, third parties are able to issue tokens (securities, stablecoins, and more).
- Confidentiality of transactions. The Liquid Network allows information such as the type and amount of assets in a transaction to be confidential between the transacting parties because it is not recorded in the public ledger.
To be able to transact on the Liquid Network blockchain using Bitcoin, a user account needs to deposit Bitcoin at an address assigned by the Liquid Network. After the Bitcoin token is locked and confirmed, the user will get a token called L-BTC, short for Liquid Bitcoin. L-BTC has the same value as BTC, 1 BTC = 1 L-BTC. The process of depositing Bitcoin tokens to an address provided, is called peg-in.
Meanwhile, the process to convert L-BTC tokens back to Bitcoin tokens, known as peg-out, is carried out in a similar way, by depositing L-BTC tokens back to an assigned address.
Links and Social:
- Website: https://liquid.net/.
- Whitepaper: https://blockstream.com/assets/downloads/pdf/liquid-whitepaper.pdf.
- Wallet download page: https://blockstream.com/green/.
- Blog: https://blog.liquid.net/.
- Twitter Account: https://twitter.com/Liquid_BTC.
- Block Explorers:
https://blockstream.info/liquid/ (BlockStream),
https://mempool.space/liquid (Mempool Space). - Support: https://help.blockstream.com/hc/en-us/categories/900000056143-Liquid-Network/.

Task 3 – Connecting Metamask Wallet to Polygon network
- I opened the Polygon Network webpage.
Screenshot image of Polygon Network webpage. - I scrolled down the page to the bottom area where I saw the “Use Polygon” segment. I clicked on the [Wallet] tab.
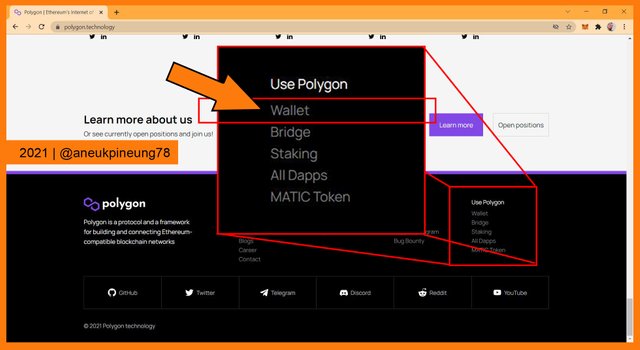
How I accessed the Polygon Web Wallet. - A new tab (Polygon wallet webpage) opened on my web browser. I clicked the Polygon Wallet thumbnail.
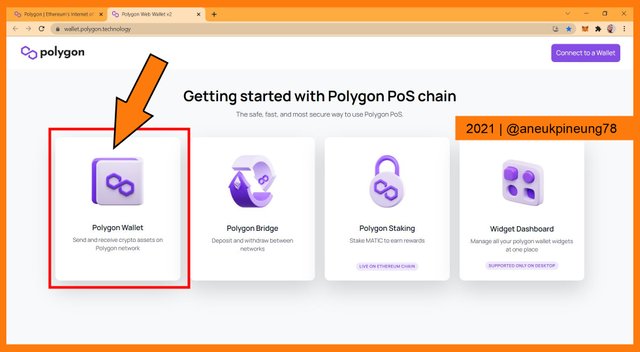
Polygon Web Wallet thumbnail. - I chose Metamask on the next page.
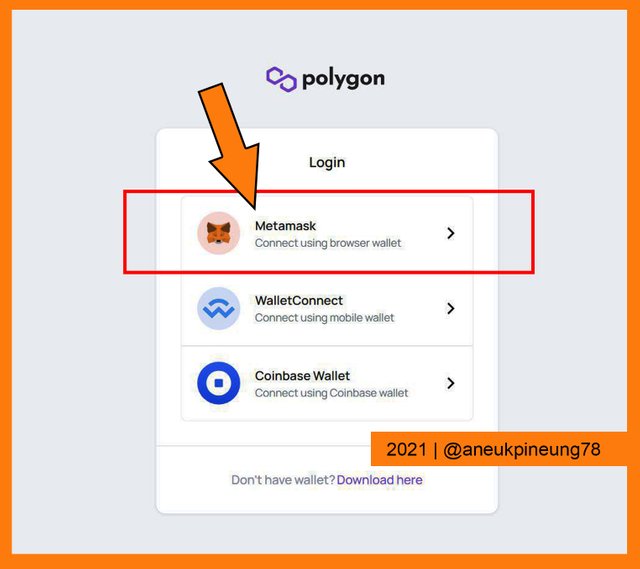
The wallets supported by Polygon Chain. - The Google Chrome Metamask wallet extension box popped-up. I filled in the extension password and clicked the blue [UNLOCK] button.
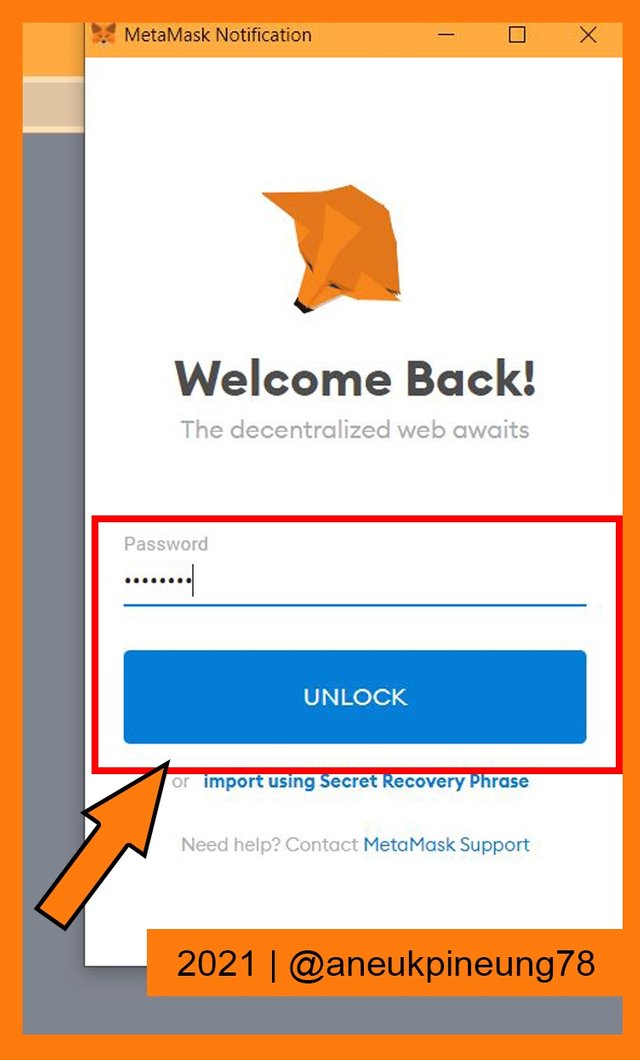
Unlocking Metamask wallet extension on Google Chrome. - When I was logged in to the Metamask wallet, it asked for my signature. I click the [Sign] button to confirm wallet connection.
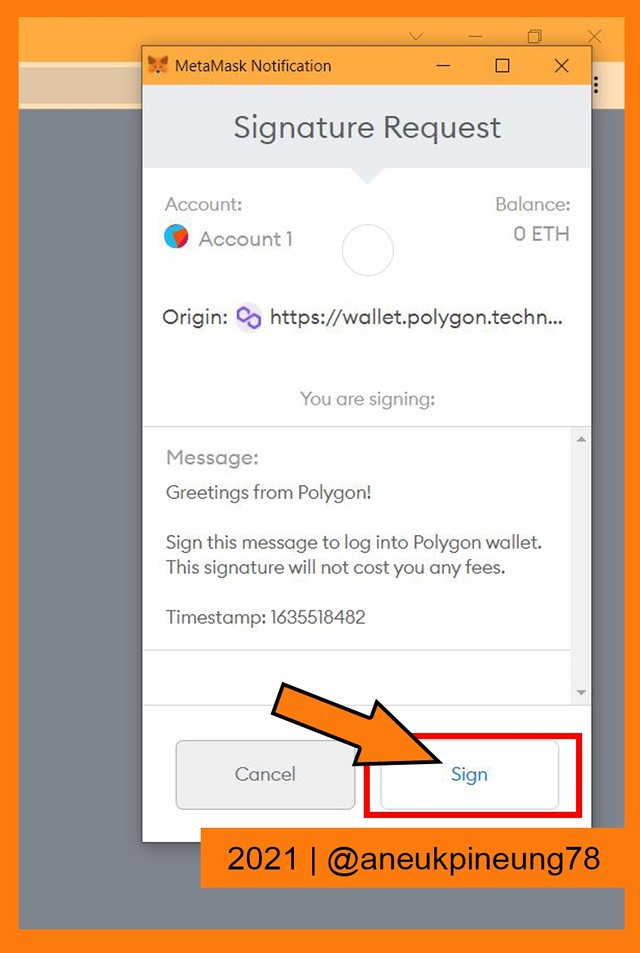
Signing the request. - The wallet connection was successfully made to Ethereum Mainnet.
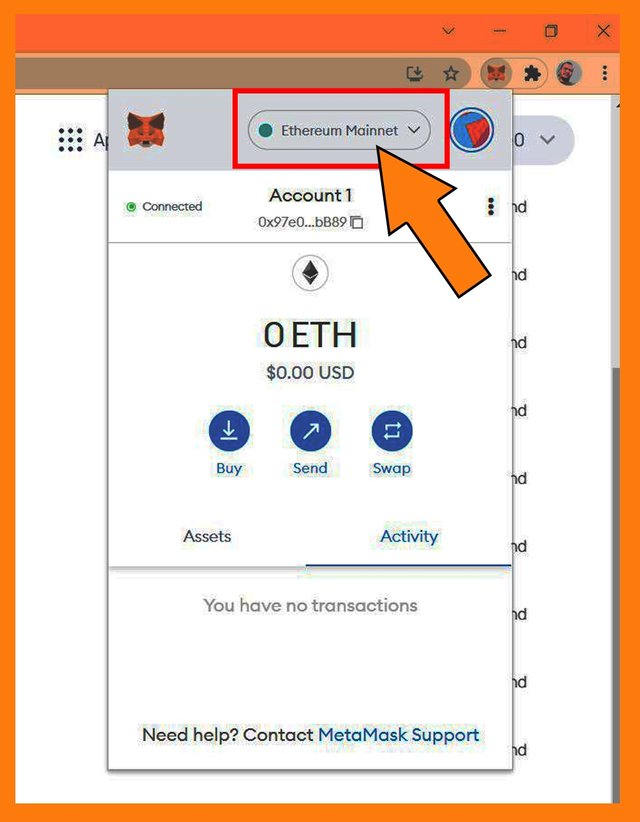
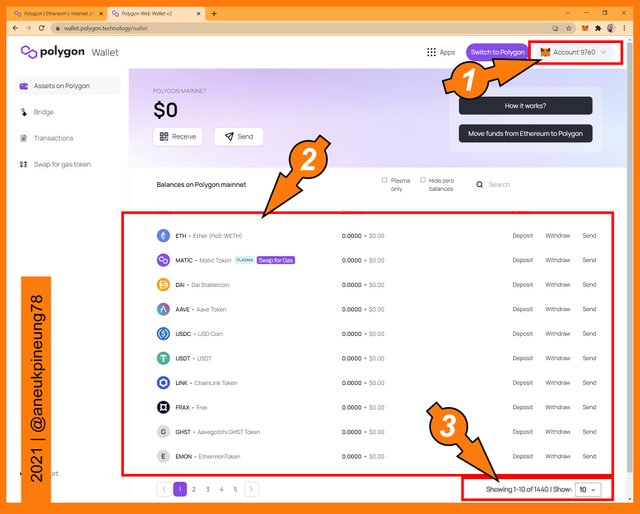
Connected ti Ethereum Mainnet. - Below is the screenshot image of the Assets on Polygon Web Wallet interface when the wallet connection was made. Marker number (1) on the picture indicates the wallet address. Marker number (2) shows the assets Polygon Wallet support and the assets balance of the connected wallet. Marker number (3) shows that at the time of writing, Polygon Wallet supported 1440 assets.
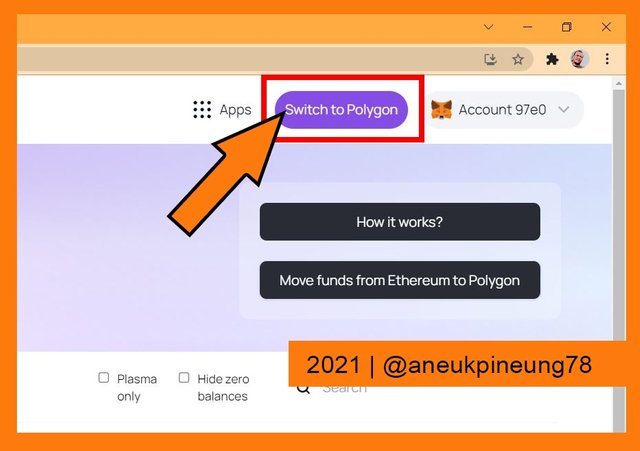
The Polygon Web Wallet page anatomy. - But the truth was that the wallet still connected to the Ethereum Mainnet. To connect it directly to Polygon Network, I clicked the [Switch to Polygon] button at upper right side of the Polygon Web Wallet page.
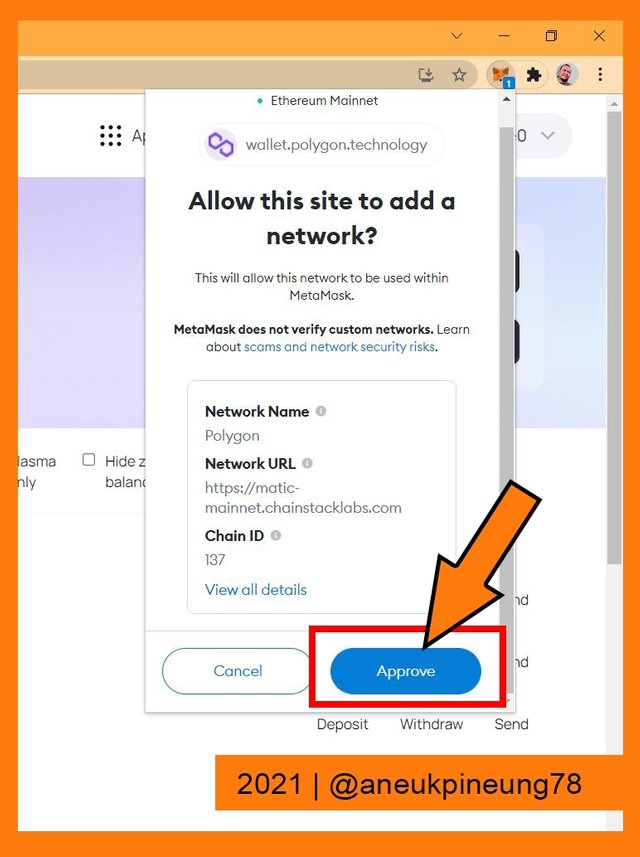
Switch to Polygonby hitting the button. - The wallet extension popped up asking for approval. I clicked the [Approve] button.
Wallet approval request. - Another confirmation. I clicked the [Switch network] button.
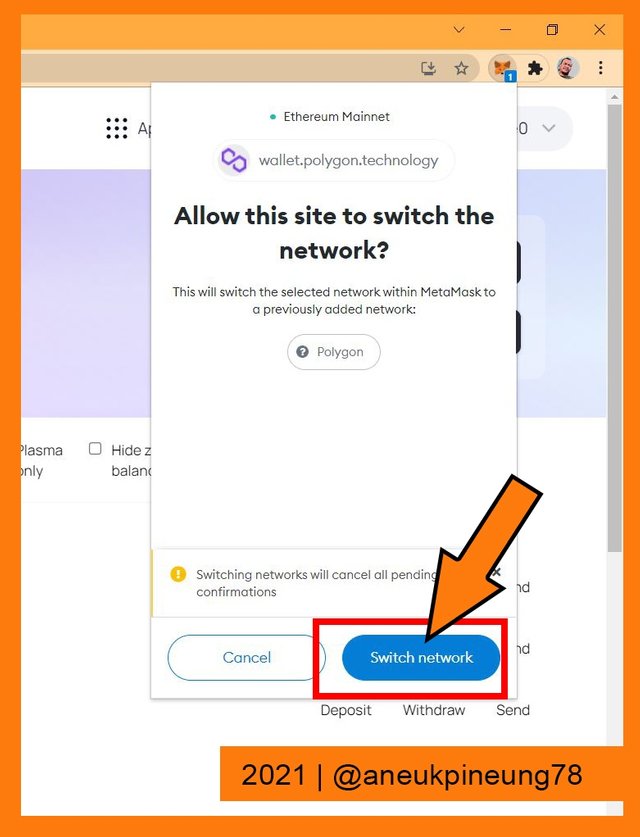
Confirmation on the request. - The wallet was then connected to Polygon Network directly.
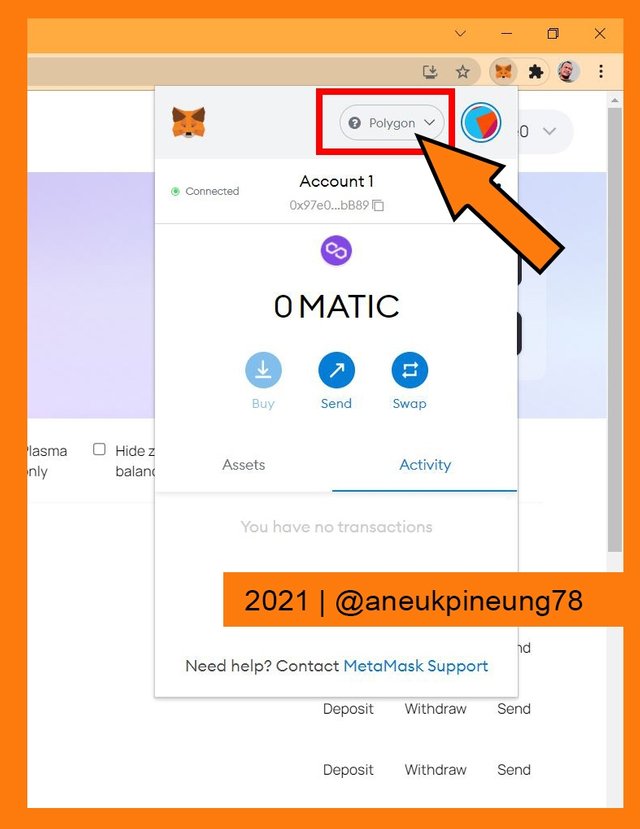
Direct connection to Polygon Network was made successfully. - No more [Switch to Polygon] button.

Task 4 - Polygonscan Block Explorer

4.1. Block #25,000,000
- I opened Polygonscan.
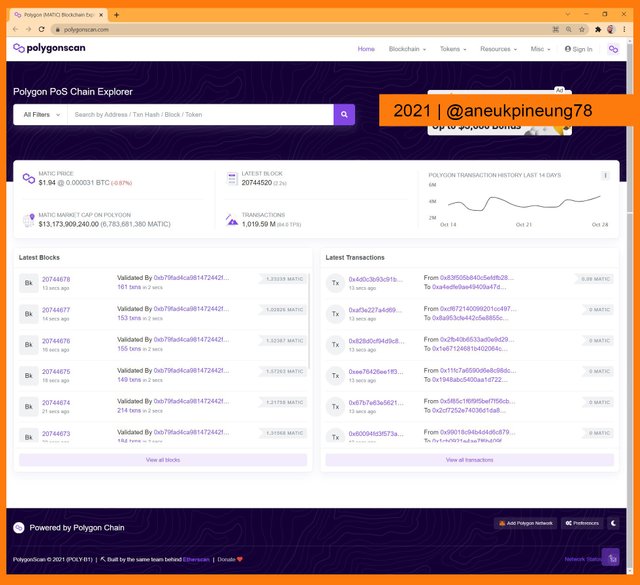
Polygonscan webpage. - I typed the block number to search (25000000) in the search box.
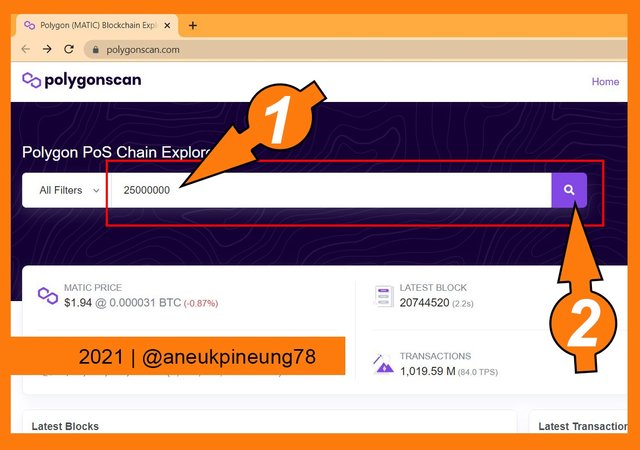
Utilizing the search box. - The result showed the data that, at time of writing, the block #25,000,000 will be produced in 113 days, 6 hours, 36 minutes, and 12 seconds. That means Sunday, February 20th, 2022, 10:59 GMT+7 or Saturday, February 19th, 2022, 3:59 UTC.
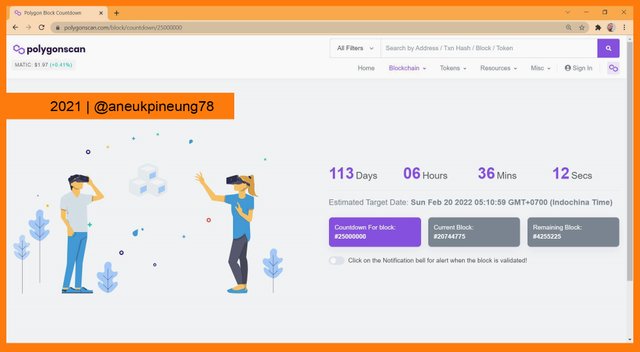
Expected time of block #25,000,000’s arrival.
4.2. Block #12,000,000
- Again, I utilized the search box. I typed the block number, 12000000 and hit the search button.
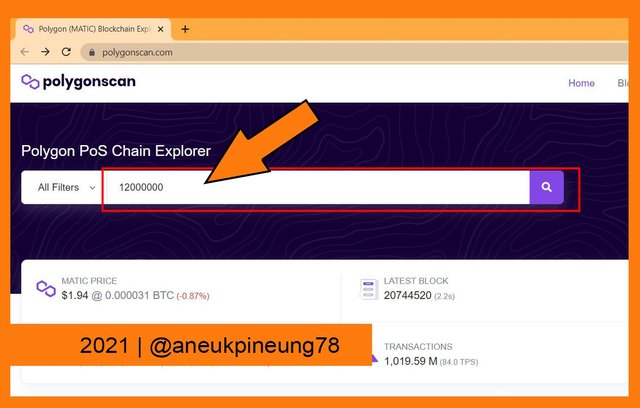
Searching for block #12,000,000. - The block #12,000,000 detail page was then opened.
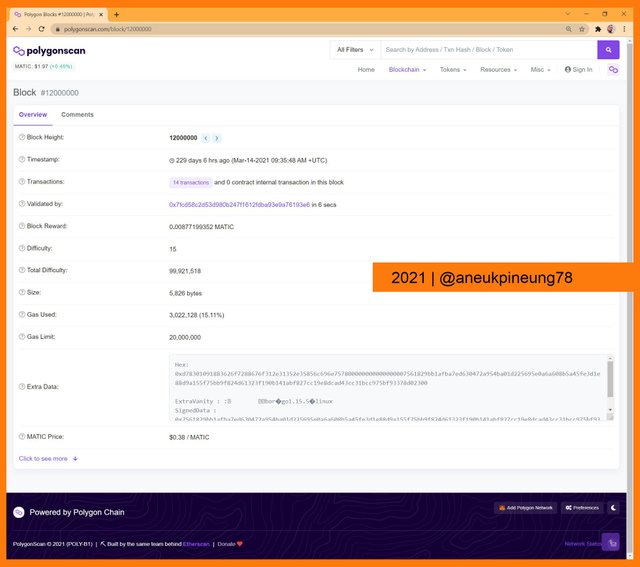
Block #12,000,000 detail page.
The page showed that the MATIC token price when block #12,000,000 produced (March 14th, 2021, 09:35:48 AM +UTC) was USD 3.08.
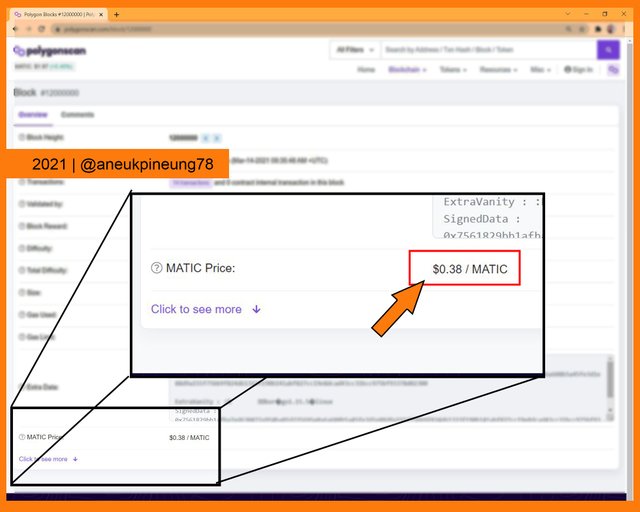
The MATIC token price when block #12,000,000 produced.

Thanks
Thanks Professor @pelon53 for the lesson titled Sidechains.
Pictures Sourcing
- The editorial picture was created by me.
- Unless otherwise stated, all another pictures were screenshoots and were edited with Photoshop CS 3.
Sources and Reading Suggestion
- https://www.blockchain-council.org/blockchain/a-comprehensive-guide-on-sidechains-rsk-liquid/;
- https://www.blockchain-council.org/blockchain/sidechains-the-five-siblings-in-the-eos-family/;
- https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/scaling/sidechains/;
- https://coinmarketcap.com/alexandria/glossary/side-chain;
- https://hackernoon.com/what-are-sidechains-1c45ea2daf3;
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2018/11/27/sidechains-how-to-scale-and-improve-blockchains-safely/;
- https://docs.ethhub.io/ethereum-roadmap/layer-2-scaling/zk-rollups/;
- https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/scaling/layer-2-rollups/;
- https://medium.com/addxyz/zk-rollup-scaling-ethereum-for-the-long-term-287aa95e3ba9;
- https://coinmarketcap.com/alexandria/glossary/zero-knowledge-rollups;
- https://blockster.com/blockdesk/1673;
- https://hackernoon.com/layer-2-rollups-projects-in-2021-a-comparison-4s1g377b;
- https://medium.datadriveninvestor.com/a-brief-guide-to-zkrollup-projects-and-products-january-2021-ebf857a8165b;
- https://www.kraken.com/en-gb/learn/what-is-loopring-lrc;
- https://medium.com/loopring-protocol/loopring-welcome-to-the-future-3a42c5c7eba8;
- https://medium.com/loopring-protocol/on-what-loopring-is-and-isnt-cdc81b96502c;
- https://kriptomat.io/loopring/;
- https://river.com/learn/terms/l/liquid-network/;
- https://blockstream.com/liquid/;
- https://help.blockstream.com/hc/en-us/articles/900002016823-What-is-the-Liquid-Network-;
- https://liquid.net/;
- https://twitter.com/Liquid_BTC;
- https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2021-10-05/liquid-network-s-platform-for-faster-bitcoin-trades-breaks-down;
- https://www.coindesk.com/business/2021/10/05/blockstreams-liquid-network-faces-delay-in-processing-as-transactions-begin-to-stack-up/;
- https://www.blockdata.tech/products/liquid-network;
- https://btcturk.medium.com/what-is-the-liquid-network-and-what-does-it-offer-379d29cc7aff;
- https://btcturk.medium.com/what-is-the-liquid-network-and-what-does-it-offer-379d29cc7aff;
- https://medium.com/stakingbits/setting-up-metamask-for-polygon-matic-network-838058f6d844;
- https://gravityfinance.medium.com/using-metamask-with-polygon-923f061054db;
- https://polygonscan.com/;
- http://bajloanfinances.com.shreeganeshfinanceltd.com/nd919i/tscoob.php?cpyrx=sidechains-vs-rollups;




shared to Twitter : https://twitter.com/aneukpineung78a/status/1454314834221101057.
Anda sangat pandai mbuat program. Itu sulit tetapi sukses selalu
terimakasih. sama-sama salam sukses juga.
#club5050 😀