Galaxy (our)
Our galaxy is the home of the Sun and other 200 billion stars, thousands of nebulae, and stargazers. It's a gigantic structure with 100,000 light years in diameter and only 1000 light years thick. It is a huge star disc in which hundreds of billions of stars rotate around the galactic center.

It is officially called "Our Galaxy" (with "Big G"), but is also known as the "Milky Way Galaxy." It is one of the hundreds of billions of galaxies in our universe, and if the Sun were a house, the Galaxy would be a metropolis.
To imagine how great the galaxy is is to imagine that it is reduced to 130 km. Then the solar system will only have 2 mm diameter!
It is very difficult to determine the shape of an object you are and astronomers have been struggling for hundreds of years to do with relative success.
As seen from within, the Galaxy appears as a whitish band in the sky, a band known as the "Milky Way." The Milky Way is diffuse, cloud-like, but is composed of billions of stars. (450 AD - 370 BC), but demonstrated by Galileo Galilei in 1610. Galileo looked at the Milky Way through the window and observed that it decomposed into thousands and thousands of weak stars as brightness.
The Milky Way travels through the following constellations: Scorpius, Sagittarius, Scutum, Aquila, Sagitta, Vulpecula, Cygnus, Cepheus, Lacerta, Cassiopeia, Perseus, Auriga, Gemini, Monoceros, Puppis, Vela, Carina, Crux, Centaurus and Norma. It has the greatest brilliance towards the Sagittarius constellation, and Orion is very "blown".
Details in the Milky Way
Also in the time of Galileo Galilei (~ 1600) astronomers realized that we live in a star disc. When you look at the plane of the disc, because there are more stars in the area, you will see in the sky in the sky the combined light of all the stars, a diffused cloud that should cut the sky in half. When you look perpendicular to the plane of the disc you will see stars but not so many. These areas will be devoid of the "milky" background.
Because the sky is divided into two equal regions by the Milky Way, it is concluded that we live in the middle of the star disc. See how simple and elegant it is to make observations and interpret them.
However, they remained unknown: how large is the star disc, what shape is it and what is the position of the Sun.
Over time, many astronomers have tried to determine the shape and size of our galaxy, the activity that seems meaningless in view of our position "in the galaxy."
One of the first was William Herschel, who at the end of the 18th century began counting the stars in certain areas of the sky. Considering that all the stars have the same brightness and where they see more, the star disk is more in space. He thus managed to determine a form of the galaxy in which the central place was occupied by the Sun.
By 1802 all Herschel realized that the stars had different shades and its pattern was not correct. At that time, distances were unknown to the stars, Herschel's estimation of magnitude was wrong
Followed by the astronomer Jacobus Kapteyn, who, knowing the distances to a few stars, by counting the stars on the photographic plates, determined that our galaxy was shaped like a 50,000-year-long ellipse (diameter) and a 10,000 year light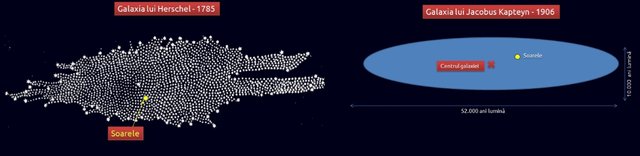
Old models of our Galaxy
The patterns of the two were wrong in size, because they did not take into account the interstellar dust that diminishes from the apparent brightness of the stars. Thus, some closer stars seemed more distant and this was a source of error.
In 1917, an American astronomer Harold Shapley notes something interstellar: most globular swarms are in the sky in the constellation Sagittarius. It concludes that there is the center of the star disc in which we live and that the Sun is not at the center of the galaxy. Shapley managed to determine the distance to the globular swarms and saw that he was far away, tens of thousands of light years, a sign that they were distributed around the star disc. The center around which they were distributed was in the constellation Sagittarius, at the 17h45m40s straight elevation coordinates, -29 ° 00 '28 ".
Shapley ultimately determined that the star disc in which we live has a diameter of about 100,000 light years and that the Sun is 26,000 light years from the center.
The structure of the galaxy
By comparing our galaxy with other galaxies, we have come to realize that we live in a galaxy with spiral arms. Seen from above, our galaxy has a spiral-shaped galaxy with a bar in the center. Such galaxies are called spirals.
Initially it was thought to be a normal spiral, but since 1980, more and more observations have shown that there is a very old red star bar at the center of the galaxy. Confirmation came in 2005, when the telescope with the Spitzer Space Telescope saw that some of the stars in a part of the galactic center were closer than the opposite.
The stars are disposed in the galaxy in two ways: the young stars are in the plane of the galaxy (the galactic disc), and the old ones in the galactic halo that surrounds the center of the galaxy. Another part of the galaxy is called the central prominence and is composed of stars of all ages with orbits of different inclinations.
The spiral arms are best seen in the radio field, along the 21cm wavelength, electromagnetic radiation naturally emitted by hydrogen atoms. As in other galaxies, hydrogen is in spiral arms, astronomers have searched for something like this in our galaxy. They have found that there are areas rich in hydrogen bounded by less dense areas. Of course, hydrogen-rich areas are the spiral arms.
Another method by which you can see if there are spiral arms is to determine distances to very bright stars of spectral classes O and B. It has been observed that in other galaxies this type of stars is often found in spiral arms.
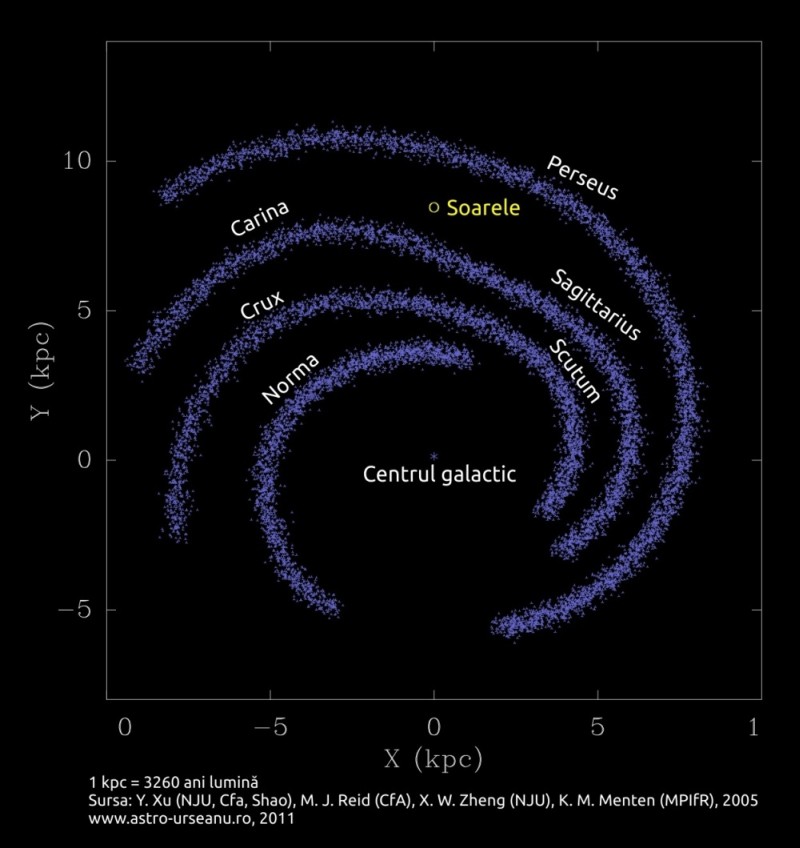
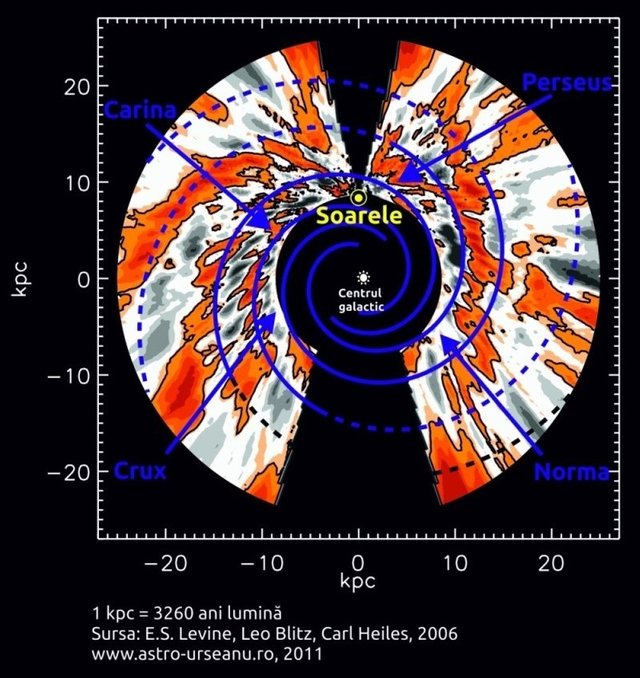
The spiral structure of the Galaxy is highlighted in two different ways.Up: The spiral arms are seen when measuring the distance to the bright and young stars. Bottom: Spiral arms (orange) are seen when measuring interstellar gas density. Spiral arms contain very young stars and interstellar gas (HI and HII regions)
Around the galactic center there are two large spirals extending from the edge of the central bar. These arms have received the name of the constellation in which they are projected:
the Perseus arm
the Scutum-Centaurus arm
There are other spiral arms, but there are arms that do not start from the bar of our galaxy:
the Norma-Cygnus arm
the Crux-Scutum arm
the Carina-Sagittarius arm
Orion arm
The sun, along with the planets, and other stars, are located in the Orion arm (also called the Local Arm), a mini-arm that unites the Perseus and Sagittarius spiral arms. The Orion arm is made up of millions of stars and immense hydrogen clouds, including a group of young stars (type O and B) called Gould's belt, which is about 2500 light years in diameter.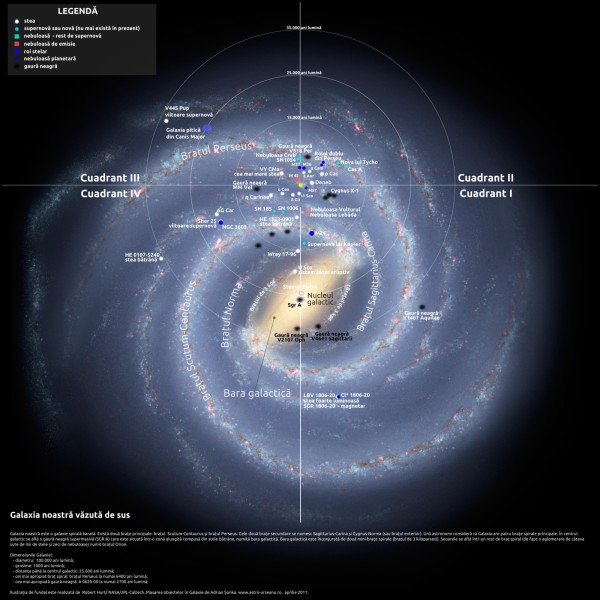
Local Bula, artistic conception.
Illustration: NASA
Initially, there was gas between the stars in the vicinity of the Sun, but the shock wave of a supernova cleared the area. This region, in which the Sun was formed, is now called the "Local Bull".
It has a diameter of 300 light years, the gas density being very low, of only 0.05 hydrogen per cubic centimeter, a density 10 times smaller than in other areas of the galaxy.
In the last 5 to 10 million years, the Sun has traveled through the Local Bula. The shape of the Local Bule is not spherical but elliptical.
All the spiral arms and most of the stars are located in the galactic disk (in the plane of the galaxy). The galactic disc, which contains young stars and a lot of gas, is surrounded by a spherical halo called the galactic halo. The halo is populated by old stars, but also by globular swarms formed with our galaxy.
Most globular swarms are located up to 100,000 light years away from the center of the galaxy. There are also some more distant globular swarms.
A surprising thing, seen from the way stars rotate around the galactic center, is that all the stars in the galaxy and all nebulae represent only 10% of its mass. The remaining 90% is a matter that has mass but is transparent to light, called dark matter.
Sun's place in the galaxy
The sun is at the edge of the Orion spiral arm in the Bula Local. " The distance to the galatic center is 26,000 light years.
Up to the next spiral arm, the Perseus arm, is a 6500 light-years away.
Interstellar local cloud.
Photo by Linda Huff (American Scientist),
Priscilla Frisch (U. Chicago)
An interstellar gas cloud found in the Cygnus constellation has been discovered that fills the sun. The gas cloud has a diameter of 25 light years and is called "Local Fluff". More scientifically, this region is called the "local interstellar cloud". It seems we are already in this cloud of gas, out of which we will go over about 10,000 years. The strong radiation of the Scorpius-Centaurus stellar association pushes the local interstellar cloud in a direction of movement perpendicular to that of the Sun.
The area where the Sun is located, away from the dense regions where stars form, is called the habitable area.
This area is close enough to the galactic center, where heavy chemical elements form the tellurian planets. The area is far away, however, by regions rich in stars and nebulae, where there may be black holes where supernovae can explode. The mere passing of a star near the Sun would move the comets of Oort's cloud and in the solar system, after a few million years, a large comet bombardment would take place.
The sun, together with the planets, makes a complete rotation around the galactic center in 225-250 million years. Its travel speed is 217 km / s (1 light year in 1400 years).
In contrast to the stars in the venom, the Sun is moving towards the Hercules constellation, this place being called the solar apex. The Sun's orbit is elliptical and shows oscillations in the galactic plane. It is believed that when the Sun reaches the plane of the galaxy, due to the high star density, there are mass extinctions on Earth. The gravity of the stars in the vicinity of the Sun destabilizes the comets on the edge of the solar system and sends them to the sun. So all planets will go through a period of collisions with comets or asteroids.
In the area where the Sun is located, the exact positions (in space) of over 100,000 stars are known. Within a radius of 10 light years there are 12 stars. Seven of the 12 stars are red dwarfs. Only the stars Sirius A and Centauri A are larger than the Sun.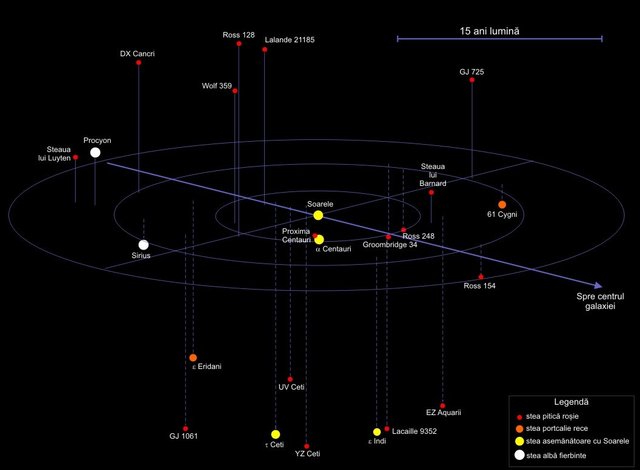
The closest star is 4.3 light years and is called Proxima Centauri.
Cosmic objects in the galaxy
Since the telescope's appearance, astronomers have noticed that star groups were present in some regions of the sky. At first sight it seemed that these groups really exist in space, but without determining the distance to the respective stars could not be said for sure.
The groups have been called the Star Wars.
Two types of swarms have been identified, their names being given by visual appearance.
Open clusters: clusters of stars without a particular shape, which can have up to several hundred stars. Open wreaths contain white or blue stars.
According to the color of the stars and their composition (called metalicity) it was inferred that the swarms consist of young stars, born together in the same interstellar gas cloud. Sometimes the nebula from which the stars were born can be seen very close to the swarm in the case of the youngest objects.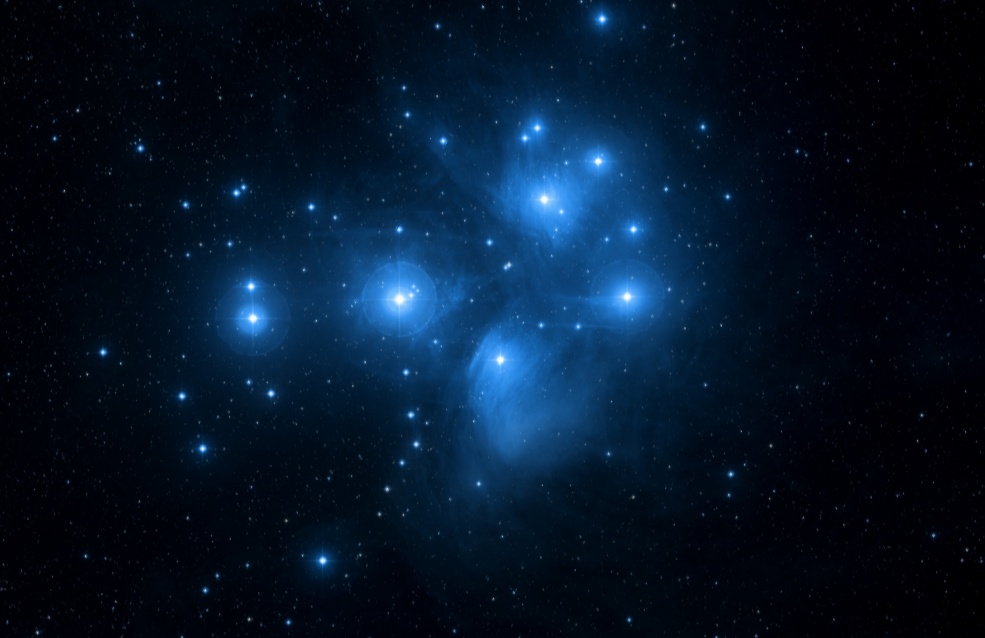 Pleiades or Messier 45 - light star cluster at 433 light years. It contains about 350 stars in a region of between 30 and 70 light years. The age of rock stars is about 100 million years old. Photo: SDSS
Pleiades or Messier 45 - light star cluster at 433 light years. It contains about 350 stars in a region of between 30 and 70 light years. The age of rock stars is about 100 million years old. Photo: SDSS
It is now known that the open-starred swarms are star-bound groups of stars, formed of young stars, with their own common movement. .
Open waves are galactic objects that rotate around the center of our galaxy. It is in the galactic plane, mainly in the spiral arms. In some regions, star formation is still observed, a process that gives rise to new starfish.
Most have a short life. As they rotate around the galactic center, the stars in the swarm escape the gravitational pull of the others. Thus, as the time passes, the swarm dissipates in the galaxy. An open swarm has an average life span of 100 million years.
Until March 2012, 1531 such objects were known. List the nearest 100 starfish and up to 3000 light years.
There are other types of star groups, such as young stars (type O and B) or star formation (type T Tauri). Because of the small number of stars, these groups are called "stellar associations". Type O and B associations are composed of stars of common origin and speeds with the same meaning and value. But the components do not attract each other, as in the case of open and globular swarms.
Globular clusters: spherical star spheres containing between 10,000 and 1,000,000 stars.
These are arranged around our galaxy, in a halo, centered around the galactic center. Spectroscopic studies show that the globular globe stars contain many heavy chemical elements with a higher age. Estimates of age show that globular swarms are between 12 and 13 billion years old.
By March 2012, 158 such objects were cataloged, the closest being Messier 4 and NGC 6397. A list of them, in the order of the Sun's distance
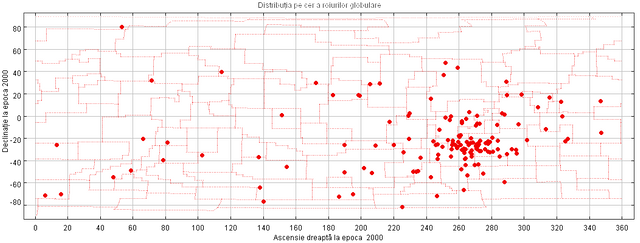 Map of the entire sky on which 147 globular swarms (with red) are passed. Dotted lines are the boundaries of the constellations. Most of the objects are in the constellations of Ophiucus-Scorpius-Sagittarius
Map of the entire sky on which 147 globular swarms (with red) are passed. Dotted lines are the boundaries of the constellations. Most of the objects are in the constellations of Ophiucus-Scorpius-Sagittarius
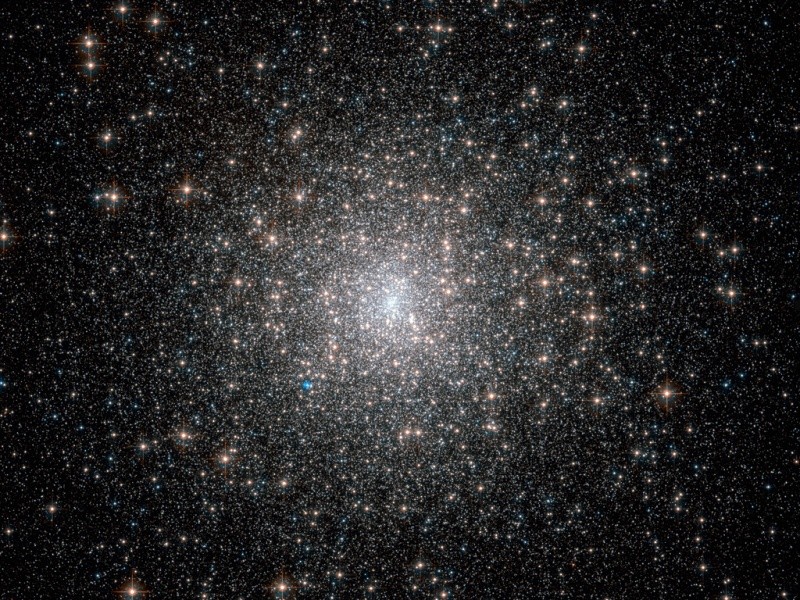 The M15 globule. It is 35,000 light years away from the sun.
The M15 globule. It is 35,000 light years away from the sun.
Its diameter is 200 light years. It is in
Pegasus constellation. Photo: ESA / Hubble & NASA
After the stars in an open star rope dissipate, they follow similar traces that can be identified. Star clusters with their own motion have been called "stellar associations". We can have young stars' associations, just formed or older stars that in the past were gravitational.
An example of a star association is given by some of the stars in the Big Dipper. They have their own movement in the same direction, at the same speed. In their composition, chemical elements have been identified to the same extent, which proves to be of common origin, forming the same cloud of gas 500,000,000 years ago. Another Star Association is the one formed by the stars around Perseus (Mirfak).
Young star groups, called O and B associations, contain between 10 and 100 young stars, up to 50 million years old. We find them in the galactic arms, where the stars are formed, and they are "spiral arms". Very bright O and B stars are visible even if they are located at a great distance, allowing the structure of the spiral arms to be traced. Usually in other galaxies only stars of this type are seen.
The closest group of this kind is the Star O and B Scorpius-Centarus Association. It consists of three subgroups of stars (Scorpius Superior, Centaurus-Lupus Superior and Centaurus-Crux Inferior) aged 5, 12 and 16 million years. In fact, this star association is the closest region in which stars have recently been formed.
Star Associations:
Melotte 25 (Hyadele) - 146.7 light years away "
the Pictoris group - 117 light years away; contains 17 stellar systems that move in parallel with the star Pictoris; the component stars are about 12 million years old;
Castor is composed of several bright stars in the sky, including Castor (α Geminorum), Vega (α Lyrae), α1 and α1 Librae, Alderamin (α Cephei), Fomalhaut (α Piscis Austrinus); a total of 22 stars aged hundreds of millions of years have a common movement through space and ages plus similar compositions;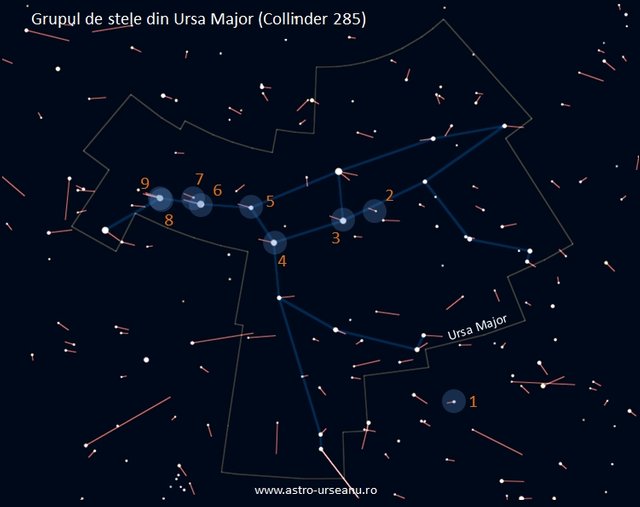 The star group of Ursa Major (Collinder 285). It is 75 light years away and consists of stars of common origin hundreds of millions of years old. The stars are: 1 - 21 Leo Minoris, 2 - 37 Ursae Majoris, 3 - Ursae Majoris, 4 - Ursae Majoris, 5 - Ursae Majoris, 6 - Ursae Majoris, 7 - 78 Ursae Majoris, 8 - g Ursae Majoris, 9-80 Ursae Majoris. The lines at the star are the direction and the travel speed (high line = high speed)
The star group of Ursa Major (Collinder 285). It is 75 light years away and consists of stars of common origin hundreds of millions of years old. The stars are: 1 - 21 Leo Minoris, 2 - 37 Ursae Majoris, 3 - Ursae Majoris, 4 - Ursae Majoris, 5 - Ursae Majoris, 6 - Ursae Majoris, 7 - 78 Ursae Majoris, 8 - g Ursae Majoris, 9-80 Ursae Majoris. The lines at the star are the direction and the travel speed (high line = high speed)
The study of stellar swarms is very important because, with the same composition, the different properties of the stars in swarms depend on their mass. Studying the state of a star, knowing its age and distance to her, we can determine her table. If we know the stars and their properties we can build star patterns.
nebulae
The term nebula comes from the Latin "nebia" and means "fog". By observing the sky through astronomical instruments, small, diffuse, cloudy spots have been discovered that have been named. Originally, the term was used for all diffused objects, but the name of this galaxy was denied.
There are several types of nebulae, some emitting others reflecting light. Some are associated with star death, others with their birth. There are also opaque clouds of gas and dust, called "obscure nebulae."
The regions where large amounts of cosmic gas and dust are encountered are called diffuse nebulae. The gas left from the formation of the Galaxy can form stars but only when it is moved, forming small clusters of molecules that begin to attract others. These regions can "light up," meaning they can emit light if they have stars that emit strong in ultraviolet (very hot stars). In this case we are dealing with a nebulae of emission, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen that emit light. Hydrogen can be in atomic (molecular) or molecular (molecular hydrogen - H2) state.
There are thousands of emission nebulae, most of them in the galactic plane (in the Milky Way), the most famous being the Orion Nebulae and Carinae Nebula. Another name for the emission nebulae is "double ionized hydrogen nebulis (H II)".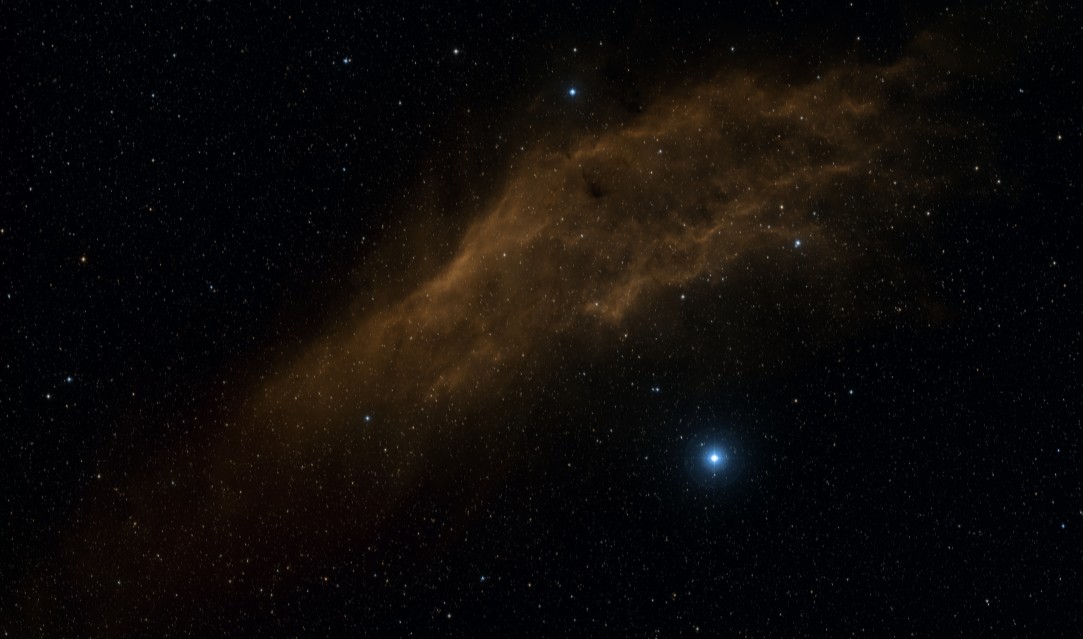 Nebulae NGC 1499 (Nebula California). This hydrogen cloud is about 100 light years long and is about 1000 light years away. The brilliant star (xi Persei) in the image makes the hydrogen emit light (ionizes it). Photo: SDSS
Nebulae NGC 1499 (Nebula California). This hydrogen cloud is about 100 light years long and is about 1000 light years away. The brilliant star (xi Persei) in the image makes the hydrogen emit light (ionizes it). Photo: SDSS
If the star formation process began, after a few million years instead of the nebula, there would be a stellar swarm (or a group of stars), the material that was not embedded in the stars being scattered in space by the solar wind.
The size of the emission nebulae varies from a few to several hundred light-years. The particle density can range from several million to a few particles per cm3. Their composition is: 90% hydroe, 9.8% helium, 0.2% other chemical elements and molecules (O, N, CO).
The nearest nebula of this kind is the one around the T Tauri star, 420 light-years away. The nebula around the Cassiopeiae gamma (680 light years), California nebula (1,000 light years) and the one around the Orionis lambda light (1000 light years) follow.
An interesting case of interstellar matter is that of reflex nebulae. There are interstellar dust clouds that reflect the light of the surrounding blue stars. From all the light emitted by the star, the wavelength giving the blue color is first scattered by the microscopic dust particles.
Reflective nebula is composed of frozen water, silicates and graphite, small cosmic dust particles (less than one micrometer) formed in the star atmosphere and outer space.
These nebulos are mostly seen around the brilliant stars because they emit enough energy to produce the phenomenon of scattering light. Because the reflection nebulae can not be seen without having a star, the distance to them is actually the distance to the star.
Reflection Nebula around the Riger Star. Photo: SDSS Consortium
Nebulae of this type can be seen in infrared because the dust is heated by stars. From the observations made it has been found that temperatures are between 100-600 K (-173-327 ° C).
Brilliant stars surrounded by reflection nebulae: the stars in Pleiade (400 light years away); Rigel - Orionis (900 light years away).
Supernova remnants - As a result of the explosion of a star, matter spreads through the galaxy at speeds of 10,000-20,000 km / s. The gas collides with the interstellar environment that makes light (excitement). Thus we see nebulae with a filamentary structure that surrounds the place where the star collapsed / exploded.
Up to now, 247 supernova remains and a table with the ones up to which the distance was estimated to be found here.
The obscure nebulae are nebulae that are not enlightened and can be seen because they project in front of bright clouds or star-rich regions. There are simple clouds of gas and dust with small masses and massive clouds that can lead to the appearance of stars. The obscure nebula often finds catalog numbers in the Barnard, Bok or Sharpless catalogs. The temperatures inside these nebuloses do not exceed 100 K (-173 ° C) and the particle density is between 107 - 1012 atoms / m3. If you ask, the density of the space is 106 atoms / m3.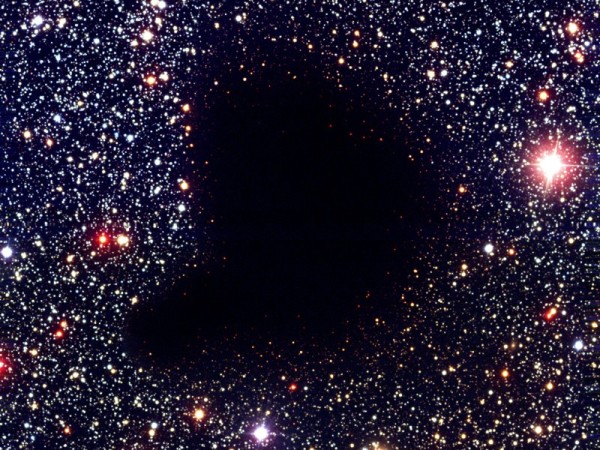 The obscure cloud of Barnard 68 at about 410 light years away. The temperature inside the cloud is 16 K (-257 ° C) its mass being two solar masses. A larger image can be found on the ESO website. Photo: ESO
The obscure cloud of Barnard 68 at about 410 light years away. The temperature inside the cloud is 16 K (-257 ° C) its mass being two solar masses. A larger image can be found on the ESO website. Photo: ESO
Planetary nebulae occur as a result of the slow (and sometimes periodic) ejection of the star's atmospheric layers. The matter spreads radially to the star and is forced to emit light from the ultraviolet radiation emitted by the star core.
As the atmosphere moves away from the nucleus of the nebula, it goes out and dissipates in space. Planetary nebulae thus contribute to enriching the interstellar environment with carbon, nitrogen and oxygen. These objects come in two "models": the protoplanetary nebulae that only reflects the light of the star to transfigure itself into the white dwarf and the planetary nebulae when the surrounding gas begins to emit light.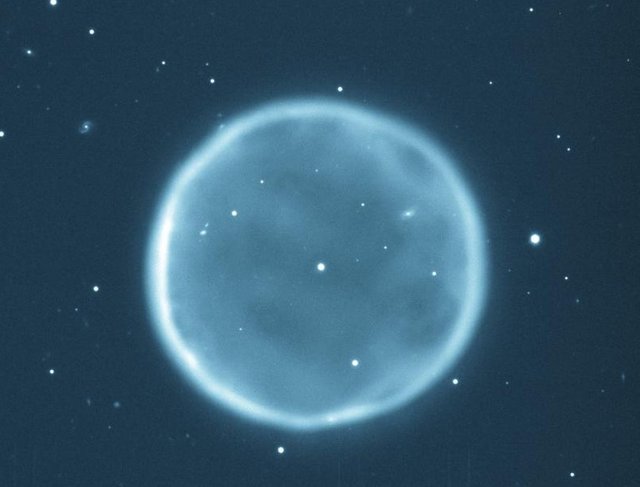 Abell 39, a classic planetary nebula. The luminous sphere is composed of the atmosphere of the central star. Photo: WIYN / NOAO / NSF
Abell 39, a classic planetary nebula. The luminous sphere is composed of the atmosphere of the central star. Photo: WIYN / NOAO / NSF
A planetary nebula has an average of 1 light year in diameter, the gas being very rare (1000 particles per cm3). So far, 1500 planetary galaxy nebulae have been discovered. Taking into account the average expansion velocity of a planetary nebula, it is estimated that they can be seen for 20,000 years, which is why so few are observed.
An interesting problem is the form of planetary nebulae: in the simplest case, we should have a sphere of gas that surrounds the nucleus of the former star. However, most objects of this type have very different shapes: multiple layers, lobes or elongated shapes.
The closest planetary nebulae are: Sh2-216, about 420 light years, PN G069.8 + 31.9, 550 light years, HDW4, 680 light years, NGC 7293 (Helix Nebula) at 700 light years, and PHL 932 to 970 light years. The distance to the planetary nebulae is measured very hard, the above having errors of +/- 100 light years. For a list of planetary nebulae up to which the distance was measured
The age of the galaxy
The latest studies show that our galaxy is 13.6 billion years old, being almost as old as the Universe. This age was estimated by studying the abundance of the berilium chemical element in globular globe stars NGC 6397.
Galactic Neighborhood
Around our galaxy, orbits several other small galaxies, called the galaxy's satellites. These galaxies are dwarf galaxies, which contain no more than 3 billion stars. The most famous satellites are the Magellan's Clouds, visible to the naked eye in the southern hemisphere. So far (January 1, 2007), 50 satellites of our galaxy have been discovered.
Magellan's great cloud has 20,000 light-years in diameter and is located 160,000 light-years away.
The smallest satellites are: the Carina Dwarf Galaxy, the Draco Dwarf Galaxy and the Leo II Dwarf Galaxy. These galaxies have only 500 light years in diameter.
These satellites, two larger galaxies plus our galaxy are part of what is called the local galaxy group.
The closest 10 galaxies
Canis Major Pitic - 25,000 light years
The star group of the Virgo - 30,000 light years
Elliptical piezo of Sagittarius - 81,000 light years
Magellan's Great Cloud - 168,000 light years
Magellan's Great Cloud - 200,000 light years
Little Bear Pirate - 240,000 light years
The sculptor pitic - 254,000 light years
Draco Pitic - 280,000 light years
Sextans Pitic - 320,000 light years
Pitica din Ursa Major - 330,000 light years
Hello @cristian07!
Since you put so much effort in writing this post, would you consider adding some references and image sources, because it's always advisable to acknowledge the work of those we turn to for information?
That way, your post will gain in credibility as well.
Keep that in mind for your future posts as well ;)
Thank you!
Thank you for the advice .
Hi, cristian07! I just resteemed your post!
I am a new, simple to use and cheap resteeming bot.
If you want to know more about me, read my introduction post.
Good Luck!