Discuss about germs - episode-7

The super-bug antibiotics that do not cease, the dead brain scientists found in another bacterium!
Antibiotics: The way to prevent super-bugs
In the previous episode, we discussed how some special bacteria developed a class enzyme called beta-lactamase (resistance to antibiotics). These bacteria are therefore called Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria or Super-Bug.Super-bug-damages the effectiveness of penicillin's antibiotics through the reaction of hydrolysis. As a result, the beta-lactam antibiotics (penicillin's antibiotics) are not able to cure diseases caused by these bacteria.
Recently, the US Health and Disease Prevention Department (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) data released through late Sunday night that strepatokakkasa (Streptococcus pneumoniae), Mycobacterium (Mycobacterium tuberculosis), staphailokakkasa ( Staphylococcus aureus), entaro kakkasa (Enterococcus), klasatridiyama ( Clostridium botulinum, listeria monocytogenes, etc. Some deadly bacteria have reached the level of super-bugs.
Now the question is what is the way to get rid of these super-bugs?
Since the discovery of beta-lactamase, scientists began to study how to find ways to prevent the antibiotics destroying the enzyme. After a series of experiments, a bacterium called Streptomyces clavuligerus is the solution to the super-bug problem.
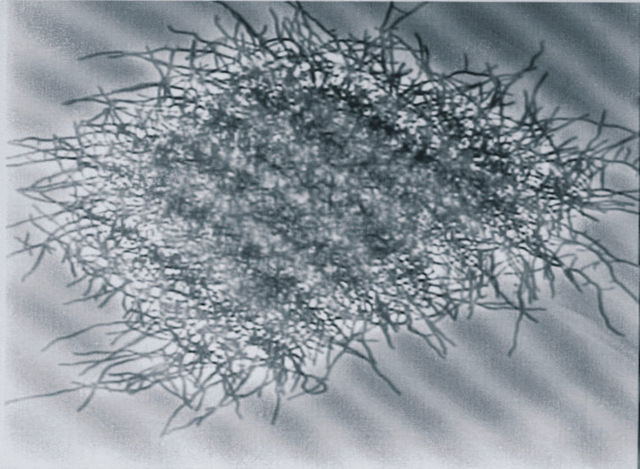
Streptomasis clavuligerous bacteria, from which the solution to the super-bug problem is solved
This gram-positive bacteria (easily dyed in gram dye) creates some chemical compounds at various stages of their metabolism process, which have a structural similarity with antibiotics. Scientists from Streptomasis Klavulijeras have found around 20 such compounds, Clavulanic acid is one of them. Many research by scientists has shown that the beta-lactamase enzyme does not work in the presence of this Clavulanic acid. So it is possible to kill super-bugs by mixing Clavulanic acid with beta-lactam or penicillin antibiotics.
Many times, if doctors do not work in antibiotics given to doctors, they give our second generation or second-generation antibiotics. Never mind, at first, maybe he gave us Amoxicillin. Let's say it is not a good thing, the next time he prescribed the co-amoxiclav or Augmentin. Co-amoxiclav or Augmentin is the second generation antibiotics that contain clavulanic acid with beta-lactam or penicillin antibiotics. And there is a great deal of action against super-bugs .
The solution to the super-bug problem is from a bacterium called strepomatosis clavulgeresus.
How does this Clavulanic acid work?
Clavulanic acid is very similar to penicillin. However, it does not react directly with penicillin-binding-proteins even though there are beta-lactam rings. So clavulanic acid is not antibiotics.
Interestingly, the bacterial enzyme beta-lactamase the structural similarity to the penicillin family of antibiotics can not distinguish with the Clavulanic Acid (remember the Molecular mimikri?). And so when the Clavulanic acid is mixed with antibiotics of the penicillin group, beta-lactamase enzymes of bacteria, beta-lactam antibiotics and Clavulanic acid react with chemical compounds in the two compounds. Scientists have found that tremulous adverse reaction to beta-lactamase stimuli with Clavulanic acid is much more. Because of this, Clavulanic acids and beta-lactamas are composed of chemical compounds, making chemical compounds very stable. As a result, the inactive enzyme beta-lactamase fall .
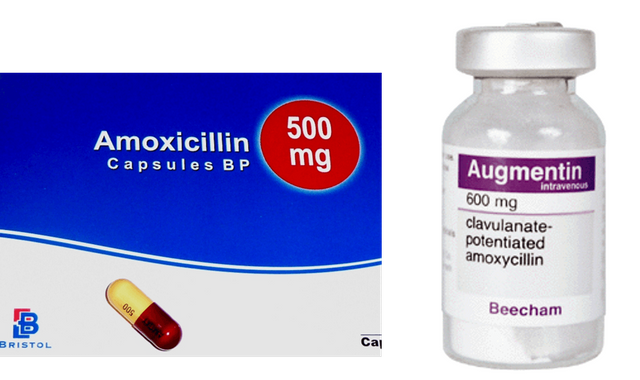
Augmentin is the second generation antibiotics, which contain clavulanic acid with antibiotics of
beta-lactam or penicillin.
When a chemical molecules react with enzymes in the enzyme that destroys the effectiveness of the the chemical molecule "suicide inhibitors" (suicide inhibitor), and such chemical reactions are called "Suicide inaekatibhesana " (suicide inactivation) is called. In the presence of clavulanic acid, so beta-lactam antibiotics became effective as before.
One question may come to mind, Streptomasis clavulgeresus is a type of bacteria, then how can it be found in their cell compounds of all chemical compounds (eg clavulanic acid) that are similar to the structure of antibiotics?
About 350 million years ago the bacteria came into this world. The emergence of eukaryotes was much later. So seeing the history of evolution , it is understood that the survival of the bacteria itself was the beginning of the struggle to survive. For this reason, many bacteria produce some chemical compounds that kill other bacteria. Later, fungal, protozoa and other eukaryotes have emerged, and among them, various chemical resistant bacteria have been found. Such a fungus penicillium, Scottish scientist Alexandre Fleming found the first penicillin antibiotic in 1929.
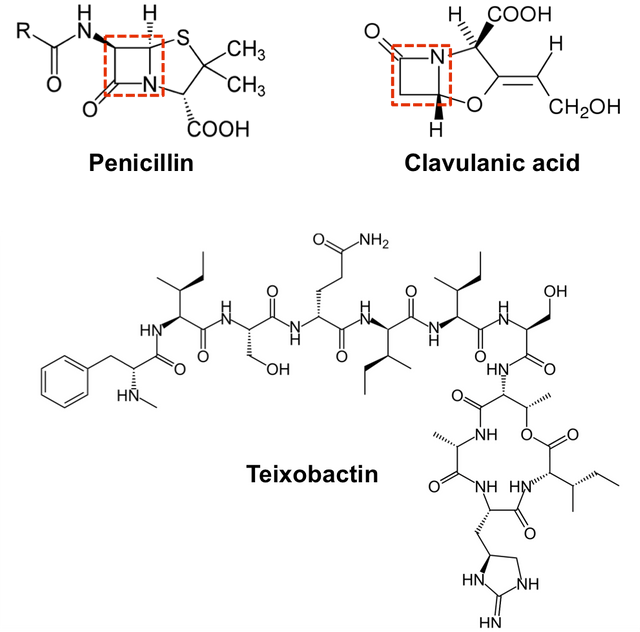
To be honest, scientists now realize that the best way to deal with bacteria is by finding other bacterial resistant chemical compounds from other bacteria, fungi, and protozoids. The science journal Nature 1 this topic, a research paper was published in the soil mixed with the various small bacteria and other single-celled or bahukosidera body of scientists from all the chemical compounds found (for example: Teixobactin) whose use in the near future, we will have byakateriyadera against the more difficult We can build resistance measures.
So far we have discussed mainly the beta-lactam-class antibiotics and their functioning. It is said that this class of antibiotics is successfully applied against Gram-positive bacteria. Because there is a layer of external cell screen outside the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria. The possibility of beta-lactam antibiotics to react with penicillin binding proteins (PBPs) by passing this layer is very low. Besides, the cell wall gravity of the gram-positive bacteria is very strong and thick, so its role is very important for cell protection. Cell wall gram-negative bacteria is much slower than that, and for their protection, this cell wall is outside the cell wall. So beta-lactam antibiotics are much more effective for Gram-positive bacteria. What is the way to get rid of all these deadly Gram-negative bacteria in Acinetobacter, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Nisseria (Neisseria gonorrhoeae)? What do we use antibiotics against them? Gram-negative bacteria - is a super-bug?
To learn more about this, keep an eye on the next episode.
Source of writing:
Brilliant writing......obosso ami sob pori ni. Ok keep it.
really great information my friend... thanks for sharing... You are sharing some really great things on how to avoid germs...
I will try. Thanks for your comment.
I wonder if those superbugs are sensitive to clay.