Understanding Earthquake: Why Science Matters?

The tension generated in the crust of the earth, due to its sudden release on the surface, moving or vibrating the surface of the earth is called earthquake. Earthquake is the most devastating disaster of natural disasters, which can lead to loss of human life. Typically earthquake has an impact in a very wide area. Earthquake causes widespread devastation at the same time as well as causing injuries to individuals and their death. Due to the sudden and rapid acceleration of this catastrophe, the public has no time to defend it.
During the last two decades of the twentieth century, there were 26 major earthquakes in various places of the earth, causing an estimated 150,000 deaths of globally. It is unfortunate that even though the result of the earthquake is very broad, so far it has not been successful in accurately predicting it. For this reason some steps are taken according to the possible response to this disaster.

The branch of science under which earthquake is studied is called seismology and scientists studying earthquake science are called seismologists. In the English word 'Sismology', 'Sismo' prefix is the Greek word meaning earthquake. Earthquake measure the magnitude of earthquake and its magnitude is measured. There are several methods to measure the magnitude of an earthquake.
Our earth is mainly made up of four layers, inner core, outer core, mental and crust. Crystals and upper mantle are called lithosphere. This 50-kilometer thick layer is divided into sections, which are called tactonic plates. These tartonic plates shake from their place but when it gets too much, an earthquake comes. These plates can move from place to place both horizontally and vertically. After this, they look for their place and in this case, a plate falls under another.
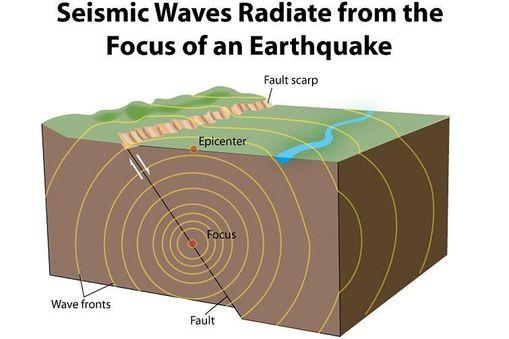
The point at which the earthquake occurs is that the point on the surface of the earth is known as the superposition or the center of the earthquake at the center of the seismic center. The position of overpay is expressed by the latitude and longitude of that place.
There is a slight shock at the time of the earthquake. Then, after some intervals, a wavy or jerky vibration is felt, which is stronger than earlier shock. During small earthquakes the land trembles for a few seconds, but in large earthquakes this period can be more than a minute. During the earthquake of Alaska in 1964, the earth trembled for nearly three minutes.
Due to the earthquake the earth tremor period depends on various factors like distance from excessive, soil condition, height of buildings and materials used in their construction.
Earthquake intensity measurement
The scale of the Richter Scale is used to measure the intensity of an earthquake. This is called the Richter Magnitude Test Scale. Measure earthquake waves on the basis of Richter scale from 1 to 9. The Richter scale scale was discovered in the year 1935 with the help of Benoit Gutenberg, a scientist working in the California Institute of Technology, Charles Richter.
Under this scale, the intensity of the earthquake per scale increases 10 times and the energy released during the earthquake increases 32 times the scale. It means that the earthquake intensity on the 3-Richter scale will increase 10 times the 3-Richter scale at 4 scale. The magnitude of the earthquake on the Richter scale can be estimated from the fact that an 8-Richter scale earthquake can generate 60 million tons of explosive-generated energy.
To measure the earthquake, the Mercalli scale is also used in addition to the Richter. But they measure the earthquake on the basis of strength rather than the intensity. The trend is less because it is considered less scientific than Richter. Several reasons can be responsible for the damage caused by earthquakes, such as poor texture of houses, poor structure, type of land, population settlement etc.
Types of earthquakes
Earthquake can be divided into two main types: -
- Earthquake coming from natural causes, and
- Earthquake from human activities
- Earthquake coming from natural causes
earthquake_diagram2 Natural earthquakes are also called tectonic earthquakes because they are related to the tectonic properties of the Earth. Most of the naturally occurring earthquakes come with fructals. The defect is the crack or breakdown caused by the stir in the crust. These deficiencies can range from several millimeters to several thousand kilometers long. During geology chronology, most of the defects create double displacements.
If the defect is vertical then the prolapse is called the normal decomposition where the rocks on each side make the opposite move. In an inverse error, one end up on the other side. The inverse error of the lower angle is called thrust. When both the edges are relative to one another, the lateral prolapse or rift error is formed.
The tectonic earthquake is again classified into two parts, the inner plate earthquake and the inter-plate earthquake. When an earthquake happens along the boundary of the tectonic plate, then it is called an internal plate earthquake. Most tectonic earthquakes are often of this category. The inter-plate earthquakes come away from the plate and away from the plate boundary.
Earthquakes also occur in the old and more permanent parts of the continent's continental continent.
Volcanic activity in the magma may also be the cause of naturally occurring earthquakes. This type of earthquake is the advance warning of volcanic eruption.
- Earthquake induced by human activities
Human activities can also inspire an earthquake. The process of man-induced earthquake may be due to the removal of oil from deep wells, waste materials in deep wells or any liquid filling, making huge dams containing large amounts of water and destructive incidents like nuclear explosions.
One of the major earthquakes due to artificial reservoirs came in the Koyna area of Maharashtra in 1967. Another notorious human activity due to earthquake has been related to the entry of liquid well into deep well in the Denver area on Rocky Mountains in Colorado, United States.
How are earthquakes Initialised?
According to the EarthQuake Diagram Plate tectonic theory, the outer layer or crust of the earth is made of big and small rigid plates, like the framework (jigsau). Thickness of these plates can be hundreds of kilometers. Probably, under the influence of convection currents, these plates move relative to one another. The earth is divided into many seismic plates. On the difference of these plates, where the plates collide or move away from each other, large earthquakes are found. The speed of these plates is very slow. Most of the strong earthquakes come where the plates meet together. Sometimes it happens that the sides of the plates are stuck in each other, so that it does not move and the pressure arises between them. As a result, the plates move away by giving a huge shock and the earth is tremendously staggered. Due to the vast alterations in this process, earth's crust is bursting.
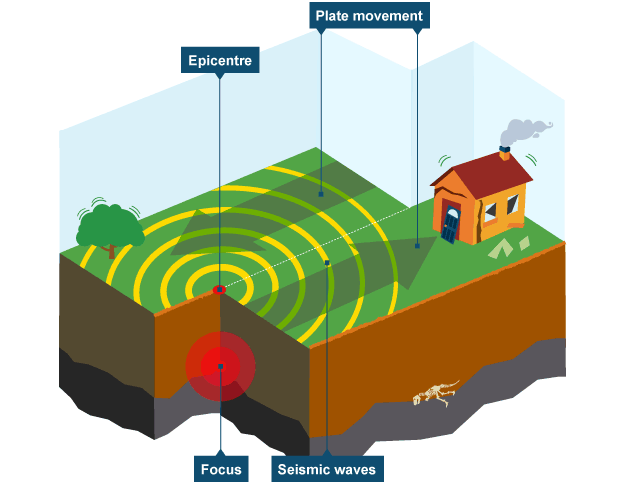
Once the faults are formed in a region, the area becomes weak. Earthquake is a medium of exit from stress, which is usually limited to within the confines of these deficiencies. When the stress inside the Earth is passed to any other location located away from the present defects, then new fractions arise.
How to detect earthquake power?
Magnitude and intensity are two ways to measure the magnitude of an earthquake. The magnitude of earthquake is measured according to the earthquake recorded in earthquake-writing. An earthquake-induced earthquake detector is a device. The magnitude of an earthquake is determined by the maximum dimension recorded in the earthquake-writing and the distance of the equipment from the site of the earthquake.
Richter scale
Based on the magnitude set on the Richter scale, the classification of earthquakes is given below.
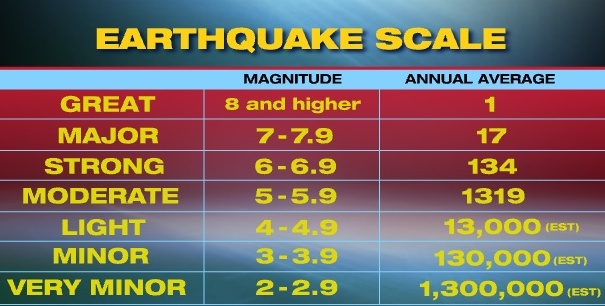
The Richter scale begins with one unit but no end has been fixed, however the intensity of the most powerful earthquake known till now has been measured between 8.8 and 8.9. Since the base of the Richter scale is small, it is therefore ten times more than its unit before its unit. If the Richter scale does not measure the impact of earthquake, this scale determines the power of earthquake on the basis of earthquake-hungry energy based on earthquake.
So far, the maximum magnitude earthquake in India has been measured at 8.7 on the Richter scale, this earthquake occurred on June 12, 1897 at Shillong Plate. The impact of the Richter magnitude is felt in the adjacent areas of the earthquake superficial. The magnitude of the most known strong earthquake has been observed from 8.8 to 8.9 in the range (range).
Earthquake intensity
Measurement of the intensity of an earthquake is done on the basis of the magnitude of the earthquake's impact on people, buildings, and land. The magnitude of earthquake in a particular area is measured by the earthquake on the basis of the force of movement in the earth, which is determined on the basis of variations in the living organisms, humans, buildings, furniture and natural environment. Unlike the magnitude of a specific earthquake, the magnitude of the earthquake depends on the distance of the excessive distance, the depth of the center of the origin, the local land configuration and the type of motion of the prognosis.
Earthquake affected area
Earthquakes can occur in any area and at any time. Most earthquakes occur in the world in the famous Ashwaar region by the name of the Pacific-Cyclical Earthquake Strip. Nearly forty thousand kilometers long, this region is also known as Pacific Fire Ring or Fire Ring.
Scientists have identified three huge areas of earth where more earthquakes than other places occur.
- Area I
The world's first earthquake area is the Pacific-cyclic earthquake strip. Of the total earthquake occurrences occurring on Earth, 81 percent of seismic events occur in this area. Found on the shores of the Pacific Ocean, moving from Chile to north, through the shores of South America, the western coast of Central America, Mexico, America, the Allianic Islands of Japan, the Philippine Islands, New Guinea, South- The West Coast is located in the Pacific Ocean and goes to New Zealand.
- Area II
The second highly sensitive strip to earthquake includes the Alpide area. There are 17 percent earthquakes in the world. This strip extends from Java to Sumatra, Himalaya, Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic area. This is the world's second most earthquake affected area.
- Area III
The third important seismic strip follows the submerged mid-Atlantic Ridge.
Seismic waves
Distraction energy, which is released in large quantities in the form of waves during the earthquake, is called seismic energy. Seismic waves are transmitted with land or its surface. Seismic waves can be experienced all over the world. Physics of seismic waves are very complex. These waves are repatriated and changed from each obstruction transmitted in all directions. These waves, which spread in all directions with the basis of the Earth, are called objects or waves. Apart from these, the waves that are close to the Earth's surface are called dorsal waves.
The mass waves are of two types: the first primary wave or P wave and the second secondary wave or S. wave. Dorsal waves consist of two waves, love wave and Raleigh wave. P waves are the most intense and these waves are supposed to follow S. waves, love waves and Raleigh waves.
- In P waves, the rocks of rocks vibrate back and forth in the medium. We first experience P waves.

- Through the waves of the waves (also called transverse dorsal wave), rocks particles vibrate up and down in the background. S. waves are not transmitted from the liquid.

- When P and S. waves reach the surface then most of their energy can return to the inner part of the earth. Some part of this energy gets reflected from the rocks and the soil, and comes back to the surface.
- Raleigh waves have been named after the scientist Lord Raleigh (1842-1919), who estimate the presence of these waves. These waves give elliptical motion to the particles of rocks, moving above the surface.

- Love waves are named after Augustus Edward Hug Love. Love waves displace the rocks particles vertically towards the direction of their dispersion and these waves have no vertical and transverse component.

Due to P waves, the first vibrations in the buildings are the same. Only after the P waves can the effect of the waves of p waves that pulsate the lateral part of a structure can be experienced. Since the transversal vibration easily damages the buildings with vertical vibrations. So the P waves are more destructive. Raleigh waves and love waves come to the end. While the vibrations of high frequency due to P and S. waves, vibrations with low frequencies are generated due to rallies and love waves. P & S waves are responsible for shaking and bump due to being subtle and fast velocity. Dorsal waves are long and slow and they produce wavy (rolling) effects. Seismic waves vary in different types of rocks. Where the dorsal waves persist for longer periods, the mass waves end in a while.
During an earthquake, loss of man-goods is more due to the fall of man-made cravings and jumping of objects and glass winds. Flexible structures formed on Basehail are less damaged than earthquake than the hard structures formed in loose or loose soil. In some areas, many people may be suppressed by the sloping of soil layers from earthquake with mountain slopes. Due to the large earthquakes, there is tremendous movement on the surface of the earth. Sometimes, due to these, huge waves arise in the sea, which carry away objects located on the edges. These waves increase the destruction caused by earthquakes in general. Often these waves occur in the Pacific ocean. These devastating waves are called tsunami.

References for Text and Images:
- http://slideplayer.com/slide/6242044/
- http://www.sanandreasfault.org/EQS.html
- http://slideplayer.com/slide/6242044/
- https://www.amazon.com/Predicting-Earthquakes-Why-Science-Matters/dp/1432918443
- http://slideplayer.com/slide/4776440/
- https://casualtravelist.com/blog/ecuador-travel-earthquake/
- http://slideplayer.com/slide/6242491/
Support @steemstem and the #steemstem
project - curating and supporting quality STEM
related content on Steemit

This post has received a 0.72% upvote from thanks to: @punjolife.
thanks to: @punjolife.
For more information, click here!!!!
Send minimum 0.100 SBD to bid for votes.
Do you know, you can also earn daily passive income simply by delegating your Steem Power to @minnowhelper by clicking following links: 10SP, 100SP, 500SP, 1000SP or Another amount. (10 SP minimum)
This post has received a 0.31 % upvote from @booster thanks to: @punjolife.
Greetings! I am a minnow exclusive bot that gives a 5X upvote!
I recommend this amazing guide on how to be a steemit rockstar!
I was made by @EarthNation to make Steemit easier and more rewarding for minnows.