The computer storage Memory
Both memory and storage are data containers for our computers. People often confuse memory for storage and storage for memory, this could be because both storage and memory are measured using the same unit. When we talk about computer memory, we're generally referring to the Random Access Memory. I believe anyone reading this piece is doing so using a web browser, either in the form of application or in the form of a program. If we suddenly pull out all the power sources in our computer, I can predict with 100% accuracy that the computer operations will be brought to an abrupt end with the system suddenly shutting down.
Image source Pxhere. CC0 public domain license
When we replace the power supply and power on the system, with a successful boot, we would discover that the system will loose all its previous operations and would likely land us at the desktop or at the starting window. This is because, computer memory looses its content(s) on the removal of power source(s). We can not say the same for computer storage. When we successfully complete a web download or file transfer and immediately remove all the power sources, after a successful boot, the files we downloaded would still be there. This is one of the basic difference between storage and memory.
Computer Memory
The computer memory is generally a workspace for computer processor. It is a temporal space for keeping data used by computer programs and these data are acted upon in real time. The computer memory storage and the computer storage works hand in hand in the sense that when there’s a need for future use of the data being processed by programs in the memory arises, such data is pushed to the storage which maintains these data even when there are no power sources.
Initially, computer memory is collectively called RAM because access is not sequential but random. A random access to memory simply means that any memory location can be referenced at the same speed without a need to make reference to a location before or after the memory location of interest. But does that mean that the Read Only Memory (ROM) access is not “random”? Does that also mean that the contents of the ROM would be lost with a lost in power supply? Well, the initial perception of the computer memory as just RAM was a bit misleading.
A little tale about price of computer memory. Back in 1996, the prices of computer memory chips were so costly that a physical memory chip costs way more that the same price in gold. A computer memory chip at early 1996 costs around 40 dollars per megabyte making the price of most modules to be around 650 dollars because the capacity of these modules were around 16 megabytes. This somehow managed to get the attention of armed robbers making these chip manufacturers a constant target.
The theft of memory chips were very difficult to curtail since these chips are not easy to trace and their demands are very high and as a result, these companies spent a whole lot of their income on physical security personnel. This trend didn’t proceed for long as the price of memory chips crashed in less than a year, this was around late 1996. The price dropped from 40 dollars per megabyte to about 4 dollars per megabyte which was about 75% price drop! That was abrupt and impressive and prices of computer memory kept on dropping even to the point of getting 1 megabyte of memory for 50 cents in early 1998.
The Rambus Dynamic Random Access Memory. Image source Wikimedia. Creative commons license
Though the price reduction trend did not continue, it never went as high as the initial price of 40 dollars per megabyte. This was partly caused by Intel Corporation. In early 1999, Intel announced a new and better computer memory, the Rambus Dynamic Random Access Memory which caused a change in taste in computer memory but they failed in providing chipsets for the RDRAM promptly. As a result, many computer memory production company produced many of this RDRAM but there were no system they could fit into and this led to the shortage of the initial memory which was already popular.
With that said, the price of computer memory has greatly stabilized and is presently at its lowest rate with 1 megabyte costing below 8 cents all thanks to the dot-com crash in 2001 which made many chip producing companies go out of business with many merging in order to stay in business. We’re currently trading price with memory lifespan in the sense that present memory chip price at its lowest but with very little lifespan. This is because faster memory chips are easily adopted and these chips are less likely to inter operate with the previous ones.
Take for instance the current trend in computer storage, the solid state drives are quickly being adopted because they’re faster but this type of storage is not compatible with the popular hard disk drive. Hence, a change in your motherboard to one that uses solid state drive automatically renders the old hard disk drive useless. This same analogy is applicable in computer memory with the replacement of DDR 2 with DDR3 and DDR4 memory chips. They’re all not backward or forward compatible.
With this being said, let’s get to know the different types of memory found in today’s computer. They’re of three types which are
- DRAM
- SRAM and
- ROM
Of all these types of computer memories, the one that is user-replaceable is only the DRAM. The rest are on-chip or on-board and are not easily replaced by the user.
The DRAM
The dynamic random access memory is one of the oldest and the most popular computer memory, till date featuring in many recent personal computers. One of the main reason for its popularity is cost, DRAMs are very cost effective type of memory. Also they can accept large number of bits in a small chip area making them a very dense memory.
))
capacitor arrays in DRAMs. Credit: Wikimedia. Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license.
On the component level, DRAMs consists of several microscopic capacitors which uses charges between its plates to indicate bits. But just like most discrete component capacitors, they can lose their charges with time and the same is applicable to the capacitors used in the design of DRAMs. For every action performed in the computer, the contents of the DRAM is modified, the entire contents to be precise. Due to the ease at which the charges in these capacitors can be lost, DRAMs requires constant data refreshing to maintain their contents.
These capacitors are maintained in what is called memory rows. In order to refresh the DRAM, the computer uses what is called memory controllers which is a tiny silver-coated oval shaped component which is usually located beside the memory slot or chip sitting. The computer uses this memory controller to reference every memory rows in the DRAM. For each refresh time, the system pauses its current operation to oversee the operation of the memory controller.
A frequent refresh rate would lead to a better memory but this will result to a slower operating speed. But reducing the refresh rate could cause some of the capacitors in the memory rows to lose their charges since all the capacitors does not have equal charge and discharge rate. This will lead to a condition known as Soft memory error. This type of errors is not due to bad chip or bad semiconductor material rather it is as a result of clocking memory refresh rates below recommended rate and this is usually caused by the user as this can be set in the basic input out system settings (BIOS).
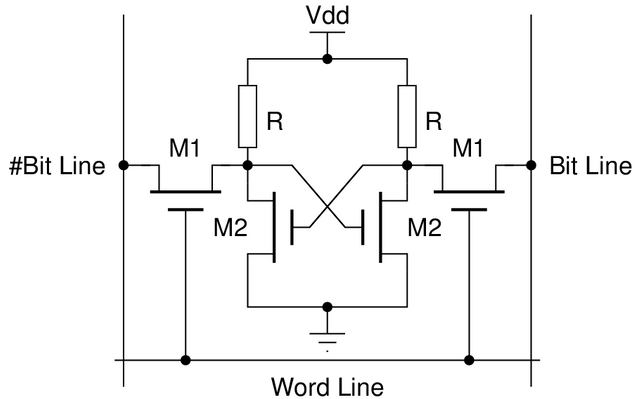
The SRAM
SRAM beats almost all the types of DRAM in terms of speed. The static random access memory gained its name from the fact that memory refresh which is explained above is not needed to maintain data in the memory, hence, the refresh overhead is completely discarded making them the best candidates for modern advanced computers.
SRAMs are also called cache memories and they can be clocked almost at the same speed as the processor memory, the register. Unlike the DRAM that makes use of charges from capacitors, SRAM though not a dense memory uses clusters of transistors, usually six transistors in a cluster, to represent a memory bit. This is the main reason why SRAMs requires no refreshing for data retention though removal of power source(s) still wipes its memory, hence, SRAMs are still volatile memories.
The arrangements of MOSFET transistor to achieve a memory cluster. Image source Wikimedia. Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license.
Also SRAMs are quite expensive when compared to legacy DRAMs and as already stated, the memory bits are in clusters of six transistors making them less dense than the DRAMs which means you need more hardware to realize memory capacities as the DRAMs. Take for instance the physical resources (in terms of size) that you could use to produce a DRAM of 120 megabytes can only produce about 6 megabytes of SRAM making them very expensive.
the ROM
The read only memory just as the name suggest means a type of memory where writing privileges has been totally removed. In other words, you can only read the content of such memories without the ability to change their contents. Unlike the above mentioned types of memories, ROMs are not volatile, i.e. their contents are not wiped out with a removal of power source. Hence, ROMs are ideal for storing information or data that are not meant to be edited, a perfect example of such information is the boot up instructions for our computers.
))
A 1999 bios chip, the computer bios are stored in the ROM chips. Image source Wikimedia. Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license.
ROMs are not to be seen as a standalone memory type, this is because ROMs are also random access memories, in fact, both ROM and RAM are used to store system information just that part of system information that are not meant to be edited are stored in the ROM and made to remain there permanently. Hence, the ROM is a type of RAM.
It is not only the system basic input output system information that is saved in the read only memory, some hardware which require fast boot-time activation like the computer display system also comes with its own specialized read only memories which allows them to boot alongside the computer. This is necessary to quickly load the drivers needed for these system to operate at boot time. Other system that require such boot speed like camera, speakers, keyboard, etc. can have their drivers loaded from the secondary memory once the system boots up.
Conclusion
Many people often refer to the computer storage when they're actually talking about computer memory or vice versa. The computer storage are those cheap, slow and large storage space for data that is mean to be retained with removal of power source. Most computer storage systems are usually user-replaceable. The same can not be said for computer memory.
Computer memories are very fast and volatile storage space meant only for the computer programs and computer processor. The only computer memory the is nonvolatile is the read only memory which is a subset of the random access memory. This post takes a deep look into computer memory system without reference to hierarchy.



Informasi yang sangat bermanfaat kawan, luar biasa.
Terimaksih telah membaca :)
Hello @yandot..
Very educative post, particularly in terms of clarification of the terms "memory" and "storage", which have been very confusing to me that sometimes when I use any I really wonder if it was wrongly used. The SRAMs are also knew to me...
Very detailed article...
Regards
@eurogee of @euronation and @steemstem communities
Thank you for your valuable feedback man!
Regards ;)
good information, many have experienced it.
Thank you for you reading!
if large RAM and small ROM what memory can store a lot of data.
If large RAM and small
ROM what memory can store
A lot of data.
- mattmcguire
I'm a bot. I detect haiku.
While cute, this superfluous comment is considered to be spam, harms the blockchain, and is the reason why we will soon have to pay for comments like this with Resource Credits. The servers that maintain the blockchain are extremely expensive because of comments like this seeking low effort upvotes, so please do not reward this behavior.
Please consider using this link to give a small downvote of 15% or so to discourage these comments.
Any bot like this should respect the community by providing a whitelist to prevent the post in the first place and then provide a way to delete the comment for those who find this intrusive.
Mantap bahasan jih bang, tapi agak sulet bacut bakbta fahami, sabab hana biligual.😂😂😂
Haha gakbisa bilingual di steemstem :D
Leh uga u
Leh lah u
Selamat hari raya idul Fitri yandot mohon maaf lahir batin
Posted using Partiko Android
Iyaa bang , mohon maaf lahir dan batin juga :)
good lesson of basic computer memory. Volatile and non-volatile.
Congratulations! Your post has been selected as a daily Steemit truffle! It is listed on rank 6 of all contributions awarded today. You can find the TOP DAILY TRUFFLE PICKS HERE.
I upvoted your contribution because to my mind your post is at least 25 SBD worth and should receive 103 votes. It's now up to the lovely Steemit community to make this come true.
I am
TrufflePig, an Artificial Intelligence Bot that helps minnows and content curators using Machine Learning. If you are curious how I select content, you can find an explanation here!Have a nice day and sincerely yours,
TrufflePigVery interesting article @yandot, the part that I found more interesting is when the differences between DRAM and SRAM were explained.
I think today everyone should be using SSDs in their computers, in my case it boot the system in less than 10 seconds, the speed is simply amazing.
That is correct man!
Thank you very much man for your valuable comment!