Business Models Explained
(as in Untamed Potential)
New Venture founders throw around several terms when discussing their ventures and planning for success. One of these terms is “Business Model”. It is one of those things we recognise but aren’t really able to define. Michael Lewis goes further by saying that business models are like art in his book entitled “The New New Thing: A Silicon Valley Story”.
In fact, several different definitions and interpretations have been provided, which doesn’t really help people who are new to the subject.
Founders (as well as any businessperson) must understand what a business model is, which one works best, and why, and how to identify if her/his venture has the right one. This will have a huge impact on the overall success of the venture.
I argue that starting a venture is and endeavour that is built upon solving a real problem (or problems) for your customers. Customers must need what you are selling and what you are selling must solve their problems. Even though being the basis upon which all ventures are built, ensuring a problem-solution fit is only the beginning.
Another key ingredient to the creation of a new venture is to know how you will make money and that is why founders must be able to develop a business model for their venture. A business model is at the core of the sustainability of any successful venture and is essential to prove the worthiness for future investment.
What is a Business Model?
Business models articulate the problem being solved, the solution itself and why it works better than competing ones as well as the costs incurred to create the asset customers buy, for a certain price. Another way to put it is that a business model describes the way in which an organisation creates, delivers and captures value.
BUSINESS MODEL IS A DESCRIPTION OF HOW A COMPANY MAKES MONEY.
Thus, A business model is essential in supporting the viability of a company (or a product) since, if efficiently communicated, it explain how the solutions offered add and create value for customers and company alike.
For a business model to be successful it must only be able to collect more money from customers than it costs to create the offering (aka profit).
Why is it different from Business Strategy?
For entrepreneurs it is important to understand the difference between business model and strategy, commonly confused. I must admit that the scientific community does not agree on this distinction. Nevertheless, for entrepreneurs I find that these nuances are not relevant at all.
In this context, I argue that the real of business strategy once you start comparing different business models. Joan Magretta provides enlightening insights in this when stating that a business is a description of how a business runs, but a competitive strategy explains how a venture will do better than its rivals.
OFFERING A BETTER BUSINESS MODEL IN AN EXISTING MARKET OR OFFERING AN EXISTENT BUSINESS MODEL TO A DIFFERENT MARKET ARE EXAMPLES OF INNOVATION.
A simple way to understand this difference is to think of a business model as the description the value creation of a venture in isolation, while strategy focuses on ensuring that this value is not redundant in the market place.
Developing a business model consists of defining the business logic of a venture at a strategic level. On the other hand, its implementation is, mostly, an operational issue.
BUSINESS MODELS ARE A PART OF BUSINESS STRATEGY.
As an entrepreneur one’s focus is to gain sustainable competitive advantages over the competition. This can, most definitely, start with the business model.
Creating a Business Model
At this point it is quite clear that a business model is key in starting a venture. Creating a business model from scratch consists of two main activities:
Business Model Design
A sketch of an initial business model mustn’t take more than 30 minutes to create. It consists of a picture of the current understanding of the founder regarding the venture’s possible business model.Business Model Development
Based in the current sketch of the business model, a validation strategy must be put into place in order to understand which are the riskiest assumptions, review them and adapt the business model.
I will further develop the business model development process on a future article regarding the Business Model – Market Fit.
Components of a Business Model
Simply put, all business models are made up of three components:
- Everything it takes to make something – product, service or platform.
- Everything it takes to sell it – marketing, distribution, processing sales, etc.
- How and what the customer pays for it
Independently of the format used to present a business model, it must communicate these three components.
How to present and communicate a Business Model
There several different framework with which one can create and present a business model, developed by scholars and industry professionals. From my understanding there is no such thing as the best framework. It is all a matter of context.
Some of the most used models are, for example, the Environment-Strategy-Structure-Operations (ESSO) Business Model, Business Reference Model, Industrialisation of Services Business Model, Business Model Canvas, OGSM Model and Lean Canvas.
Given that I am focusing on innovation, entrepreneurship and new venture creation I have decided to focus on two widely known frameworks: Business Model Canvas and Lean Canvas.
Both these frameworks/canvas are quite intuitive and good at helping the user:
- Assessing if the business model makes sense;
- Identifying opportunities for improvement;
- Discussing it with a team;
- Understanding the competitive environment;
- Devising competitive advantages.
Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas is considered to be one of the most comprehensive frameworks. Developed by Alex Osterwalder, it consists of nine parts and is nothing more than an organised way to present one’s assumptions.
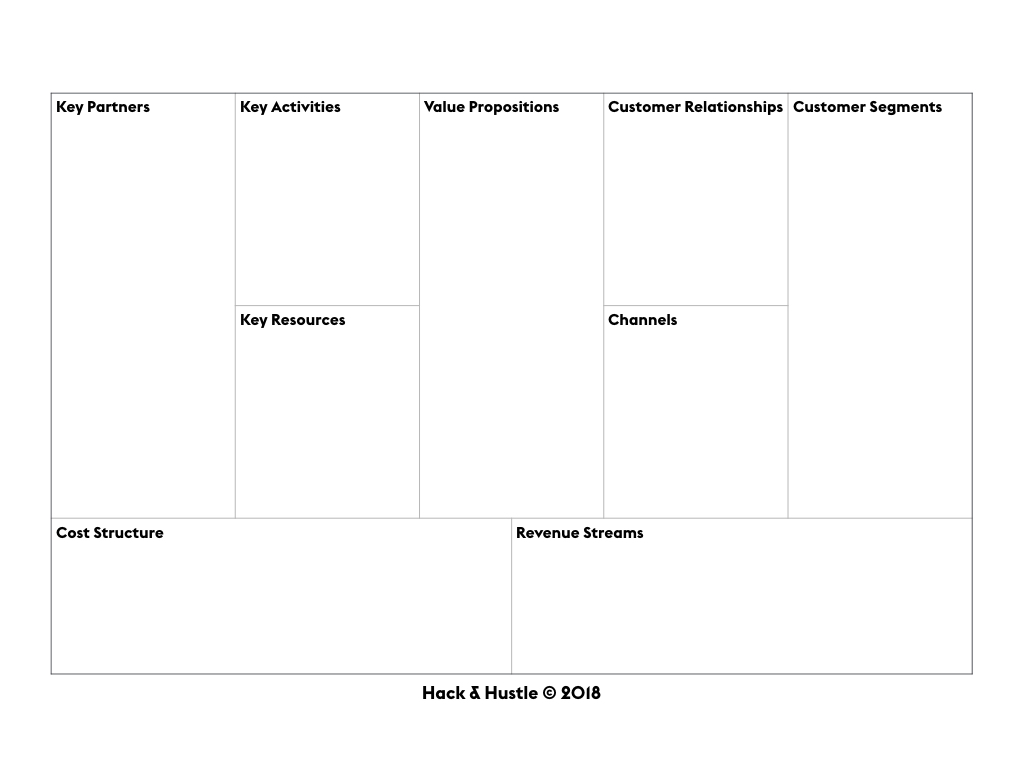
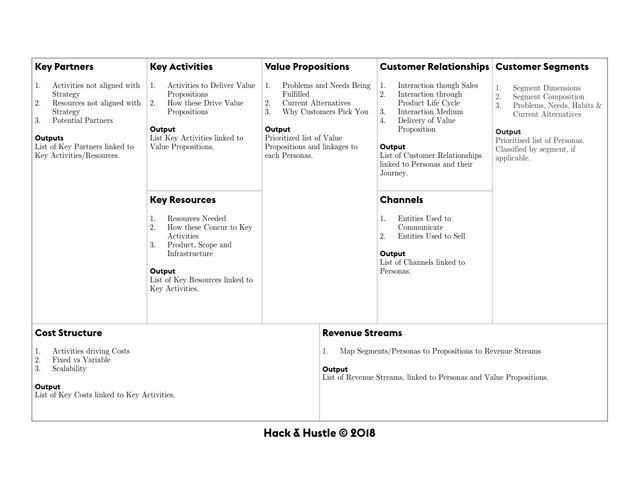
The Business Model Canvas communicates the assumptions about the value proposition, the key resources and activities, customer relationships, channels, customer segments, cost structure and revenue streams. This allows for entrepreneurs to evaluate their business model and critically compare it to others.
Lean Canvas
The Lean Canvas is an adaptation of the Business Model Canvas. It presents several similarities to the Business Model Canvas.
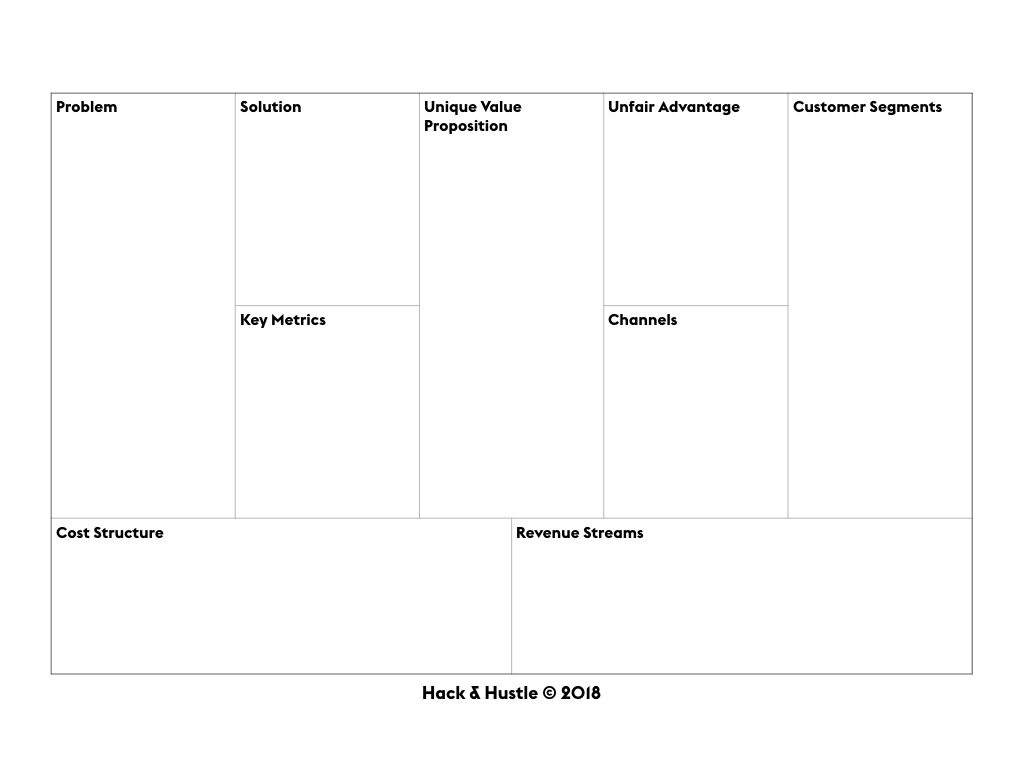
It builds from the need to be fast, concise and effective and, therefore, is very much applicable to entrepreneurs, innovation and new venture creation. It intends to be extremely actionable and entrepreneur-oriented. So much that it ends up being quite self-explanatory.
Customer Value Creation
The Unique Value Proposition (UVP) creates value for the customers. In order to create it, one must understand the customer and their problems.Customer Value Delivery
The solution delivers the value to the customers and customers find this solution through the channels. The cost of delivering the value is captured on the cost structure.Customer Value Capture
By anchoring a pricing model to the value created one defines the process of capturing back the value created through the revenue streams.
Examples
At a very basic level a business model consists of making something and selling it directly to customers, whilst making a profit. Nowadays, a lot more creative is needed. Competition is fierce, global and ever-changing.
Entrepreneurs might feel tempted to create a completely innovative, previously unseen, business model. In some, exceptional, cases this might actually be a good strategy. Nevertheless, investors might perceive this as an unproven way to try to make money and will most likely not trust its ability to bring a return on an investment.
From all the already proven business models entrepreneurs must figure out which one is the best for their venture. In the extraordinary case where none of these apply, then there is the need to develop something completely new from scratch. Considering and, eventually, combining a number of business models can be relevant since it allows to derive revenues from several different sources at different stages of the product life cycle.
I have developed an extensive list of proven business models used around the globe by several successful ventures. Download it here for free!
For help in developing your business model feel free to leave your comment to ask for a more detailed explanation of a specific issue. If needed I am happy to write a more detailed article on any specific framework. By the way, don’t forget to share this article with your network and other potential future entrepreneurs.
I help entrepreneurs in building companies that sell stuff people actually want. Feel free to reach out to me. Refer to this article for a special offer on a one hour consultation.
Congratulations @davebcs! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Do not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!