The Ethereum Casper protocol: Vitalik’s vs Vlad’s protocols

Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH), two of the largest blockchains in the world today, face several setbacks in their quest to mass adoption.
One of the issues raised on the inefficiencies of the two blockchains is the energy-intensive proof of work (PoW) consensus mechanisms that the blockchains use. The latter blockchain, however, has a plan to switch to the proof of stake (PoS) consensus from the PoW. The development community behind Ethereum have introduced the Casper Protocol that will ease out the update to staking mechanisms.
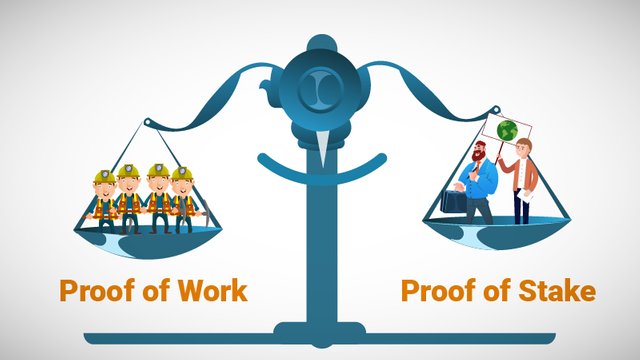
Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake (Image: Draglet)
Table of Content
- Problems facing the PoW consensus mechanisms
- Proof of Stake (PoS) as a solution
- Nothing at Stake problem
- What is Ethereum’s Casper Protocol?
- Casper: The friendly finality gadget
- Casper: The friendly GHOST (Correct by Construction)
Problems facing the PoW consensus mechanisms
While the Proof of work mechanism is used to mine a couple of cryptocurrencies across the board, it causes challenges to the systems and protocols used. Such problems include:
Excessive use of electricity
One of the factors causing outrage on Bitcoin and other PoW coins is the energy-intensive mining process of these cryptocurrencies. The massive amounts of energy required to mine cause the system to be inefficient and slow in some cases. Furthermore, these miners are known to destroy the environment due to excessive energy consumption.
Less decentralization
Proof of work requires massive amounts of energy and heavy mining rigs for users to be able to profit. The process requires huge amounts of cash to acquire the fastest connection speeds, optimized mining rigs, and ASICs. This makes the mining process only viable to a select few hence killing the dream of total centralization among the PoW coins.
As seen in the figure above over 65% of the total hashing power on the Bitcoin network is owned by the top 5 mining pools. Ethereum mining pool distribution is no different (actually it surpasses Bitcoin) as the top 5 mining pools own over 75% of the total hashing power on Ethereum.
Security concerns
The huge mining pools also pose a threat to the overall blockchain as these players can gang up and launch a 51% mining attack.
Proof of Stake (PoS) as a solution
The PoS consensus mechanism allows users to stake some amount of Ethereum in order to validate a block. The user’s staked amount is placed on a bet on the most likely block to be validated and added to the chain. If the chosen block is validated and added then you are paid a proportionate amount to what you had staked in the bet.
“The blockchain keeps track of a set of validators, and anyone who holds the blockchain’s base cryptocurrency (in Ethereum’s case, Ether) can become a validator by sending a special type of transaction that locks up their Ether into a deposit. The process of creating and agreeing to new blocks is then done through a consensus algorithm that all current validators can participate in.” – Ethereum.org PoS definition.
PoS mechanism does not use up excessive amounts of energy while offering users a fair way to earn the block rewards. However, the PoS mechanism is not foolproof as it has its own issues such as the “Nothing at stake” problem.
Nothing at Stake problem
Imagine a scenario where you have two blocks competing to be validated as well as added to the chain, Block A and Block B. As an investor, it would be much safer to stake your tokens on both blocks and wait for the best outcome. If block A wins, you will have won the bet and if block B wins validation on the chain, you still will have won the bet. However, this causes a problem of constant hard forks on the platform as people double vote.
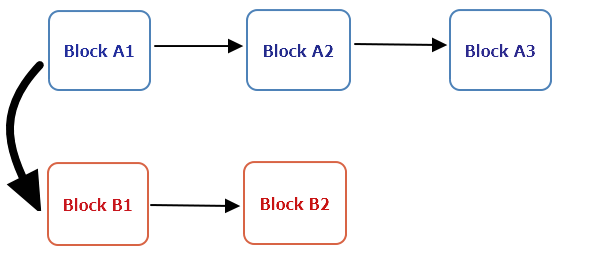
Illustration: Nothing at stake causes a split?
Such an issue is not possible in the Proof of work system as mining requires a lot of energy and resources to validate a block. If a user wants to hard fork, they will require a community behind them. However, miners will not simply switch to the new chain as the old chain offers more profitable and risk-free mining.
The nothing at stake problem pushed the Ethereum development team to come up with the Casper protocol that will be implemented in two faces.
What is Ethereum’s Casper Protocol?

Casper Ethereum logo
The Ethereum Casper Protocol is an update scheduled on Ethereum to solve the issues pertaining to scalability, energy-intensive mining and improve decentralization of the platform. The update was first proposed by Vlad Zamfir, a Solidity developer, back in 2017. The Casper protocol aims to solve these problems through integrating the proof of stake system to Ethereum blockchain.
The Ethereum Casper protocol is set to solve the nothing at stake problem as well as integrate the PoS consensus mechanism to the platform. The protocol is set to be implemented in two key stages.
Ethereum Casper Protocol, the Friendly Finality Gadget (FFG): The upgrade is led by Vitalik Buterin, founder of Ethereum.
Ethereum Casper Protocol, the Friendly GHOST: Correct-by-Construction (CBC): Led by Vlad.
Casper: The friendly finality gadget
The Casper friendly finality gadget, also known as Vitalik’s Casper, will be the first to be implemented On Ethereum. The Casper FFG will be built as a layer on top of the various Ethereum PoW chains such as ethash. The process of adding blocks to the chain uses the PoW consensus mechanism but every 50 blocks is a PoS “checkpoint” where finality is assessed via a network of validators.

Vitalik Buterin (Image:Shutterstock)
Casper: The friendly GHOST (Correct by Construction)
The Casper friendly Ghost CBC (Vlad’s Casper) will differ from how normal protocols work as it will not be fully specified in the beginning. This is how normal protocols usually work;
First, the creator of the protocol has to formally specify the protocols then define the properties the protocol will satisfy. Finally, the creator must prove that the protocol satisfies these set properties.

Vlad Zamfir (Image: Ethereum.org)
However, the Casper CBC protocol partially but formally specifies the protocol and defines the properties of the protocol. Finally, the Casper CBC derives the protocol in a way that it satisfies all the properties that it was stated to specify.
As mentioned above the Casper protocol will solve the problems associated with Ethereum’s scalability, decentralization, and security. With more lobbying for the PoS consensus mechanism, more cryptocurrency/blockchain projects using Proof of work to validate blocks will need to switch up.
Want to know more about it, join us on our Discord and Telegram channels and get into the discussion, or join our 8000 member community on our ICO DOG Investment Platform:
Discord: https://discord.gg/d4EpnZc!
Telegram: https://t.me/ICO_DOG_POOL!
ICODOG: https://icodogpool.com/! ; https://icodog.io/
You can also find the original article on our website here: https://icodog.io/analysis/the-ethereum-casper-protocol-vitaliks-vs-vlads-protocols/
To listen to the audio version of this article click on the play image.

Brought to you by @tts. If you find it useful please consider upvoting this reply.