Steemit Crypto Academy Season 3 Week 4 - homework post for @awesononso | blockchain forks by @alexanderpeace
Greetings.
This is my homework post for Crypto Academy/season 3 /week 4- for @awesononso | blockchain forks.
Thank you professor for the lecture. Your style of delivery made it easy to comprehend.
1. What is a Fork? (In your own Words)
In life we know that human needs are insatiable and men will always demand for upgrades and changes in anything they find themselves in. The blockchain network is not exempted from this attribute of men. In the history of blockchain technology, certain situations and ideas have risen that demanded for a change in the way things run in this decentralized world. We know that the blockchain is decentralized hence rules and decisions do not come from a central body. Many nodes are involved in decision making when there is a call for a change or an upgrade. Some may agree with the change while some may not. When these couldn't come to a common agreement, it always lead to a division in the blockchain and this division results to what we know as forks. Those who agreed with the idea will remain with the blockchain and go ahead to implement the change while those who doesn't will breakout from the blockchain. Either of these changes always lead to a fork.
A fork is the word use to describe the change in the protocol of a blockchain.
There are reason why forks happens. They include but are not limited to;
• A fork can be used to correct security risk which may be existing in the blockchain.
• A fork can be used to integrate new functions which were not available in the original blockchain to make it better.
• It can be used to reverse transactions as we see in the case of Ethereum. I'll elaborate on this later as I proceed with the homework.
It's is important to note that the prices of Cryptocurrencies fluctuate when they are undergoing a fork.
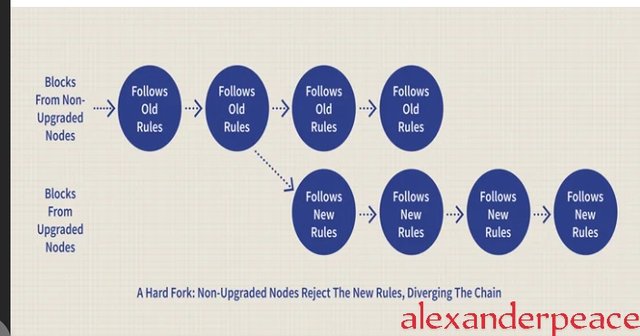
The changes in the block chain protocol may be radical or not. If the change is radical, it will result to a hard fork but if it's not, it will result to a soft fork. Hard fork and soft fork are the two types of forks we have.
2. Explain in details what a Hard Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).
A hard fork is a change in the blockchain protocol that results into a split in the blockchain. One of the branches follow the new protocol while the original blockchain continue with the old protocol. When a hard fork occurs in the blockchain, coin owners in the original blockchain also owns coins in the new blockchain but they must choose which blockchain to follow. The new blockchain in a hard fork does not accept the original block hence this is a permanent split. The new blockchain follows a different path from the old blockc and both run concurrently. The new blockchain uses a different currency from the original blockchain.
Hard forks are the reason why we have two blockchain with same genesis block like we saw in the beginning of the lecture.
• I. Copied the hash provided by the professor
000000000019d6689c085ae165831e934ff763ae46a2a6c172b3f1b60a8ce26f
• I pasted it on the link https://www.blockchain.com/explorer/
and clicked on search.
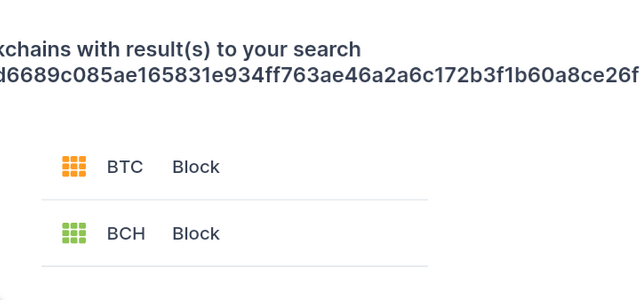
• I noticed there where two blocks with the same hash

• I explored the two blocks separately and saw they had similar data but different crypto denomination.
These blocks are the genesis block of bitcoin and bitcoin cash. Bitcoin cash been a hard fork of Bitcoin.
Examples of Hard forks.
Ethereum classic
I mentioned earlier that forks can be used to reverse transactions and that was the case of Ethereum. The original Ethereum now known as Ethereum Classic was hacked due to security loopholes.
The Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) in 2016 raised a fund of $150milliin worth in Ether in a crowdfunding effort but the DAO at it's launch was hacked and they lost Ethers worth $60million from 11,000 investors. After so many delibration, the founder later proposed a hard fork which is Ethereum in order to recover the lost funds. The hard fork recovered the lost money back to the DAO but some persons did not agree with the idea. The ones that agreed switched over to Ethereum while the others continued with the original blockchain now known as Ethereum classic. So Ethereum is a result of the hard fork of Ethereum classic.
Bitcoin hard fork.
Bitcoin in 2017 experienced a hard fork which led to the creation of Bitcoin Cash. There was a disagreement among the miners on increasing bitcoin block size from 1MB to 8MB. This dispute lasted for a long time but was resolved when the Bitcoin Cash blockchain was created. Both bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash have their own. Blockchains and runs parallel to each other. Bitcoin uses it's currency dicpicted ad BTC while bitcoin cash's currency is depicted with BCH.
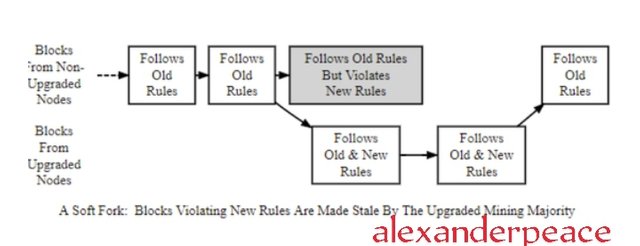
3. Explain in details what a Soft Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).
A soft fork is an upgrade in the block protocol of a blockchain that does not lead to the creation of a new blockchain from the original. A soft fork is a modification of the blockchain. In soft fork, the old nodes and new nodes still communicate. The new rules added does not conflict with the old ones. The users in the blockchain are not under compulsion to switch to the upgrade because the older nodes will still be working. There are two types of soft fork, they are;
• Miner - activated soft fork (MASF) and
• User - activated soft fork (USAF)
In miner - activated soft fork, a majority of the miners upgrade causing the new rules to be accepted while in User - activated soft fork, the users applies the new rules without the support of the miners.
Examples of soft fork is bitcoin soft forks which are segregated witness and bitcoin taproot. Let's look at bitcoin tap root.
Bitcoin tap root.
Bitcoin taproot is a proposed soft fork to upgrade bitcoin. The ideas behind the taproot is to improve the scalability, security and privacy of Bitcoin. Greg Maxwell a bitcoin developer brought the taproot proposal in January 2018. It was engrafted into the Bitcoin core Library after Pieter Wuile created a pull request. There's another upgrade known as Schnorr Signatures with which taproot is expected to be implemented along with.
4. What are the differences between Hard Forks and Soft Forks?
| SOFT FORK | HARD FORK |
|---|---|
| In soft fork, the blockchain still remains valid while the users adopts the upgrade | hard fork gives birth to two blockchains. The old and new run parallel to each other. |
| Does not result to the creation of a new Cryptocurrency | Results to the creation of a new Cryptocurrency pair |
| The new nodes acknowledge the old nodes | The new nodes sees the old nodes as invalid and vice-versa |
| There's no repetition of block height | there's repetition of block height |
5.Explain the following Bitcoin Forks and explore the blockchain where necessary. Indicate if they are hard forks or soft forks;
Bitcoin Cash
Segregated Witnesses
EXPLORING THE BITCOIN CASH
Bitcoin cash is a Cryptocurrency gotten from the hard fork of Bitcoin. Bitcoin cash was created in 2017. The developers of bitcoin wanted to make some changes but couldn't come to an agreement. A group of them forked Bitcoin and came up with Bitcoin cash. Bitcoin cash is different from bitcoin in some ways which includes;
• Bitcoin cash does not take much time in transfers unlike Bitcoin which takes 10 minutes.
• Many People use Bitcoin cash at the same time than they do with Bitcoin because it can do more transactions per second.
• Bitcoin cash transaction fees are cheaper than Bitcoin hence saves more money.
Exploring bitcoin cash blockchain
I took the following steps in Exploring bitcoin cash
Step 1
I copied the hash given by the professor @awesononso.
000000000019d6689c085ae165831e934ff763ae46a2a6c172b3f1b60a8ce26f
Step 2
I clicked on https://www.blockchain.com/explorer/
I clicked on the search space and pasted the link and clicked and searched as shown below
Step 3
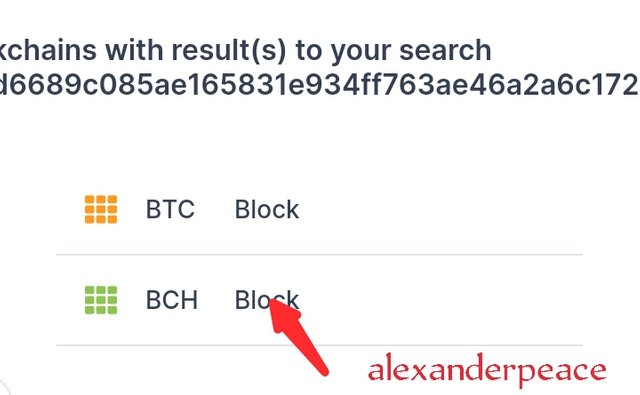
It showed two blocks with the same hash

Step 4
I clicked on bitcoin Cash block (BCH)
STEP 5
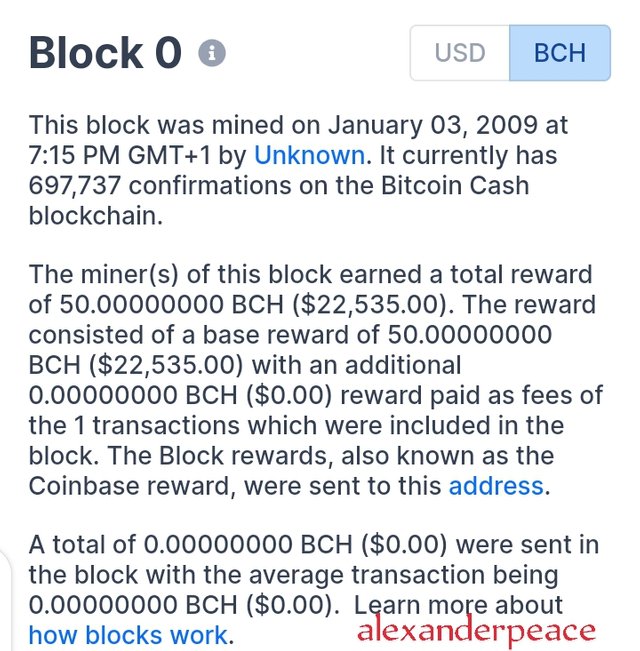
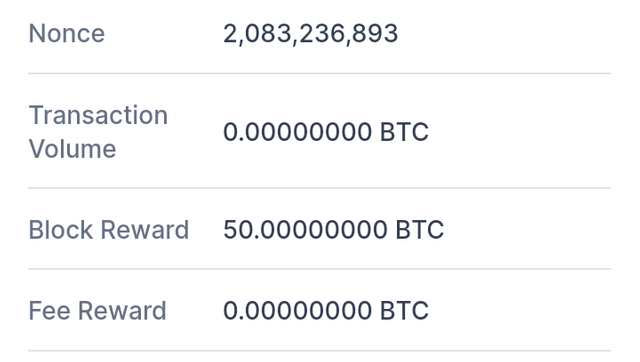
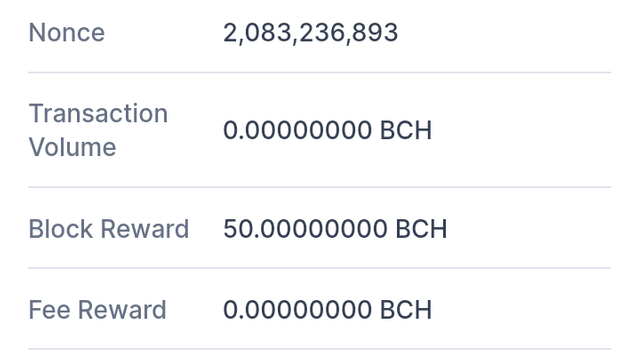
On opening it showed block 0 which is the genesis block which contained the date mined, the miners reward.
On scrolling down, there were more details of the hash, time stamp, height, number of transactions etc and the block transactions.
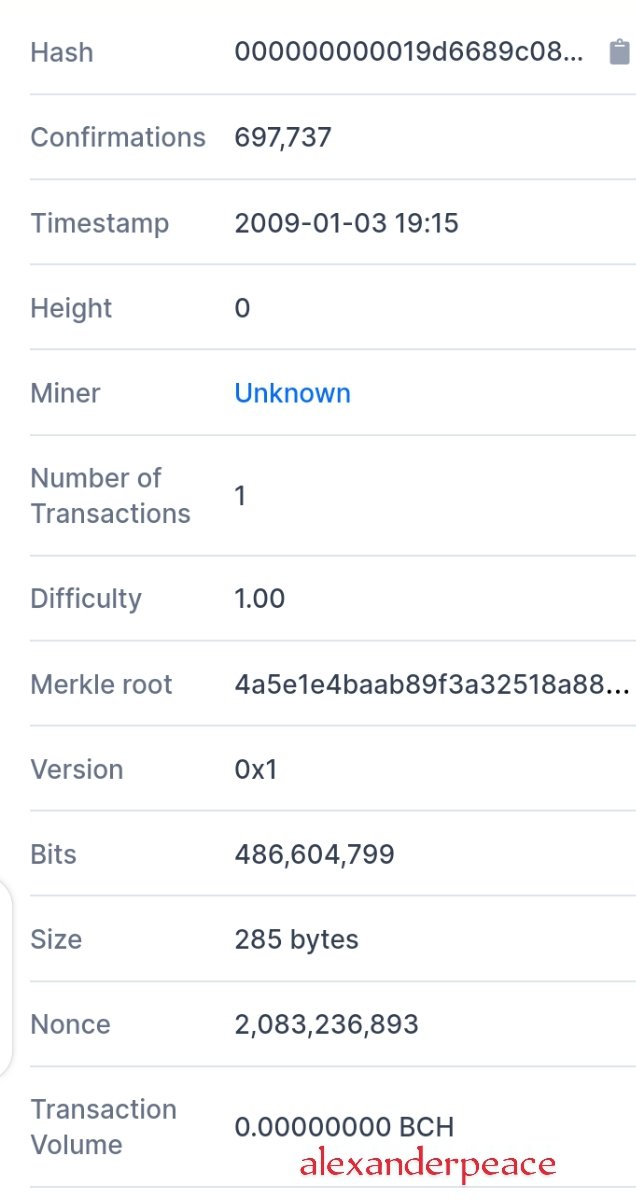
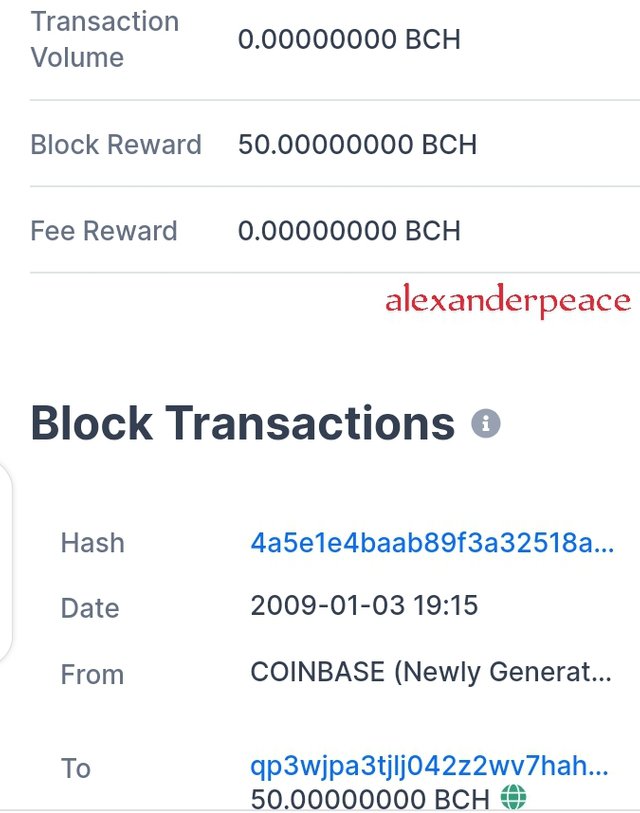
• Identifying the Type of fork
Bitcoin cash is a hard fork.
SEGREGATED WITNESS
Segregated witness also know as segwit is a soft fork of Bitcoin.
The Bitcoin Community in 2015 was seeking for how to speed up the Bitcoin transaction time, so they came up with segregated witness as a means to create space within the blocks so that the blocks can store more transactions. Segwit allowed some old blocks which frees space to Communicate with the new blocks hence it was a soft fork. But some miners believed that it was Segwit that was making the Bitcoin transaction too slow hence they forked it and came up with Bitcoin cash.
• Identifying the Type of fork
Segregated witness is a soft fork.
6. Write on the Steem and Hive Hard fork and show similarities in their Genesis Blocks(Provide screenshots).
STEEM AND HIVE HARD FORK
Hive is a blockchain created from the hard fork of steem blockchain on 20th of March 2020 and runs independent of steem blockchain. A disagreement arouse in steem Community with the integration of Tron in February 2020. The developers couldn't reach a consensus and this led the steem developers to launch the hive blockchain in March 2020 with hard fork 0.23. Steem uses steem, steem dollars, steem power and Tron as it's tokens while
Hive uses hive and hive-backed dollar (HBD).
There are similarities between the genesis block chain of the two blockchains.
Let's explore them.
Exploring the similarities between steem genesis block and hive Genesis Block
To explore the similarities between steem genesis block and hive genesis, I first logged into steem world https://steemworld.org/ on my browser
• I clicked on block explorer
• I clicked on search and typed 1
• I clicked ok
• It took me to the genesis block showing its details

• I proceeded to login into hive blockchain
https://hiveblocks.com/
• I typed 1 on the search icon, it brought out the genesis block
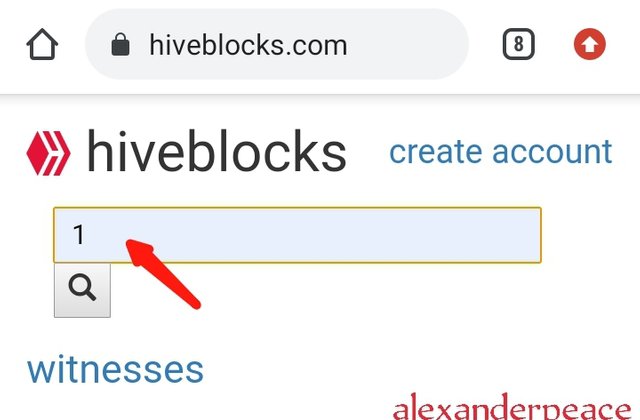
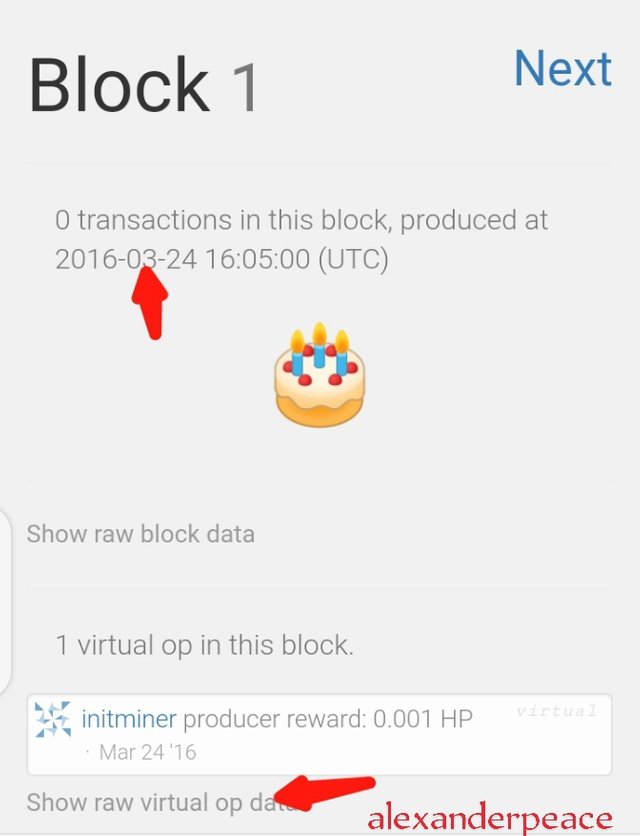
• I clicked on show raw virtual op data and it brought out further details
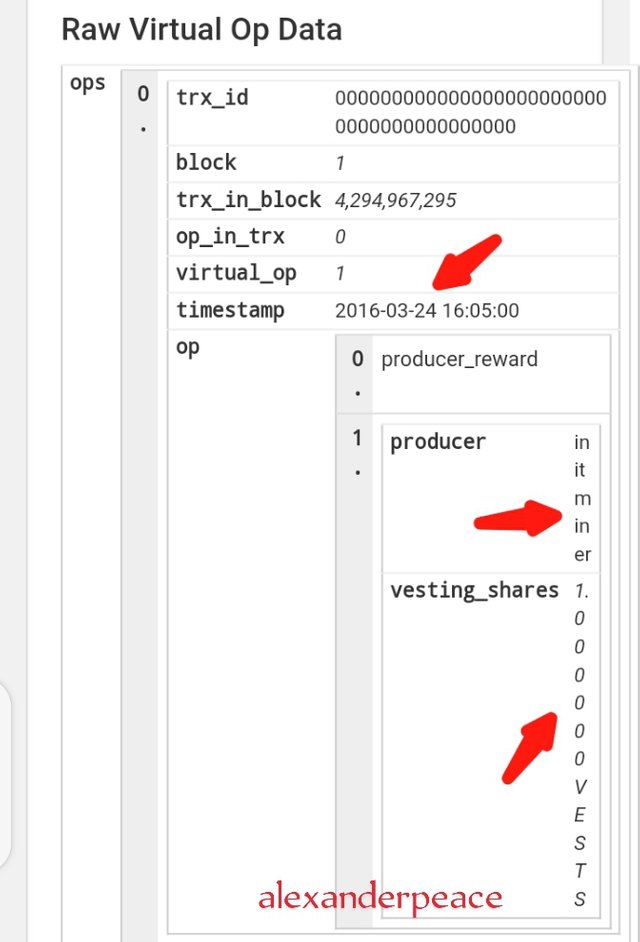
After Exploring the genesis blocks of both blockchains, the similarities includes ;
• Both steem and hive Genesis Block have the same mining date and time.
• the names of the miners are the same
• They both have the same number of vests
Conclusion
Changes are inevitable in any system and no man can satisfy everyman at the same time hence the blockchain network is not left out of these changes with man. Every one on the system is empowered to have their desires met through forking.
Soft forks points towards upgrades while hard forks leads to a new blockchain with a different Cryptocurrency. Forks makes for expansion and settling of disputes in a blockchain