Discuss about germs - episode-6
People and bacteria fight: Super Bug vs. antibiotics
In the previous five episodes we discussed about the habitat of germs, their different types, diversity, etc.Although we are small in size, we have learned a lot about the complexities of structural and also about the extra protection of their cells that are much more organized. The main difference in the outer coating of bacterial cells from advanced Eukaryote is that outside the bacterial cells, there is a strong cover of the cell wall besides the cell-screen.Bacteria can protect themselves from the turgor pressure, and in the adverse environment due to the presence of this cell wall. If for some reason the bacterial cells lose the defense force, then the bacterial cells die due to the pressure of the circulatory pressure. And for this reason, most of the antibiotics used in daily life are aimed at bacterial cells cell walls.
In this episode we will discuss how antibiotics spoil the structure of the cell wall and some 'super' bacteria will fight against it.
A common problem such as chills, raging, or an epidemic like plague, hooping cough is the solution - antibiotics!
When our body is bad, when we go to a doctor, they often ask us to eat antibiotics. A common problem such as chills, raging, or an epidemic like plague, hooping cough is the solution - antibiotics! Do you really want to know that this antibiotic is a magic that does not find all the dangerous bacteria to escape?
Before we can learn about this, we will get rid of the previous episode of socks. In the previous episode (episode -5) we discussed that NAG and NAM are made up of two peculiar sugars, the Peptidoglycan polymer. Numerous Peptidoglycan polymers combine together the bacterial Periplasm into a three-dimensional mesh cell wall. NAG and NAM, these two sugar molecules are made up of polymers, and these polymers work together to form three-dimensional decorations, very important group of proteins or enzymes. They are called penicillin-binding proteins or PBPs.
Can you guess why are they called penicillin-binding-proteins? The reason is very simple! Any antibiotics of the penicillin or penicillin species actually react with these enzymes and destroy their function. So these proteins are called penicillin-binding-proteins. Because of this process the cell wall of the bacterial cell is not formed and the cell is damaged.
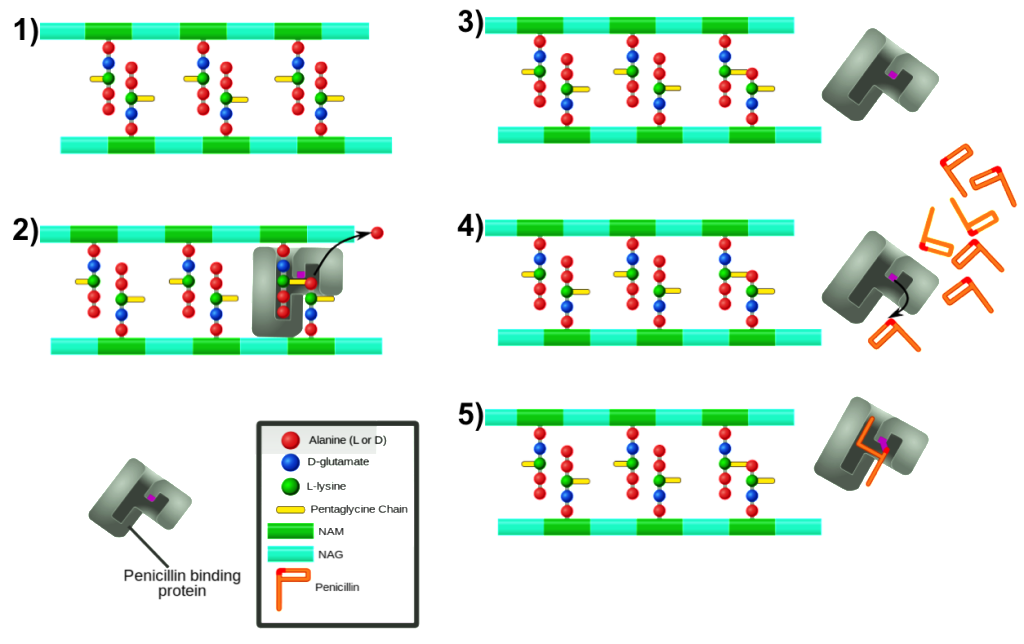
The role of PBP is essential for the survival of bacterial cells. Any antibiotics of the penicillin or penicillin species
react with these PBPs and waste their functioning. Click to see better resolution.
PBP is present in almost all bacteria and their role is essential for the survival of bacterial cells. Therefore, many antibiotics of the penicillin group (Amoxicillin, Cephamycins, Carbapenems, Flucloxacillin etc.) are often given by doctors to remove our bacterial-caused disease.
You think, the diameter of the diameter is gone! The bacteria have been quite seized. The weevils came to fight with us! Actually everyone thought so. In 1929, Scottish scientist Alexander Fleming published the concept of antibiotics for the first time in the Journal of Experimental Pathology. After that, the use of penicillin began to be used to repair bacterial diseases. There are many references to the use of penicillin to cure the wounded soldiers in World War II.
The problem arose in 1967. In one village Papua New Guinea (then in Australia), penicillin is not working on one patient's streptococcus infection (Streptococcus Pneumonia). At the same time in Guatemala, the same trend was noticed in the case of another bacterium named Shigella (Shigella spp.). After seven years, the same phenomenon is repeated in America - in other types of bacteria called Neisseria (Gonococcus). In the nineties, many bacterial infections were found in different countries and can not be rectified with the usual penicillin-class antibiotics. These bacteria have been named Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria or Super-Bug!

Super-bugs make an enzyme called beta-lactamase. This enzyme breaks the beta-lactam ring of antibiotics
through the reaction of hydrolysis.
You are sure that these bacteria have PBPs. Again, their cell wall also has a special need. Why penicillin is not working? Actually we will seize them as easily as I thought it was not so easy. Because bacteria have survived for approximately 360 billion years in a very hostile environment, their adaptation capacity is very high. In this case, they have developed a resistance mechanism for penicillin.
Bacteria have survived for many millions of years in a very hostile environment, so their adaptation capacity is very high
What is that arrangement?
Super-bugs have developed a special type of enzyme called bita-lactamase (β-lactamase). This enzyme breaks down the beta-lactamase ring (β-lactamase ring, red color in the top image) of the main structural unit of the penicillin's antibiotics through the reaction of hydrolysis. Due to the loss of beta-lactam ring, penicillin 1 can not react with PBP or penicillin-binding-proteins . As a result, the function of antibiotics is damaged and there is no harm in the normal formation of bacterial cell wall. Bacterial infection continues!
What is the way to get rid of these super-bugs ? Scientists took action to fight them? Watch them in the next episode to know them.
will continue...
Writing source: