Alcohol and the Brain #2: The medulla oblongata
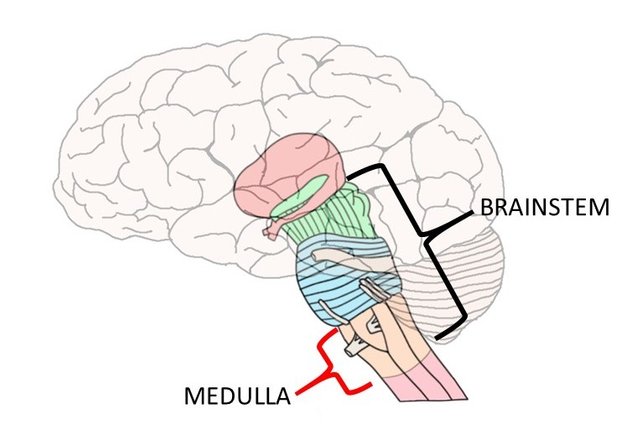
Image Source
The medulla, or also known as the medulla oblongata, is the last part of the brain stem before it extends as the spinal cord. It is the 'vital center' for the brain, which means its functions are necessary for survival. Examples of this are breathing, regulation of heartbeat, blood pressure, and the general transfer of information from the brain to the spinal caord. This is part of the autonomic system (involuntary functions), and are all controlled by different neurotransmitters that functions as on and off switches for other parts of the body
| Neurotransmitter | Function |
|---|---|
| Epinephrine and norepinephrine | Fight-or-flight response |
| Acetylcholine | Rest and digest, cognitive functions |
| Serotonin | Mood and behaviour |
| Dopamine | Muscle control, motivation |
The fight and flight response is well linked to not only cardiovascular control (heartbeat and breathing), but also blood glucose control. When affected by excess alcohol, breathing and heartbeat slows down, which affects another important physiological process: oxygen intake. Oxygen is required for yet another important function of the medulla oblongata, which is attention and consciousness. Blackouts are very common in those who get drunk, and this is one of the reasons why.
Acetylcholine helps in gut muscle tone for digesting, but also aids in focus and attention in the central nervous system. The outcome here would be obvious: Alcohol disruption on acetylcholine disrupts our focus, and often those who get drunk could not pay close attention to a conversation or actions such as walking and driving. Alcohol also disrupts the nerve endings responsible for bringing down food through our gut, which explains why many people complain of indigestion.
Alcoholism has often been linked to disrupted psychological behaviours. Some of the most notable are suicide, depression and violence. Serotonin actually helps control these behaviours by increasing our adaptability to our environment and stress-coping abilities. It helps modulate the limbic system in the brain (emotion and memory), preventing us from impulsive actions. As people we need to be aware of this, as socially, it can harm people in more ways than one.
Dopamine is responsible for skeletal muscle control, and also motivation (reward-mediated behaviour). Alcoholism therefore, has been linked to Parkinson-like effects (slow movement, tremors, stiffness, postural instability), and possibly acquiring Parkinson's disease in the long term. So unless you don't mind taking L-Dopa in the long run, again, please drink responsibly.
A big thank you to @myreader, @lordkipas and everyone from #teammalaysia for supporting my posts!
Congratulations @kennethlegada! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click here to view your Board of Honor
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPDo not miss the last post from @steemitboard: