SEC S20W4 || Hematology [Etiopathogenic Anemias - Module 4]
Hello everyone, I hope you all are doing well. I am here to share my participation for Steemit engagement challenge season 20 week 4. This is gonna be fun & learn new things at same time by participating in this challenge.
Etiopathogenic anaemia means that when there is an imbalance between the production and the release, what is going to happen in etiopathogenic anaemia, immature RBCs in our circulation are called reticulocytes.
So whenever there is a decrease in the production of red blood cells, it means that there is reduced haemoglobin in our circulation, which ends up in reduced oxygen supply to the body and tissue and which is causing hypoxia. If I talk about in detail why there is a problem in production and release there are a lot of factors
Iron deficiency anaemia is the most common worldwide anaemia. For example, the person is folic acid, vitamin B12 deficient, Malaria, thalassemia, sickle cell and certain leukaemias. Chemotherapy, the world, for example, during pregnancy or when a child is growing age, also lacks the production and release imbalance.
For example, bone marrow is not able to form New RBCs, and active molasses are going on in our body or acute blood loss and chronic blood loss, which will end up in micro, macro or normocytic Anemias.
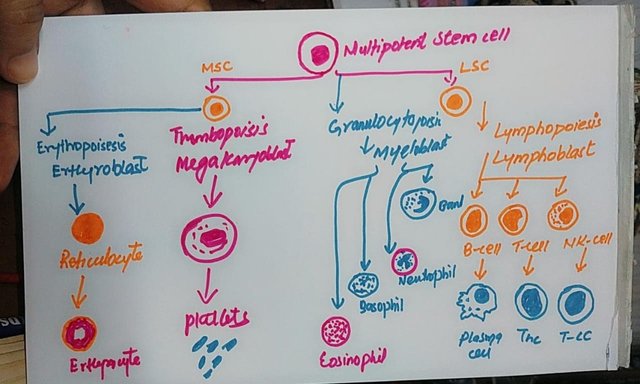
Etiopathogenic anaemia is divided into two types: generative anaemia and non-regenerative anaemia. I will talk about this in detail. There is a very important index which is called the IPR index, which helps in the classification.
What it means non-regenerative or aregenerative means there is less production of reticulocytes and regenerative means more production and it's named it is obvious excessive production is more dangerous to handle.
IPR is telling about reticulocyte count in percentage. Normally, it is less than one per cent. When bone marrow is making more reticulocytes and at full speed, the bone itself also undergoes breakdown.
| Aregenerative anaemia | Regenerative anaemia |
|---|---|
| There is a problem with bone marrow bone marrow is unable to form the amount of red blood cells that is required for a normal body | In this more dangerous time, the bone marrow is efficiently working making a good amount of red blood cells |
| The reticulocyte count is less than 2 per cent. | There is also increased production of reticulocyte count >2 per cent. |
| There may be certain bone marrow diseases, for example, leukaemia, or aplastic Anemia, in which there is a viral infection in the bone marrow, and the bone marrow suddenly shuts down, and all lines of the blood cells will not form, and the maybe I didn't deficiency of folic acid and vitamin B12. | Git bleeding, Active hemolysis due to any cause like malaria, thalassemia< sickle cell anaemia |
If any patient comes up with bleeding, you need to apply local pressure to stop bleeding. The second step is cleaning the site. Most importantly, depending upon which part of the bleeding is going on, you have to calibrate the body so that there can be reduced blood flow, most importantly, we can also apply ice on the effective areas. Ice will do the vasoconstriction of the blood vessel, and this will lead to reduced blood supply to that area.
If a patient comes to me with excessive bleeding, the first thing I would do is inject transaminase to decrease blood flow. There are certain other injections as well, but the most commonly used for the primary complaint of bleeding is this one.
Now, what is the pathogenesis behind bleeding or what is happening in the body when there is excessive bleeding going on this message is sent to our bone marrow, and bone marrow has to compensate for this bleeding. So firstly, one hormone which is most specifically produced in our kidneys is called erythropoietin.
Erythropoietin leads to the stimulation of red blood cell production in our bone marrow to increase the red blood cells now in our part of the world where there is CKD is very common, which means there is less production or no production of erythropoietin.
When the bone marrow sends this message, there are certain stages, for example, proethyroblast, erythroblast, reticulocyte, and red blood cell, which will lead to circulation.
To all this happening, a very immediate response to compensate for the bleeding is to increase production. The precursors will increase, and automatically, there will be mature and immature RBCs in circulation.
But if the bleeding process and what is happening in the long term, then there is, you know, we take more iron supplements. This iron is going on reabsorb, and then it goes to the bone marrow, and there will be more production of the red blood cells. So, the key thing which are produced is the erythropoietin hormone.



Upvoted! Thank you for supporting witness @jswit.
Upvoted. Thank You for sending some of your rewards to @null. It will make Steem stronger.