SLC | S21W2 | Costs for entrepreneurs - Cost elements.
Hello friends!
Welcome to my 4th participation for the week. Cost still happens to be one vital element that plays a role in our entrepreneurship goals. We cannot talk about profitability, performance, and growth without the strong input of costs. Let's get started.
 |
|---|
Cost is an integral element in financial accounting, which helps determine effective reporting and analysis of financial performance in any given organization. The financial account helps decipher the entire financial health of a company's overall growth. Let's look at it's correlation with financial accounting using the following;
Measurement of Cost: In financial accounting, costs are primarily considered by what is entirely considered and out while rendering a service of product production. If A, B, & C cost is required to initiate and finish product X, then financial accounting would consider all these cost implications for product X for its financial statement.
Expense Recognition: Notwithstanding that costs could be referred to as investments as they are those costs put in for the production of product X that help generate revenue, they could also be considered as expenses in financial accounting. Costs are simply those incurred expenses and, at this time, considered reported alongside revenue in financial accounting for purposes of determining profitability and performance.
To Determine Budgeting and Forecasting: This could only be accurately done by previous data showing trends and possibly recent happenings. Costs help in ensuring adequate budgeting and forecasting by aligning with all factors of production, including possibly inflationary trends.
To Generate Profitability Analysis: During income statement analysis, cost plays a vital role in understanding how profitability is generated through cost-net income analysis.
During Decision-Making: This is one leverage we get from financial accounting presentations. A collection of all indices including cost variables,
products and competition, available history data, current trends, and inflation help in effective decision-making.
 |
|---|
Each time cost is mentioned, it is best to align ourselves to knowing these vital components that make up the term cost, ¹Fixed and ²Vaibale costs. Let's give a little meaning to these elements for clarity.
Fixed Costs
As the name implies, these are costs that are constant irrespective of other factors of production. The activities of other factors do not alter their costs. In a typical company that is into production, production volumes, high or low services rendered, etc, do not distort the already fixed costs. Their business activities do not influence its cost at any time.
Examples:
Office Property Rent. This is paid irrespective of business trading volume and transactions done over time. It comes with a fixed price.
Salaries. These are remuneration packages.to workers/employees and does not fluctuate due to business activities.
Depreciation. Purchasing assets or machinery is done on a one-off basis, and the cost of these assets is spread all through their useful production cycle.
Variable Costs
In contrast to the fixed cost definition, variable costs are not constant but rather change as business activities demand. When the production line increases, we find changes in costs. Therefore, we have variations or fluctuations observed with overall business activities as they derive their cost from there.
Examples:
Raw Materials: Materials used during increased production activities due to volume demands would also increase costs.
Sales Commission: Due to the increased volume of production, more volume sales are expected, and this also means more commissions for sales staff commissions from increased volume traded.
Hourly Wages: More production line entails more hourly engagements required. Overtime and longer working hours entail more hourly wages.
Simple tabular representation:
| Fixed Asset | Variable Asset |
|---|---|
| Rigid and constant over time | Flexible and changes |
| Not influenced by business activities | Influenced by business activities |
| Not directly tied to factors of production | Directly tied to production factors |
| Need simple forecasting to determine through decision making | Require an effective analysis for decision making |
| Examples are Rent, Salaries, and Depreciation | Examples are Raw Materials, Commissions, and Hourly wages |
 |
|---|
In this case, we will look at a real-life situation of a company called "Evangel," which produces bread of all types in the neighborhood. There are some direct and indirect cost elements involved in the production cycle.
Flour: Flour is the primary raw material for the production of bread.
Packaging: This serves as the face of the brand. It includes the bags and labels used for packaging bread.
Workers (Permanent/Contract): Salaries and wages for employees
Quality Control Staff: the use of staffers to achieve the entire production process.
Utilities: These are essential costs like Electricity, Water, Oven, etc
Depreciation: The cost of machinery (e.g., roasters, grinders) spread over its useful life.
Rent: Monthly lease payments for the production facility.
- Staff Salaries
- Insurance
- Pensions
- Machinery and Equipment
- Transportation Costs
- Sales Commissions on Target achievements
- Raw Materials
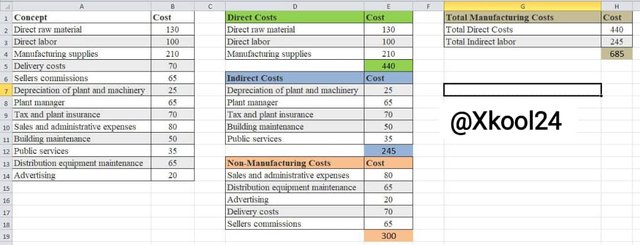
| Concept | Cost |
|---|---|
| Direct raw material | 130 |
| Direct labor | 100 |
| Manufacturing supplies | 210 |
| Delivery costs | 70 |
| Sellers commissions | 65 |
| Depreciation of plant and machinery | 25 |
| Plant manager | 65 |
| Tax and plant insurance | 70 |
| Sales and administrative expenses | 80 |
| Building maintenance | 50 |
| Public services | 35 |
| Distribution equipment maintenance | 65 |
| Advertising | 20 |
It is requested to separate direct costs from indirect and non-manufacturing costs and also to calculate total direct and indirect manufacturing costs.
You can present the example using Google Sheets.
 |
|---|
My Responses
- Direct Raw Material: 130 steem
- Direct Labor: 100 steem
- Manufacturing Supplies: 210 steem
Total Direct Costs: = 440 steem
- Depreciation of plant and machinery - 25 steem
- Plant manager - 65 steem
- Tax and plant insurance - 70 steem
- Building maintenance - 50 steem
- Public services - 35 steem
Total Indirect Costs = 245 steem
- Delivery costs - 70 steem
- Seller's commissions - 65 steem
- Sales and administrative expenses - 80 steem
- Distribution equipment maintenance - 65 steem
- Advertising - 20 steem
Total Non-Manufacturing Costs = 300 steem
Calculating Total Manufacturing Costs
- Total Direct Costs: 440 steem
- Total Indirect Costs: 245 steem
Total Manufacturing Costs = 685 steem
Thank you for this hands-on task. It was worth the time put in to create this piece. I will invite @chant, @wilmer1988, and @stef1
💯⚜2️⃣0️⃣2️⃣4️⃣ This is a manual curation from the @tipu Curation Project
@tipu curate
Upvoted 👌 (Mana: 5/6) Get profit votes with @tipU :)
Greetings @xkool24
1.- You have shared the relationship between costs and accounting, these predict and/or deduce situations, which will serve to make business decisions.
2.- You have mentioned the differences between fixed and variable costs. Each of them impacts the production or manufacturing of products in a different way, but they always impact the performance of the company.
3.- You have shared a real case to present the cost elements. It is important to keep in mind that packaging is considered a direct cost, if the product ends up packaged at the end of the process, for example such as the package of rice, flour, if the bag is independent, it should be considered as an indirect cost.
4.- You have developed the proposed exercise in an acceptable manner. It is important to differentiate direct materials with manufacturing supply (general), the first should be considered direct cost, and the second indirect.