Crypto Academy Season 3 Week 6: Homework Post for @stream4u
• What is Blockchain and What are the types of Blockchains / Explain in detail the types of Blockchain?
• What are the benefits of blockchain?
• Explain Blockchain Distributed ledger.
• What Is Blockchain Double Spending and how Bitcoin handles this problem?
• Visit Blockchain Demo and check section Blockchain, then explain in detail how Blocks Hashes Work in Blockchain, what will happen when any middle of the block gets changed, try to give screenshot for each possible details.
• What Is Race Attack in blockchain? OR
What Is Finney Attack in blockchain? OR What Is Vector76 Attack in blockchain?
• Limitations/disadvantages of Blockchain.
Conclusion(Overall understanding of Blockchain.).
Introduction
Halo everyone. Warm welcome to week 6, of the academy. We are disecting the Blockchain today and I am glad I can finally be apart of this class. The Blockchain is a topic that we will keep learning about since the Crypto space and the Blockchain will always go hand in hand. So let me now take on my homework task.
What is the Blockchain?
A blockchain is literally a digital data ledger of transactions that is reproduced or distributed across the entire network of computer systems on the blockchain. A Blockchain begins with the 'Genesis Block' as the start block which was a foundation for other blocks to be created into existance. The blockchain uses the hash mechanism to have 'Resistance to Collision' on the blocks.
What is necessary to note is that it is decentralized as the nodes each stand independent to make individual decision on the network. When a transaction is made, a duplicate of that very transaction is distributed across all other connected nodes within the Blockchain using the Distributed Ledger Technology and secured using Cryptography.
Cryptographic protocols protect sensitive data transfers or transactions. The developers of cryptocurrencies built strong cryptography through advanced mathematics and engineering computer principles, that is impossible to break meaning that they cannot be counterfeited or duplicated.
Cryptography therefore is encrypting of sensitive data transfers or transactions through advanced engineering and maths principles so that they cannot be accessed or altered by a third party.
A blockchain has four major components for it to function as intended and these include;
- Blocks
These are permanent files (digital) that have encrypted data. They contain stored data, a 32 bit number known as the nonce and a 256-bit set of alphanumeric characters called HASH. The blocks are interconnected using the Hash Algorithm.
A hush is a function or algorithm that maps data by converting an input length into an encrypted output length. It is a one-way function and is therefore practically impossible to invite or reverse its computation.
Hashing algorithms are used to write new transactions into the blockchain through the mining processes there by validating the authenticity and integrity of various types of input. It's useful in a sense that it is widely used to avoid keeping long and plain texts as passwords on the blockchain.
- Chain
What makes us connect the links to the blocks to form the Blockchain is the Hash function. Every new block contains the Hash of the Previous block that shows the block position and maintains an organized chain of data.
Miners
These are users who use very high powered computers to solve complex mathematical equations to validate the Hash of new blocks. The miners form a network that validates blocks and transactions by a process called 'mining'.Nodes
These are computers that are on the Blockchain. They create, mine and validate blocks as every node on the network gets notified of the current block following a decentralized system of access to data.
What are the types of Blockchains?
The types of Blockchains include the following;
• Public Blockchain
This is a Blockchain that allows access to it's network for anyone through an internet connection by using the DLT (distributed ledger technology). This is the same type of Blockchain that is used by Cryptocurrencies to maintain even distribution of data to all online nodes. Currencies such as Bitcoin were pioneers to this type of Blockchain system and all earlier blocks are public.
Because it is Public, it is decentralized, and there is a high level of transparency and this makes it a trustless system of transactions. The Cryptographic technology employed in the public blockchain makes key transactions private or anonymous.
However, on one hand, the public blockchain is expensive with an ever increasing number of nodes. This is because a higher bandwidth is needed to mine and validate transactions. High powered computers use up alot of electricity and this is costly. The blockchain is also liable to hackers since it's public and may have alot of congestion making the networks very slow.
To add to the above, the scalability of the public blockchain also leaves alot to be desired.
• Private Blockchain
Unlike the public blockchain, the private blockchain is restricted to a number of connecting computers / nodes. This can be related to a private Network at places of work where all computers are connected to a specific Network and only the computers that are connected can access the data to all other computers on the network. The data stored needs authorization for access to the computers within that Network and authorization can be given with passwords or keys.
The advantages to this private blockchain are that the security is on better surveillance as there is access control on the network. The small scale size of this kind of blockchain makes the transactions faster as well.
Nevertheless, this blockchain system may not enjoy all advantage of the decentralized blockchain based system as it is controlled by a central authority.
• Consortium Blockchain
This type of blockchain incorporates both private and public blockchains running them simultaneously but the notes from different consortium blockchains connect to verify transactions and blocks.
The Blockchain has got nodes that perform different functions together. These computers that connect from different block chains serve as validators that can initiate receive and verify a transaction while other connected nodes can only initiate and receive transactions.
The advantage with the consortium blockchain is that it incorporates the private and public advantages of both chains. They have a fast and secure network due to ease of access to data and verification of transactions. There is also access to multiple blockchains.
• Hybrid Blockchain
This type of Blockchain combines all the features of both public and private blockchains at a go. A private blockchain is set up to restrict access to data from connected and unconnected nodes and then joining the connected nodes to a public blockchain where data can be accessed.
Connected networks enjoy anonymity and their identity is only revealed when a transaction is performed by one node. In a hybrid blockchain, smart contracts are used to manage the public aspect of the Blockchain connections.
Yes, this type is also fast and secure since it restricts access to non- connected nodes and authorization is granted to the necessary administrative ones. It's cheaper than a majorly public one as it encompasses an aspect of privacy and limitation in computational power.
However, it fails to be completely decentralized and thus is limited on transparency.
What are the benefits of blockchain?
The Blockchain's unique characteristics increase trust, security, transparency and bring other benefits to businesses. The blockchain is indeed a great innovation that will be beneficial to the world for time on end! Among it's many benefits are the following;
EQUAL SHARE OF AUTHORITY.
Blockchain transactions take place in a decentralized accounting ledger. The authority is separated and dispersed evenly to all users hence each individual using this payment system has equal authority by the power of the transactions that they make. The blockchain eliminates middlemen, vendors and third-party providers that have traditionally provided the validation and processing that the blockchain can now do
All power is transfered from the topmost user to the least down below and so every person gets a chance to develop his/ her abilities according to their potential. This in turn leads to motivation of bottom level users.
There is better supervision and control of assets.
PERMANENCE & TRANSPARENCY
- Permanence
The other important thing to note about the Blockchain technology is that data is only added through group concensus. No one owns the data, and every owns it. Transactions are irreversible and impossible to over-ride or change. Once payment has been made it cannot be reversed or manipulated supposing things go wrong.
The reason for this is that it's a network of computers that verify transactions and store them permanently one block to another) which is achieved through Encryption
Encryption (transforming data into codes to prevent unauthorized access) on the blockchain seals all transactions in the network. If a transaction has been made, or if there is an engagement on the blockchain, there cannot be an override.
What is the advantage in this? The system cannot be manipulated by a third party for their own gain as opposed to the centralized system where many conspiracies are possible, slowing down on accountability and service delivery.
- Transparency
Decentralized systems on the Blockchain enable mutual trust and verification between users, giving real visibility into data and documentation processes. They are reliable to give unbiased or forged data as quickly as need arises. This also eliminates corruption practices and gives users comfortability and stress free interactions.
Every user has got the same copy of the distributed transaction ledger, the priority being put on security and transparency.
SECURITY
Since it's impossible to change the information on Blockchain systems, data is safe from manipulation and the interactions need no trust (trust-less contact) for daily activity.
- Anonymity
The bockchain makes this possible by making data available for all users, yet protecting sensitive transactions hence limiting and controlling fraud.
In a decentralized system, traders can trade willingly and buy/sell from/to whomever they so desire. The power of their money is in their hands. Due to their nature, cryptocurrencies are not regulated and are managed by a decentralized system. So the risk of fraud when trading is very reduced because of the security of the transactions on the Blockchain.
EFFICIENT COMMUNICATION.
Everyone enjoys freedom of expression and there are no limitations to interactions on the public Blockchain. Even in trading on a decentralized platform, a trader has better negotiation for trade without a third party and can trade without revealing his identity.
With this freedom, the feeling of being magnalized or deprived is eliminated. There is satisfaction of human needs.
The exchange of information between different parties is made easier for instance bank beauracies, tax evasion, and international monetary transfers.
CONTINUITY
Blockchain systems tend to do away with succession problems as the traceability of data is shared across a business network — All entities or users develop managerial skills and are independent. In case one slows down or does off, there is the assurance of continuity. This promoted growth in the long run.
CURRENCY CONTROL
The Blockchain system keeps a firm grip on the currency flow on the market and the use of funds can be checked to measure how much have been spent in what sector or by what entity.
The control comes from having, individual decision making, being in the know and being a determinant in operations.
REAL TIME DELIVERY
Transactions are done in an efficient and swift manner that is timely in both centralized and dencentralized blockchain. This saves the user alot of bureaucracies, unnecessary delays, and ease of transaction.
For instance on the decentralized Steem Blockchain, all the conversion processes take less than 3 seconds to be reflected. Trading would be easier, health systems faster, sending money across the world and access to justice would be hugely realized.
EXPERTISE & DIVERSIFICATION
In any given setting, delegation of duty is good in increasing specialisation and consequently, increasing experience and expertise. The blockchain makes it possible for users to enjoy equal experience each according to their potential, giving many a chance to have the knowledge required on the platform. Motivation for each also increases.
Explain Blockchain Distributed ledger.
This is the distribution of data and transactions contained in blocks, to all authorized and connected nodes within the blockchain. The distributed ledger is makes all the difference between centralized and decentralized systems like the traditional banking systems.
The blockchain distributed ledger ensures that each node has the updated details of blocks and transactions performed and permanently stored in the network, this adds extra security to the network.
When a node mines a block, the block is validated and a new block is created, the blockchain Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is used to distribute a copy of the new validated transaction and the details of the new block created.
Properties of Blockchain Distributed Ledger
The Blockchain Distributed Ledger has the following Properties;
1- Even Distribution
The property of blockchain distributed ledger makes it possible for all connecting nodes have a distributed copy of the ledger and current blocks, to aid transparency as well as security.
2- Security
A distributed ledger is secured through the use of hash-cryptographic functions to encrypt and validate blocks by calculating the equivalence of the nonce number.
3- Programmed
The Blockchain Distributed Ledger is programmed to function through the use of smart contracts. The Smart contracts are used to manage and maintain transactions between users on the Blockchain systems.
4- Encryption
This property of the distributed ledger ensures that any validated record stored in a block cannot be reversed or removed. Date and time stamps are added to the distributed ledger for easy referencing for any needed data.
5-Anonymity
The blockchain distributed ledger ensures that the identity of nodes and all users are kept hidden to improve the security of the blockchain.
What Is Blockchain Double Spending? and how Bitcoin handles this problem.
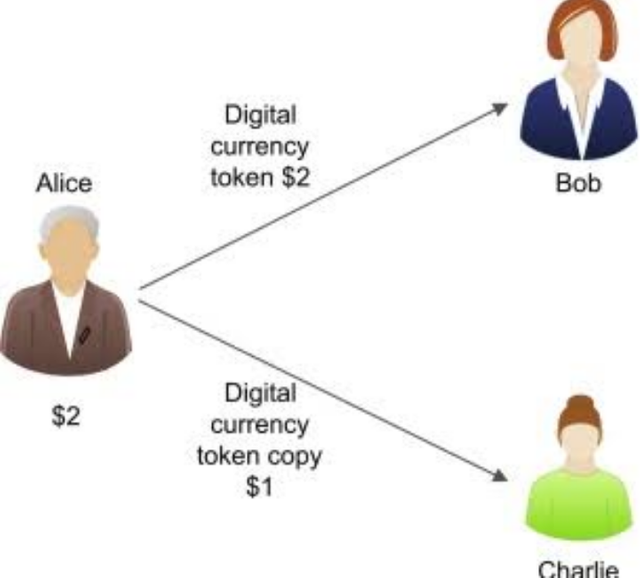
Blockchain Double Spending is a situation whereby the same crypto amount is used in multiple transactions as a result of an attack on the blockchain by a user where details of transactions can be copied and rebroadcasted within the network.
It is highly unlikely that Double Spending will occur in physical cash transactions as it's practically impossible to do so.
Example
Let's assume that a Blockchain user wants to buy hardware material and can use his crypto coin to buy them. The user can procure material worth $2000 and he can claim to spend it twice by copying and rebroadcasting( duplicating the details of a transaction) in different blocks through sending multiple transactions using the same crypto amount to a blockchain network to spend them before they can yet be confirmed.
There are various types of blockchain double-spending, some of which include the following:
Vector 76 Attack
This occurs when hackers use smart software to make crypto assets that are fake and send them to any recipients within a network on the Blockchain.
Race Attack
This type of double-spending occurs when a user or scammer sends many transactions using the same amount of cryptocurrency to a blockchain network to spend them before they can be confirmed. It's supposed to be fast so as to get the goal easier. It occurs only when the recipient accepts an unconfirmed transaction.
Finney Attack
This double-spending occurs when a miner duplicates the details of a completed spent transaction in different blocks and uses them over again. It also occurs when the recipient accepts the unconfirmed transaction.
How Bitcoin handles this problem?
Different blockchains have ways of handling Double Spending including the Steem Blockchain. However, Bitcoin blockchain uses the Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) as well as miners to validate and confirm transactions to eliminate double-spending.
• Confirmation
On the Bitcoin Blockchain, when a transaction is initiated and hasn't been confirmed, it is not reflected on the block. After the miner has verified the transaction, it is confirmed and the crypto delivered to the receiver. The transaction is then added to the Distributed Ledger of the blockchain. Adding the transaction to the Public Ledger ensures that the crypto asset and transaction details are not changed.
Therefore it is of utmost importance that the receiver gets confirmation of the completed transaction. The confirmed transaction will be verified and sent to the recipient, while the unconfirmed transaction will be removed from the blockchain.
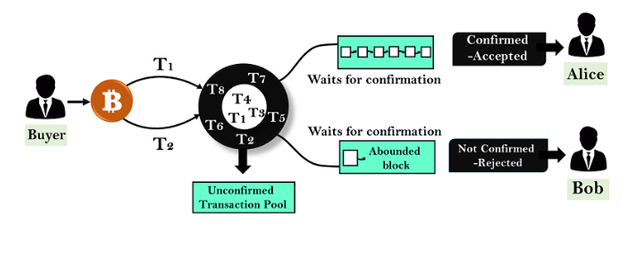
• UTXO- Complete Spending
Another way is to use complete spending where users cannot partially spend the UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output). In this instance a user can't partially spend funds in wallet as it's sent to two outputs and withdrawal goes to the receiver wallet after confirmation. The remaining is sent back through a change address.
Explain in detail how Block Hashes Work in Blockchain; What will happen when any middle of the block gets changed?
Hashing algorithms are used to write new transactions into the blockchain through the mining processes there by validating the authenticity and integrity of various types of input. It's useful in a sense that it is widely used to avoid keeping long and plain texts as passwords on the blockchain.
a) Resistance to Collision
Resistance to collision is a property of the hashtag function that is impractical or where it is impossible to find two colliding inputs with the same hash value.
Resistance to collusion or simply collision resistance (CR) is an important factor when basing on hash functions to to map to input to two different values. It's a security function of cryptographic hash properties, where a weak collision resistance means that the probability of failing to find a collision is not too small to be ignored and therefore minimally possible and a strong CR the probability is almost impossible.
Values X and Y are impossible to find, where X≠Y, H(x)=H(y)
b) Resistance to Preimage
When a property of a hash function is computationally difficult or impossible to find an input that maps to that element, it is known as Preimage Resistance. Pre-image resistance usually will cause the output value to repeat itself thereby enabling the hash function to ensure that it is uniformly distributed.
For a hush function to be pre-image resistant the length of its result should at least be 80 b i t s.
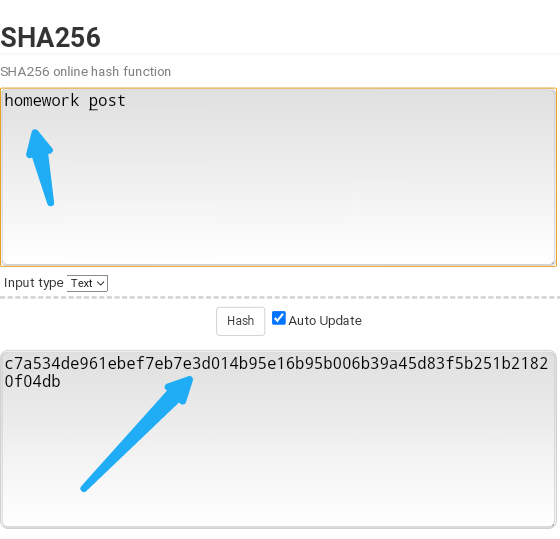
The input can be small or big but hush output is always the same fixed length to understand this we will see the SHA-256 which is used by Bitcoin blockchain.
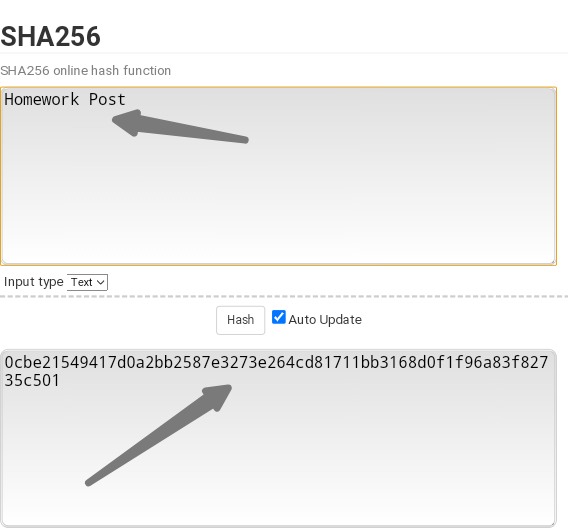
Source
In this stimulator, the words both begin with a capital letter H,P. They gave us an output beginning with 0cbe2.......
In this stimulator, the words both begin with a small letter h,p. They gave us an output beginning with c7a534.....
Block Hashes Work in Blockchain
On the Blockchain, a block has a number, data section and Hash output that is connected to the Nonce. The output should always come out with zeros at the start. These are important in showing if the block is valid or not.
For further illustration, we can visit Blockchain Demo
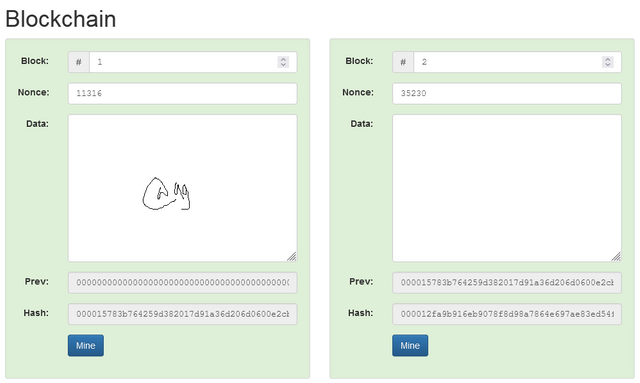
As seen above, Block 1 has a previous hash of 0, and a Hash of;
000015783b764259d382017d91a36d206d0600e2cbb3567748f46a33fe9297cf.
This is because it is the first block of the Blockchain, the Genesis Block.
The block 2 has a previous Hash:
000015783b764259d382017d91a36d206d0600e2cbb3567748f46a33fe9297cf, which is the hash of block 1.
The Hash of block 2 is:
000012fa9b916eb9078f8d98a7864e697ae83ed54f5146bd84452cdafd043c19
Both blocks are directly linked.
Adding Data to a Block.
When new data is added to the blockchain, it automatically generates a new Hash for the block as seen below. I have used the words "New Season Crypto Academy" and "Homework Post" as my new data in data section.
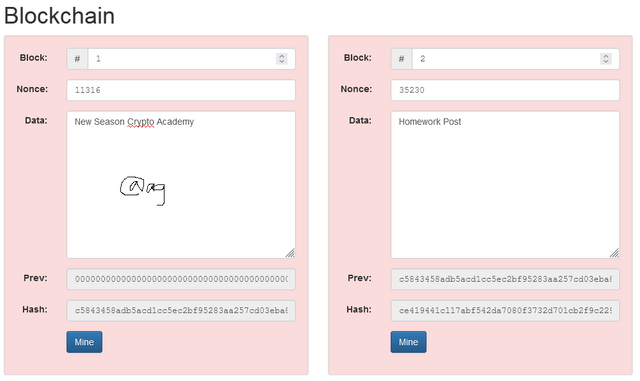
Changing Nonce
Since the data given above cannot give a valid Hash, we change the Nonce number. I have changed it from 11316 to 11308 of the first block. For the second block, i have changed the Nonce from 35230 to 31180. It still gives me an invalid Hash that doesn't begin with zeros.
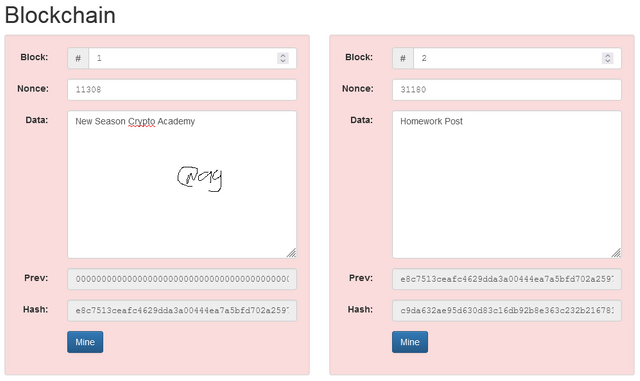
Mining the block.
To get a valid Hash, let me mine the block. Mining is the process of using high powered computers to validate blocks in a blockchain mining process. It is got by calculating the Nonce value and if it is a correct Nonce, it is maintained and confirmed on the blockchain. So we click the 'MINE' button for Block 1.
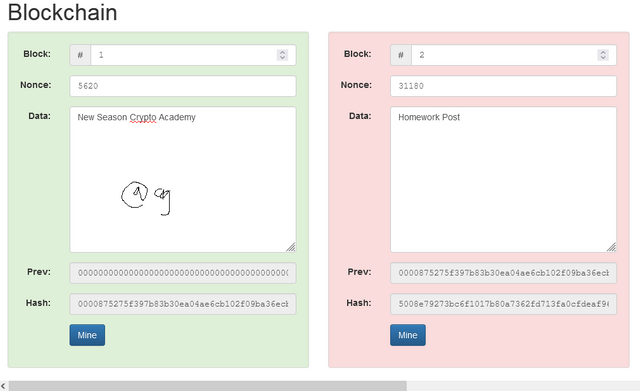
The Nonce that was 11308 changes to 5620 to get a valid Block with the Hash beginning with Zeros.

We do the same for Block 2 by Clicking 'MINE'. After Clicking the button, the Nonce that was 11308 changes to 5620 to create a valid Hash beginning with Zeros as seen above. For block 2, we do the same.
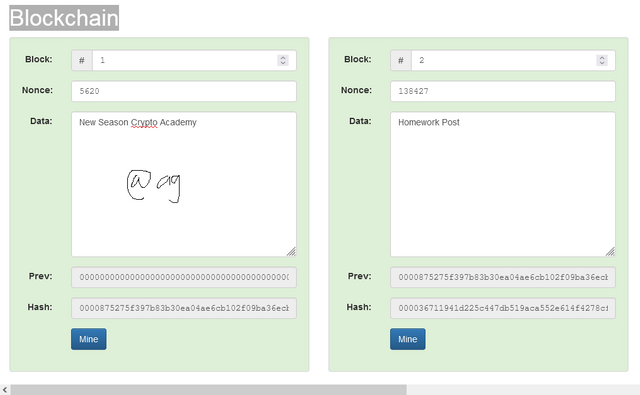
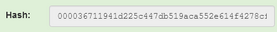
The new Hash generated for Block 2 begins with zeros and is therefore valid. From 31180, the Nonce changes to 138427 after mining. I mined two blocks!!!
N.B It is important to note that the Hash of the previous is reflected in the New Block mined and Block 1 is called the Genesis Block that will have its DNA in all proceeding blocks. The New Blocks are linked in a 'Chain' through this Hash Mechanism as seen in the two Blocks below.
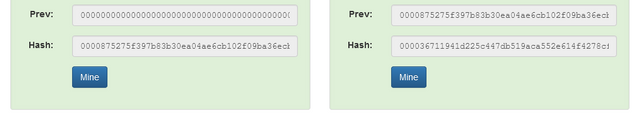
What Is Race Attack in blockchain?
This type of double-spending occurs when a user or scammer sends many transactions using the same amount of cryptocurrency to a blockchain network to spend them before they can be confirmed. It's supposed to be fast so as to get the goal easier. It occurs only when the recipient accepts an unconfirmed transaction.
In this instance, a buyer can create two transactions and sends the first to the trade partner who sells to a buyer before any confirmation is made. The buyer broadcasts second the transaction to the network which is sent back enroute his wallet and he gets his asset back. This can be illustrated as below.
For example the buyer can agree to pay 5 Ethereum for another asset. He creates two transactions worth the same or another amount and one is sold without confirmation. The second broadcast transaction will be broadcast on the network and consequentIy routed back to wallet.
Limitations/disadvantages of Blockchain.
The Blockchain system may have many advantages. Nevertheless, it also has disadvantages such as;
a)Low Coordination
Blockchain technology creates problems with co-ordination considering that all the power lies across many users in a decentralized system. Not every one works at a certain pace or speed. Nor does everyone think the same way.
It is almost impossible to follow certain policies or standard procedures whilst each works towards their own goal, according to their own abilities.
b)No Qualification
In daily life, having specific qualification makes specialization easier by dividing individuals each according to their work. However, on a Blockchain system, the factor of qualification and competence is often overlooked, creating a low quality workforce or network. This creates a loophole for hackers and scammers.
In such instances where there is unqualified personnel in control of decision-making, the output is low, and blockchain decentralization becomes useless.
c)High Expense
To add to the above, the technology needs highly trained people who know how to run operations and in addition, the public blockchain uses alot of electricity to mine and validate blocks and can be very costly.
d)Scalability
The Blockchain is highly scalable as it handles many transactions at a go. Scalability in blockchain is the amount of transactions per second the blockchain system is capable of computing
e)Attacks
There are many attacks such as 51% attacks that happen to blockchains. A viable example is the Ethereum classic ETC Blockchain that suffered a 51% attack on August 29 2020. It was caused by re-organization of over 7000 blocks of approximately two days' mining. In this attack, Okex exchange suffered a loss of $5.6 Million.
SOME OF THE WORK IN THIS ARTICLE IS IN MY CRYPTO ACADEMY POST WITH THIS LINK
Conclusion
To conclude this homework task, let me say that the Blockchain technology is indeed a much needed advancement in day to day transactions that has been picked up by the crypto- world and which will soon be picked up by other institutions of commerce or health around the world. Thank you professor @stream4u, I submit my homework post.


This content appears to be plagiarised as indicated by @stream4u
If you have not already done so, you should head to the newcomers community and complete the newcomer achievement programme. Not only will you earn money through upvotes, you will learn about content etiquette;
Notification to community administrators and moderators:
@steemcurator01 ADMIN
@sapwood MOD Professor[Advanced]
@steemcurator02 MOD
@yohan2on
Mmmmmm. Does this mean I can't participate in the academy anymore?
You have been curated by @yohan2on, a country representative (Uganda). We are curating using the steemcurator04 curator account to support steemians in Africa.
Keep creating good content on Steemit.
Always follow @ steemitblog for updates on steemit
Asante!