"Temples of Abu Simbel: Ramses II and Nefertari" history through time

Abu Simbel is an archaeological place of interest made up of two temples carved directly into the rock. It is located at the southern tip of Egypt, on the western shore of Lake Nasser about 230 km southwest of Aswan. The temples are part of the Open Air Museum of Nubia and Aswan, which was declared a World Heritage Site by Unesco in 1979 under the name Nubian Monuments, from Abu Simbel to File.

Ramses II fought both the enemies of the north, and the south. But his most important battle was that of Kadesh, in Canaan against the Hittites. And although Pharaoh boasted on the walls of Abu Simbel of having won the battle, in reality, it ended with a treaty of peace between the two groups.
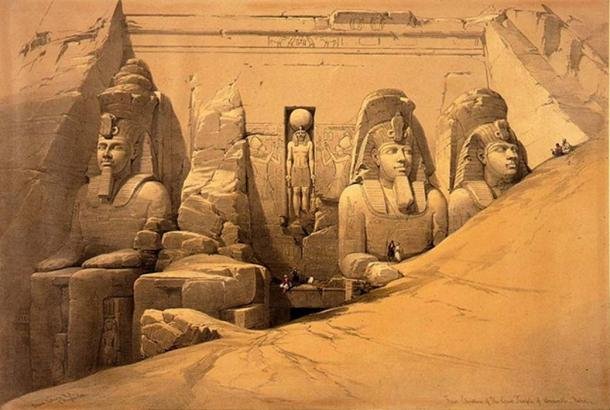

When the ancient Egyptian civilization declined and with the passage of time, the temple was left in oblivion and little by little it was covered with sand, until in 1813 it was visited by the Siuzo Johan Ludwig Burckhardt, who commented his discovery with the Italian Giovanni Belzoni, who in 1817 was able to free access to the temple and loot all valuables he could transport.
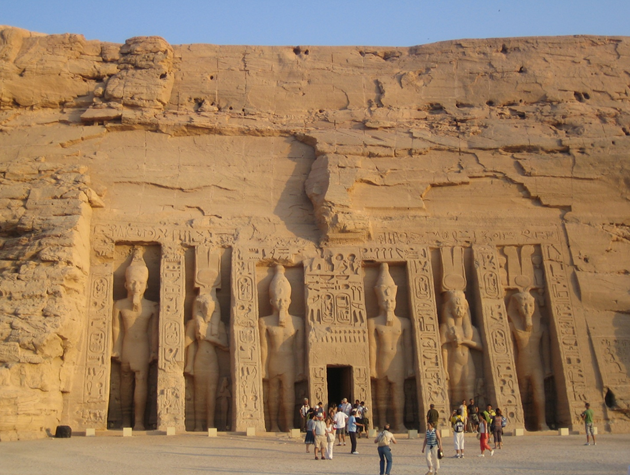
The facade of the temple is 33 m high and 38 m wide, and in it four sitting statues guard the access, each measuring about twenty meters high and sculpted directly on the rock. The statues represent Ramses II, seated on a throne and with the double crown of Upper and Lower Egypt, symbol of the domination that exerted over the entire valley of the Nile. One of the statues was damaged by an earthquake, which does not reduce the majesty of the temple, which still astonishes its visitors.
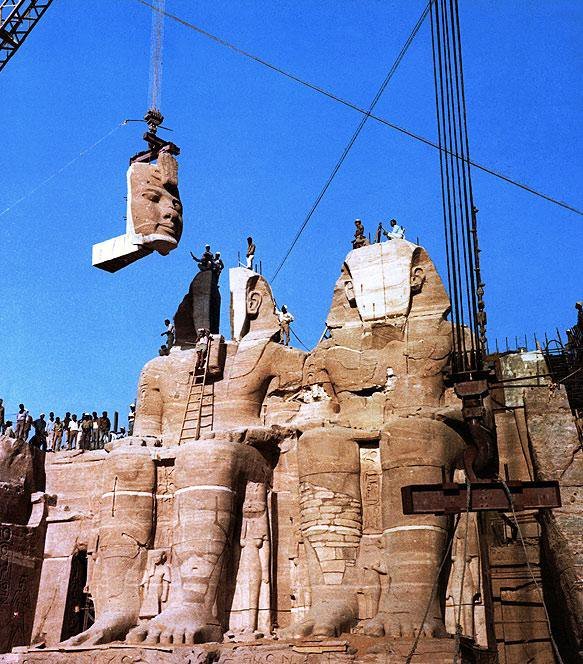
Between 1964 and 1968, and due to the construction of the high dam of Aswan, the temple had to be relocated to a higher area of the same slope where it had been originally carved. For this, a team of international experts, with the support of UNESCO, made a job that consisted of cutting the temple into huge blocks of more than 20 tons, which were then assembled in their new location; This titanic work is considered one of the great achievements of engineering.

Already inside the temple is the great hall hypostyle, 18 meters long and 16 wide whose roof is supported by 8 osirian pillars on which rest so many colossi, 4 on each side representing Osiris with the features of Ramses II. Those on the left carry the crown of Upper Egypt and those on the right crown the Pschent (the double crown symbol of the unification of the 2 Lands). Each of the colossi measures approximately 10 meters in height. The ceiling of the room is decorated with paintings depicting the goddess Nejbet with wings spread and real texts. The decoration of the walls shows, from left to right from the entrance: Immolation of prisoners and courtship of princes, scenes of battles in Syria, Libya and Nubia next to offerings, presentation of prisoners to Ra-Harmajis and Ramses II deified, the battle of Qadesh and immolation of prisoners and princesses with the sistro.
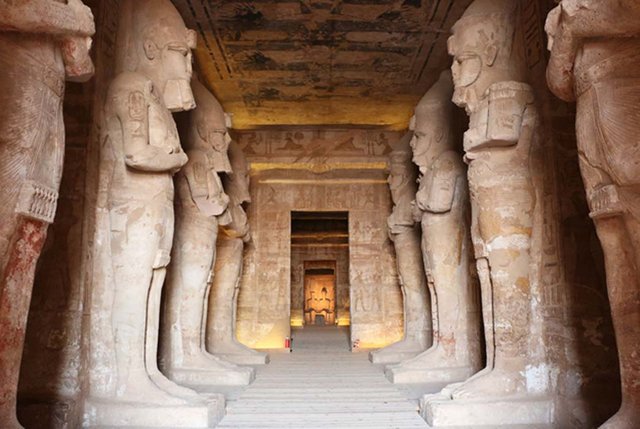

To the right of the room there are 4 side chambers that, with starry ceilings, contain different engravings. Two of them are accessed from the hypostyle hall and the other 2 through a passage that also opens in the room. On the left another camera leads to another 2 rooms, used as auxiliary rooms of the temple, to store objects and were never finished
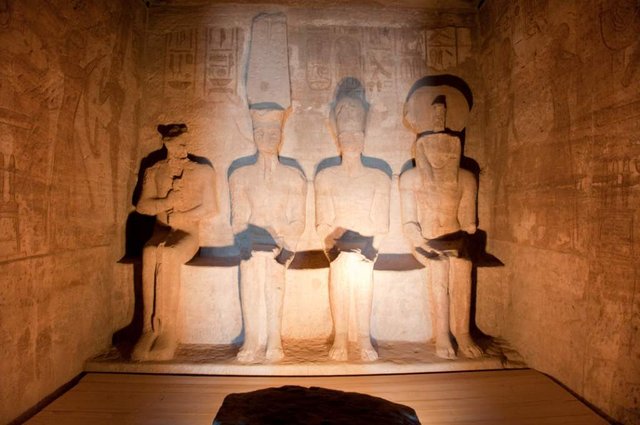
The second hypostyle room has 4 square pillars with scenes of the king embraced by different deities. This chamber, 11 meters long and 7.70 meters wide, leads, through three doors, to the offering room, 3.30 meters long, decorated with scenes of offerings and adoration. After this is the sanctuary which is accessed by three other doors aligned with the previous ones. The central door leads to the sancta sanctorum itself with 4 statues carved into the rock representing from left to right Ptah, Amón-Ra, Rameses II deified and Ra-Horajti while the 2 laterals give access to 2 chapels.

Lesser temple
The temple of Nefertari is also known as "Temple of Hathor" or "Temple Minor". It was built by Ramses II as a tribute to his wife and dedicated to Hathor, goddess of love and beauty. It is one of the few temples dedicated to women in Ancient Egypt.
It began to build about the year 1284 a. C, like the temple of Ramses II and its duration was also 20 years. Its façade is made up of 6 colossal statues of the same size (10 meters high) each with an advanced leg, simulating that they are walking. 4 of the statues are by Ramses II and the other 2 by Nefertari.

In the first room of the temple of Nefertari we find a great hypostyle hall 11 meters long and 10.8 wide. In it we find 6 columns, 3 on each side, decorated on their capitals with images of the head of the goddess Hathor. On these images we find inscriptions of the history of the king and the queen.
After this hypostyle hall we enter the lobby, the last step before reaching the sanctuary, where the representation of the goddess Hathor is found.
To the right and left of the lobby we have two secondary rooms, which, like those of the Ramses II temple, would serve to store objects.

I hope you enjoy my publication and see you in the next to continue sharing with all of you !!!!!!!!@brianrg13!!
.jpg)
World of Photography Beta V1.0
>Learn more here<
Thank you for participating in #architecturalphotography, the weekly selection will be released on Thursday.
You have earned 5.10 XP for sharing your photo!
Daily photos: 1/2
Daily comments: 0/5
Multiplier: 1.02
Server time: 23:12:39
Total XP: 28.30/100.00
Total Photos: 5
Total comments: 3
Total contest wins: 0
Follow: @photocontests
Join the Discord channel: click!
Play and win SBD: @fairlotto
Developed and sponsored by: @juliank
Excelente
¡Bien!
thanks!!!
I've seen the picture in the movie, good work
Thanks friend, greetings,,,
your welcm :)
Thank you @brianrg13 for promoting this post together with https://steemit.com/budget/@jerrybanfield/introducing-steem-budget-proposals