How you been spied on your whole life, sold out and became a slave. The Real Deepest Darkest Web. ENTER MARINA

Titanpointe, 33 Thomas Street
The former AT&T Long Lines Building at 33 Thomas Street is a 550 foot tall skyscraper in the Borough of Manhattan, New York, United States. It stands on the east side of Church Street, between Thomas and Worth Streets, in the Civic Center neighborhood of New York City. The building is an example of the Brutalist architectural style with its flat concrete slab facade. The building is a telephone exchange or wire center building which contained three major 4ESS switches used for interexchange (long distance) telephony, two owned by AT&T and one formerly owned by Verizon (decommissioned in 2009). It also contains a number of other switches used for competitive local exchange carrier (CLEC) services, but is not used for Incumbent local exchange carrier (ILEC) services, and is not a central office. The CLLI code for this facility is NYCMNYBW. The building is reportedly home to a National Security Agency surveillance facility.

SERCO
Serco Inc. is the Americas division of Serco Group, plc, one of the world's leading and most admired service companies. Serco serves Federal, state and local governments, along with the Canadian government and commercial customers. We help our customers deliver vital services more efficiently, while increasing the satisfaction of their end customers. Serco brings deep domain expertise and proven processes informed by over 50 years' experience, with over 50,000 people across four geographies: UK & Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East and North America, which includes 8,000 people in the U.S. and Canada.

OPIC
The Overseas Private Investment Corporation (OPIC) is the United States government's development finance institution. It mobilizes private capital to help solve critical development challenges and, in doing so, advances the foreign policy of the United States and national security objectives. Because OPIC works with the U.S. private sector, it helps U.S. businesses gain footholds in emerging markets, catalyzing revenues, jobs and growth opportunities both at home and abroad. OPIC achieves its mission by providing investors with financing, political risk insurance, and support for private equity investment funds, when commercial funding cannot be obtained elsewhere. Established as an agency of the U.S. government in 1971, OPIC operates on a self-sustaining basis at no net cost to American taxpayers. All OPIC projects adhere to high environmental and social standards and respect human rights, including worker's rights. By mandating high standards, OPIC aims to raise the industry and regional standards in countries where it funds projects. OPIC services are available for new and expanding business enterprises in more than 160 countries worldwide.

Crown Agents
Crown Agents Ltd is an international development company with head office in the United Kingdom. Its main focus is to help governments around the world to increase prosperity, reduce poverty and improve health by providing consultancy, supply chain, financial services and training. In April 2016 its financial services arm (Crown Agents Bank and Crown Agents Investment Management) was sold to Helios Investment Partners, leaving Crown Agents Ltd to focus on offering expertise in the areas of "health, economic development, governance and state building, supply chain services and humanitarian response". Incorporated as a private limited company Crown Agents Ltd has only one shareholder – the Crown Agents Foundation, a not-for-profit company. Crown Agents Ltd's registered office is in Southwark, London.

USAID
The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) is an independent agency of the United States federal government that is primarily responsible for administering civilian foreign aid and development assistance. With a budget of over $27 billion, USAID is one of the largest official aid agencies in the world, and accounts for more than half of all U.S. foreign assistance (which in absolute dollar terms is the highest in the world). Congress passed the Foreign Assistance Act on September 4, 1961, which reorganized U.S. foreign assistance programs and mandated the creation of an agency to administer economic aid. USAID was subsequently established by the executive order of President John F. Kennedy, who sought to unite several existing foreign assistance organizations and programs under one agency. USAID became the first U.S. foreign assistance organization whose primary focus was long-term socioeconomic development. USAID's programs are authorized by Congress in the Foreign Assistance Act, which Congress supplements through directions in annual funding appropriation acts and other legislation. As an official component of U.S. foreign policy, USAID operates subject to the guidance of the President, Secretary of State, and the National Security Council. USAID has missions in over 100 countries, primarily in Africa, Asia, Latin America, the Middle East, and Eastern Europe.

Section 702
Under Section 702, the NSA collects billions of communications, including those belonging to innocent Americans who are not actually targeted. These communications are then placed in databases that other intelligence and law enforcement agencies can access—for purposes unrelated to national security—without a warrant or any judicial review.
NUCLEON
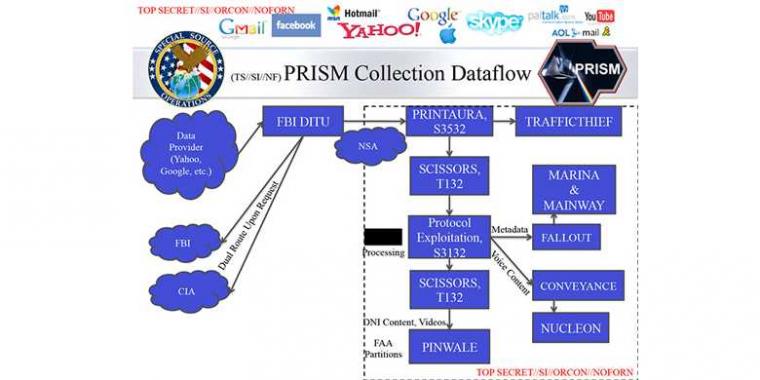
The nature of the Skype data collection was spelled out in an NSA document dated August 2012 entitled “User’s Guide for PRISM Skype Collection.” The document details how to “task” the capture of voice communications from Skype by NSA’s NUCLEON system, which allows for text searches against captured voice communications. It also discusses how to find text chat and other data sent between clients in NSA’s PINWALE “digital network intelligence” database. “The full capture of voice traffic began in February of 2011 for “Skype in” and “Skype out” calls—calls between a Skype user and a land line or cellphone through a gateway to the public switched telephone network (PSTN), captured through warranted taps into Microsoft’s gateways. But in July of 2011, the NSA added the capability of capturing peer-to-peer Skype communications—meaning that the NSA gained the ability to capture peer-to-peer traffic and decrypt it using keys provided by Microsoft through the PRISM warrant request.”
SPINNERET
SSO entry, dated February 6, 2013, described ongoing plans to expand metadata collection. A joint surveillance collection operation with an unnamed partner agency yielded a new program "to query metadata" that was "turned on in the Fall 2012". Two others, called MoonLightPath and Spinneret, "are planned to be added by September 2013." A substantial portion of the internet metadata still collected and analyzed by the NSA comes from allied governments, including its British counterpart, GCHQ. An SSO entry dated September 21, 2012, announced that "Transient Thurible, a new Government Communications Head Quarters (GCHQ) managed XKeyScore (XKS) Deep Dive was declared operational." The entry states that GCHQ "modified" an existing program so the NSA could "benefit" from what GCHQ harvested. Transient Thurible metadata has been flowing into NSA repositories since 13 August 2012.
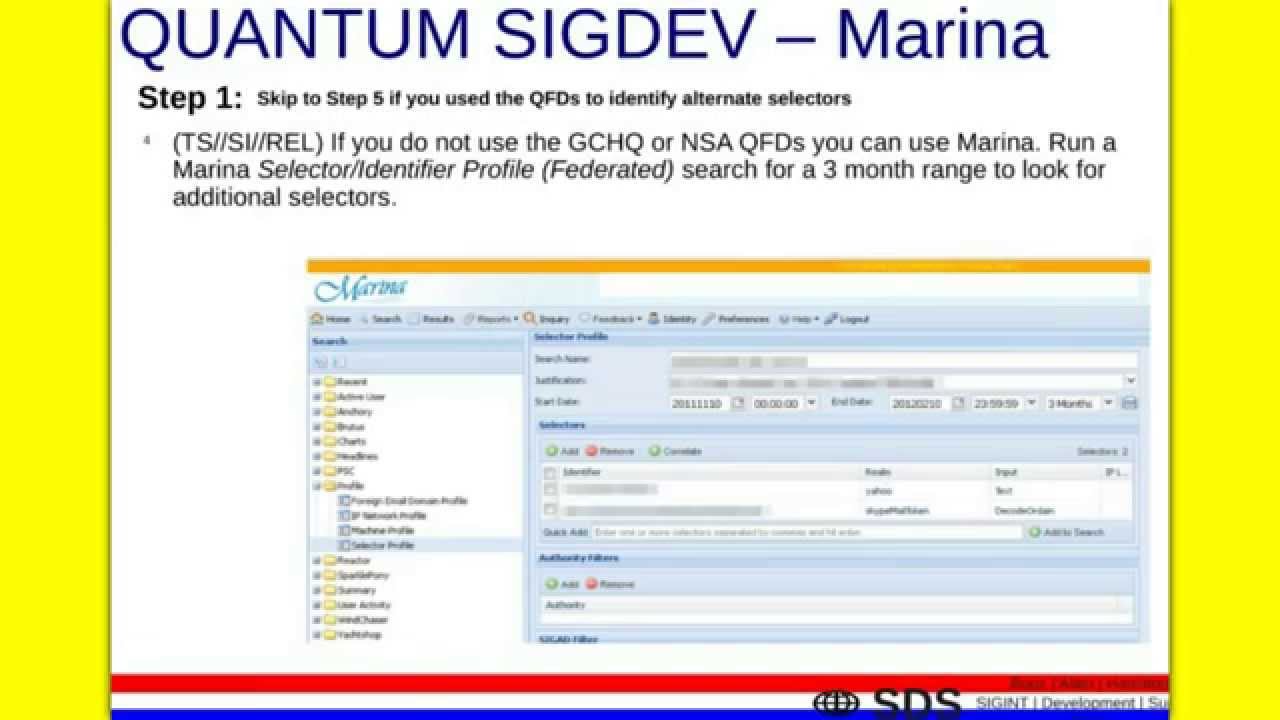
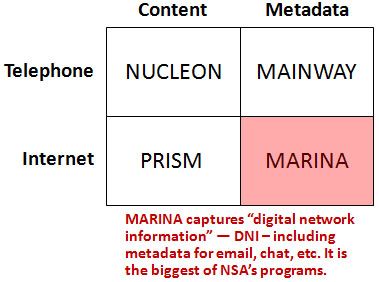
MARINA (Original Marianas Web?)
MARINA is an NSA database and analysis toolset for intercepted Internet metadata (DNI in NSA terminology). The database stores metadata up to a year. According to documents leaked by Edward Snowden: "The Marina metadata application tracks a user's browser experience, gathers contact information/content and develops summaries of target" and "of the more distinguishing features, Marina has the ability to look back on the last 365 days' worth of DNI metadata seen by the Sigint collection system, regardless whether or not it was tasked for collection." [Emphasis in original NSA document.] The stored metadata is mainly used for pattern-of-life analysis. US persons are not exempt because metadata is not considered data by US law (section 702 of the FISA Amendments Act). MARINA's phone counterpart is MAINWAY.
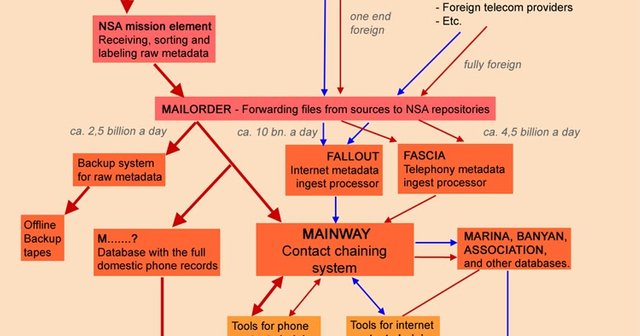
MAINWAY
MAINWAY is a database maintained by the United States' National Security Agency (NSA) containing metadata for hundreds of billions of telephone calls made through the four largest telephone carriers in the United States: AT&T, SBC, BellSouth (all three now called AT&T), and Verizon. According to Pulitzer Prize winning journalist James Risen, MAINWAY was the most important of the four components that comprised the ThinThread program. The existence of this database and the NSA program that compiled it was unknown to the general public until USA Today broke the story on May 10, 2006. It is estimated that the database contains over 1.9 trillion call-detail records. According to former NSA director Michael Hayden, the NSA sought to deploy MAINWAY prior to 9/11 in response to the Millennium Plot but did not do so because it did not comply with US law. Hayden wrote: "The answer from [the Justice Department] was clear: '...you can't do this.'" As of June 2013, the database stores metadata for at least five years. The records include detailed call information (caller, receiver, date/time of call, length of call, etc.) for use in traffic analysis and social network analysis, but do not include audio information or transcripts of the content of the phone calls.[citation needed. The database's existence has prompted fierce objections. It is often viewed as an illegal warrantless search and a violation of the pen register provisions of the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act and (in some cases) the Fourth Amendment of the United States Constitution.
The George W. Bush administration neither confirmed nor denied the existence of the domestic call record database. This contrasts with a related NSA controversy concerning warrantless surveillance of selected telephone calls; in that case they did confirm the existence of the program of debated legality. That program's code name was Stellar Wind. Similar programs exist or are planned in other countries, including Sweden (Titan traffic database) and Great Britain (Interception Modernisation Programme). The MAINWAY equivalent for Internet traffic is MARINA.
ICREACH
ICREACH is an alleged top-secret surveillance-related search engine created by the United States National Security Agency after the September 11 attacks. The existence of ICREACH became public through documents leaked by former NSA contractor Edward Snowden. Classified documents published by news site The Intercept state that ICREACH is accessible to 23 government agencies, including the FBI, Drug Enforcement Administration, and the CIA, and was designed to store more than 850 billion records about phone calls, emails, cellphone locations, and text messages. According to Ryan Gallagher, the reporter for The Intercept who revealed the ICREACH program, the data accessed through the system is swept up and stored on this database en masse using this Reagan-era presidential order, which is called Executive Order 12333. And this thing is subject to no court oversight from the secret foreign intelligence court and minimal congressional scrutiny.

SIGINT
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is intelligence-gathering by interception of signals, whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly used in communication (electronic intelligence—abbreviated to ELINT). Signals intelligence is a subset of intelligence collection management. As sensitive information is often encrypted, signals intelligence in turn involves the use of cryptanalysis to decipher the messages. Traffic analysis—the study of who is signaling whom and in what quantity—is also used to derive information.
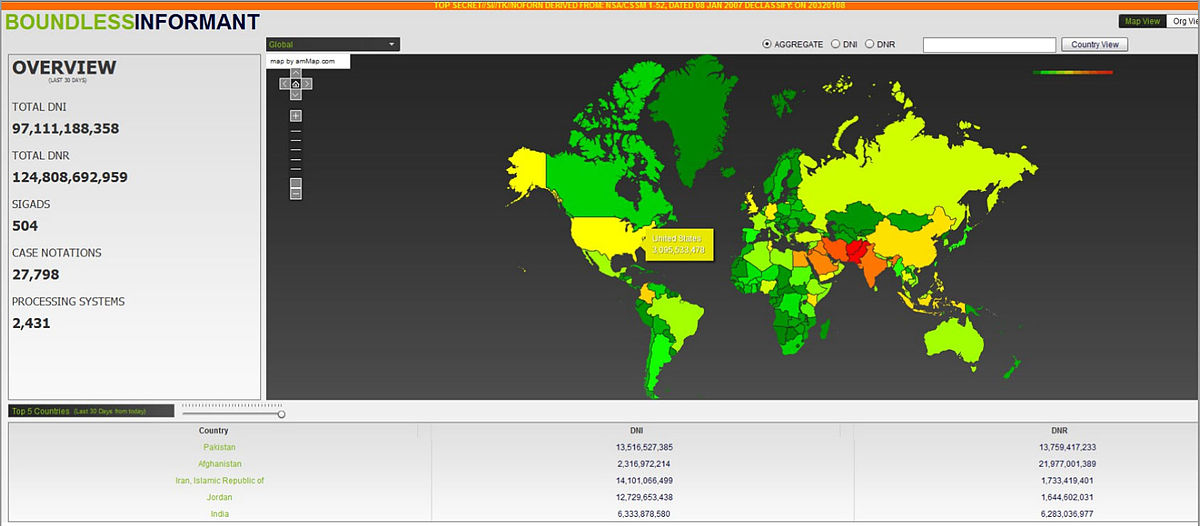
SIGAD
A SIGINT Activity Designator (or SIGAD) identifies a signals intelligence (SIGINT) line of collection activity associated with a signals collection station, such as a base or a ship. For example, the SIGAD for Menwith Hill in the UK is USD1000. SIGADs are used by the signals intelligence agencies of the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia and New Zealand. There are several thousand SIGADs including the substation SIGADs denoted with a trailing alpha character. Several dozen of these are significant. The leaked Boundless Informant reporting screenshot showed that it summarized 504 active SIGADs during a 30-day period in March 2013. XX-N-XX-NN-XX-NNNx-XXX-NNNNxn

RAPLEAF
RapLeaf was a US-based marketing data and software company.
On May 15, 2006, eBay removed a number of auction listings where the seller had included links to Rapleaf, claiming they were in violation of its terms of use. In late August 2007, Upscoop began e-mailing entire contact lists that were provided by their users when they log in. This caused some criticism, and the company later apologized for doing so. On July 10, 2008, Rapleaf changed its interface so that it no longer allows users to search people by email addresses. Instead, the service only allows a registered user to view their own reputation and the websites (social and business networking) to which their own e-mail address is registered. There was an immediate negative backlash by companies and individuals who had been using Rapleaf to both manage reputations and investigate the authenticity of people. In October 2010, the Wall Street Journal reported that Rapleaf had transmitted personally identifiable information, including Facebook and MySpace IDs. Rapleaf said it had inadvertently transmitted that info and had ceased the practice. On October 28, 2010, Facebook banned Rapleaf from scraping data on Facebook, and Rapleaf said it would delete the Facebook IDs it had collected. A 2011 report said the company could tell the food preferences of employees of major companies. Between 2007-2013, Rapleaf received significant backlash over the data collection practices and sale of individuals' personal information to advertisers. As a public spokesperson for the company, much of the criticism was directed at the CEO Auren Hoffman personally. A 2010 investigation by The Wall Street Journal revealed that the company transmitted identifying details about individuals to at least 12 companies, violating the terms of service of Facebook and MySpace. A spokesperson at Facebook said it had "taken steps. . .to significantly limit Rapleaf's ability to use any Facebook-related data." When confronted by The Wall Street Journal and CNet, it quietly revised its privacy policy both times. CNNMoney described RapLeaf as "selling your identity," and TechCrunch characterized its method of identifiable data extraction of Google and Microsoft employees as "creepy." RapLeaf later became known as LiveRamp after entering new markets. LiveRamp spun off the RapLeaf business and sold it to TowerData in 2013.
PINWALE
Pinwale is the code name for an NSA collection and retrieval system for so-called "Digital Network Intelligence", including internet e-mail. It is searchable by monitored NSA analysts.The existence of the system was first revealed by an NSA analyst who was trained in its use during 2005. However, according to Homeland Security Today, Pinwale has in it much more than email, it also contains other forms of Internet data, and other forms of digital communications as well. Its software has built-in protections against collecting from any of the Five Eyes members. Unlike its successor XKeyscore, targets for PINWALE have to be approved beforehand by the FISC. According to information obtained by The Guardian from Edward Snowden, Pinwale is part of a "multi-tiered system" to address the issue of NSA "collecting so much internet data that it can be stored only for short periods of time." The system allows analysts to store "interesting" content in databases such as Pinwale, which is capable of storing material for up to five years.Pinwale consists of at least two known partitions referred to as "Sweet" and "Sour". According to the documents leaked by Snowden, Pinwale normally processed about 60 GB of data per day without trouble. Pinwale was overwhelmed however when Yahoo started mass mailbox transfers between its datacenters, which were captured by the NSA's MUSCULAR program that taps the private clouds of Google and Yahoo. Monitored email accounts being hacked by spammers also present a challenge to Pinwale, because they can cause the database of suspect email addresses to grow exponentially with information of no intelligence value.
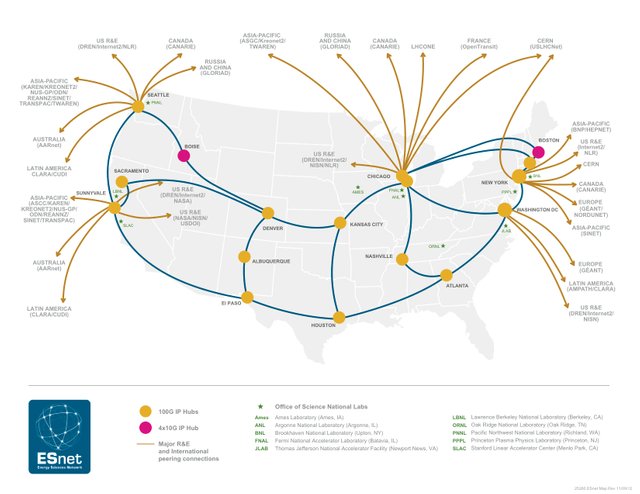
ESNET
The Energy Sciences Network (ESnet) is a high-speed computer network serving United States Department of Energy (DOE) scientists and their collaborators worldwide. It is managed by staff at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. More than 40 DOE Office of Science labs and research sites are directly connected to this network. The ESnet network also connects to more than 140 other research and commercial networks, allowing DOE researchers to collaborate with scientists around the world.
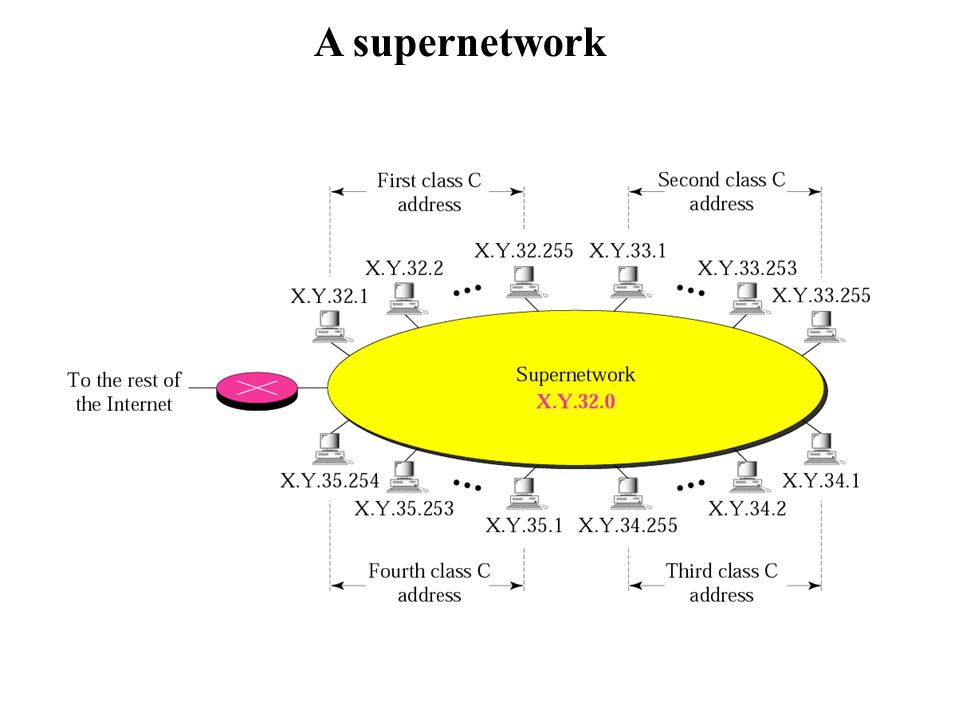
SUPERNET
A supernetwork, or supernet, is an Internet Protocol (IP) network that is formed, for routing purposes, from the combination of two or more networks (or subnets) into a larger network. The new routing prefix for the combined network represents the constituent networks in a single routing table entry. The process of forming a supernet is called supernetting, prefix aggregation, route aggregation, or route summarization. Supernetting within the Internet serves as a strategy to avoid topological fragmentation of the IP address space by using a hierarchical allocation system that delegates control of segments of address space to regional network service providers. This method facilitates regional route aggregation. The benefits of supernetting are conservation of address space and efficiencies gained in routers in terms of memory storage of route information and processing overhead when matching routes. Supernetting, however, can introduce interoperability issues and other risks.
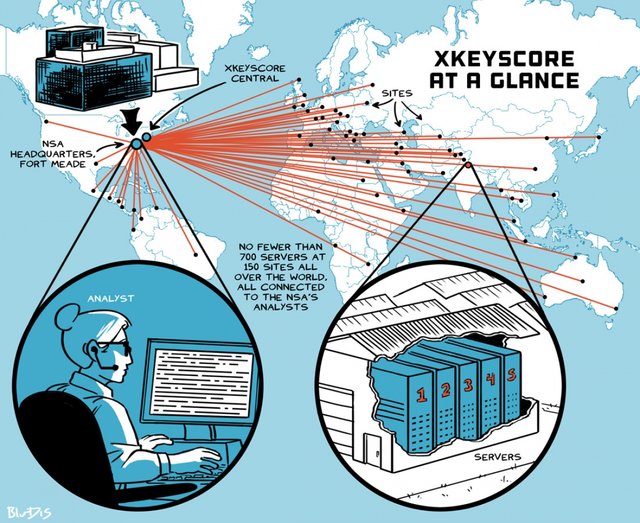
XKeyscore
XKeyscore (XKEYSCORE or XKS) is a formerly secret computer system first used by the United States National Security Agency for searching and analyzing global Internet data, which it collects on a daily basis. The program has been shared with other spy agencies including the Australian Signals Directorate, Canada's Communications Security Establishment, New Zealand's Government Communications Security Bureau, Britain's Government Communications Headquarters and the German Bundesnachrichtendienst. The program's purpose was publicly revealed in July 2013, by Edward Snowden in The Sydney Morning Herald and O Globo newspapers. The code name was already public knowledge because it is mentioned in earlier articles, and like many other code names can also be seen in job postings, and in the online resumes of employees. On July 3, 2014, excerpts of XKeyscore's source code were first published by German public broadcaster Norddeutscher Rundfunk, a member of ARD. A team of experts analyzed the source code.
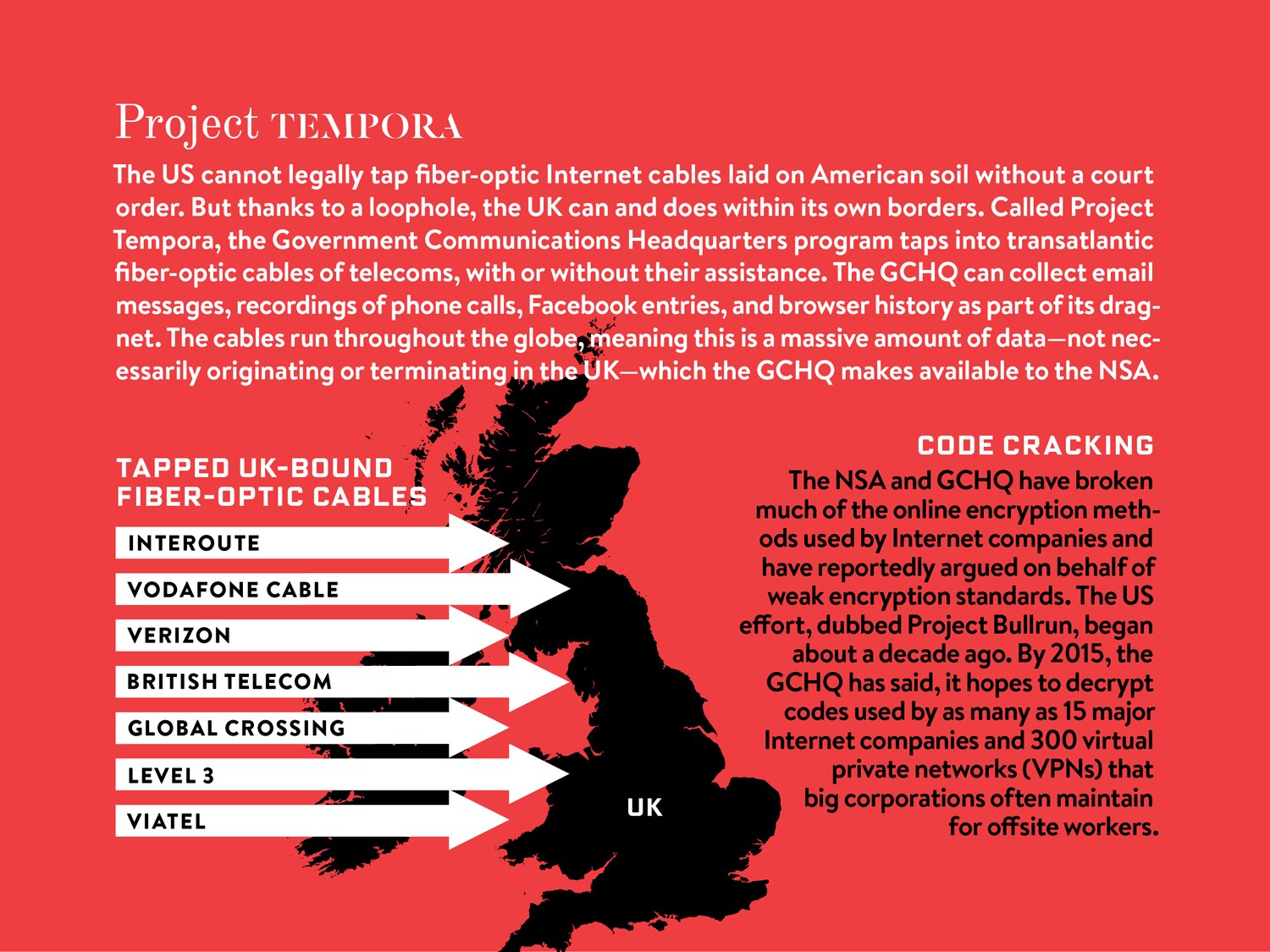
Tempora
Tempora is the codeword for a formerly secret computer system that is used by the British Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ). This system is used to buffer most Internet communications that are extracted from fibre-optic cables, so these can be processed and searched at a later time. It was tested since 2008 and became operational in the autumn of 2011. Tempora uses intercepts on the fibre-optic cables that make up the backbone of the Internet to gain access to large amounts of Internet users' personal data, without any individual suspicion or targeting. The intercepts are placed in the United Kingdom and overseas, with the knowledge of companies owning either the cables or landing stations. The existence of Tempora was revealed by Edward Snowden, a former American intelligence contractor who leaked information about the program to former Guardian journalist Glenn Greenwald in May 2013, as part of his revelations of government-sponsored mass surveillance programs. Documents Snowden acquired claimed that data collected by the Tempora program is shared with the National Security Agency of the United States.

STINGRAY
The StingRay is an IMSI-catcher, a controversial cellular phone surveillance device, manufactured by Harris Corporation. Initially developed for the military and intelligence community, the StingRay and similar Harris devices are in widespread use by local and state law enforcement agencies across Canada, the United States, and in the United Kingdom. Stingray has also become a generic name to describe these kinds of devices. The StingRay is an IMSI-catcher with both passive (digital analyzer) and active (cell-site simulator) capabilities. When operating in active mode, the device mimics a wireless carrier cell tower in order to force all nearby mobile phones and other cellular data devices to connect to it. The StingRay family of devices can be mounted in vehicles, on aeroplanes, helicopters and unmanned aerial vehicles. Hand-carried versions are referred to under the trade name KingFish. A StingRay can be used to identify and track a phone or other compatible cellular data device even while the device is not engaged in a call or accessing data services. The FBI has claimed that when used to identify, locate, or track a cellular device, the StingRay does not collect communications content or forward it to the service provider. Instead, the device causes a disruption in service. Under this scenario, any attempt by the cellular device user to place a call or access data services will fail while the StingRay is conducting its surveillance. In passive mode, the StingRay operates either as a digital analyzer, which receives and analyzes signals being transmitted by cellular devices and/or wireless carrier cell sites or as a radio jamming device, which transmits signals that block communications between cellular devices and wireless carrier cell sites. By "passive mode," it is meant that the StingRay does not mimic a wireless carrier cell site or communicate directly with cellular devices.
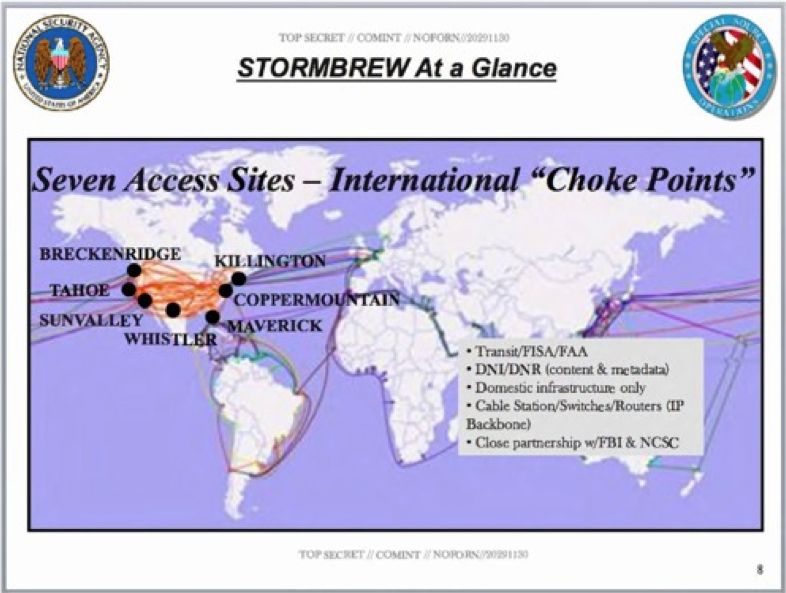
STORMBREW
STORMBREW is a secret internet surveillance program of the National Security Agency (NSA) of the United States. It was disclosed in the summer of 2013 as part of the leaks by former NSA contractor Edward Snowden. The FY 2013 budget for STORMBREW was $46.06 million. STORMBREW is an umbrella program involving surveillance of telecommunications. It falls under the category of "Upstream collection", meaning that data is pulled directly from fiber-optic cables and top-level communications infrastructure, which allows access to very high volumes of data. A first pre-selection is done by the telecommunication providers themselves, who select the Internet traffic that most likely contains foreign communications. Then the data is passed on to the NSA, where a second selection is made by briefly copying the traffic and filtering it by using so-called "strong selectors" like phone numbers, e-mail or IP addresses of people and organizations in which NSA is interested.

What is Ddate?
Ddate, a program that prints the current date in the Discordian calendar, was part of the util-linux package containing basic system utilities.As such, it had been included at least since 1994 in nearly all Linux distributions. In August 2011 however, one of the maintainers of util-linux made ddate optional, and by default omitted. In October 2012, ddate was completely removed from util-linux.The ddate program now has an upstream source. There was some controversy, but in the end, anyone wishing to reintroduce ddate to a distribution will have to create a separate package based on the new upstream. This has been done for Debian, FreeBSD, Fedora Linux, and Gentoo Linux for example.There are many other programs with similar functionality, such as HodgePodge, an Android widget. Discordian-calendar is an implementation using Java 8's date and time classes.
DERN
THAT DERN DIRNSA: NSA Director Admiral Mike Rogers is taking some heat for the
“second Snowden” – the case of an NSA contractor who reportedly managed to make off with mounds of highly classified info – for reasons that remain unclear. With pressure increasing to split NSA from the Cyber Command – there is speculation that NSA may end up with a civilian leader and that a stand-alone Cyber Command may have a new uniformed leader before long. On Tuesday, Rogers said at a public forum that he supports splitting the two commands if it is done “in the right way.”
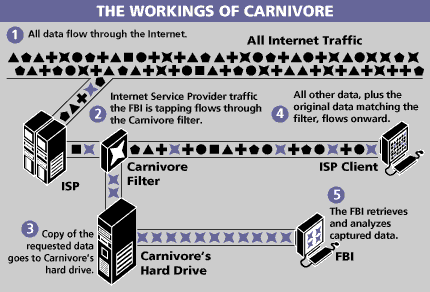
Carnivore
Carnivore, later renamed DCS1000, was a system implemented by the Federal Bureau of Investigation that was designed to monitor email and electronic communications. It used a customizable packet sniffer that can monitor all of a target user's Internet traffic. Carnivore was implemented in October 1997. By 2005 it had been replaced with improved commercial software. Carnivore grew out of an earlier FBI project called "Omnivore", which itself replaced an older surveillance tool migrated from the US Navy by FBI Director of Integrity and Compliance, Patrick W. Kelley, which had a still undisclosed name. In September 1998, the FBI's Data Intercept Technology Unit (DITU) in Quantico, Virginia, launched a project to migrate Omnivore from Sun's Solaris operating system to a Windows NT platform. This was done to facilitate the miniaturization of the system and support a wider range of personal computer (PC) equipment. The migration project was called "Phiple Troenix" and the resulting system was named "Carnivore. The Carnivore system was a Microsoft Windows-based workstation with packet-sniffing software and a removable Jaz disk drive. This computer must be physically installed at an Internet service provider (ISP) or other location where it can "sniff" traffic on a LAN segment to look for email messages in transit. The technology itself was not highly advanced—it used a standard packet sniffer and straightforward filtering. The critical components of the operation were the filtering criteria. To accurately match the appropriate subject, an elaborate content model was developed. An independent technical review of Carnivore for the Justice Department was prepared in 2000. The Associated Press reported in mid-January 2005 that the FBI essentially abandoned the use of Carnivore in 2001, in favor of commercially available software, such as NarusInsight, a mass surveillance system. A report in 2007 described the successor system as being located "inside an Internet provider's network at the junction point of a router or network switch" and capable of indiscriminately storing data flowing through the provider's network.
NarusInsight
Narus Inc. was a software company and vendor of big data analytics for cybersecurity. Narus is one of the first companies to combine patented machine learning algorithms, automation, and data fusion technologies to provide the incisive intelligence, context, and control network operators need to protect against cyberthreats and ensure information security. Narus software primarily captures various computer network traffic in real time and analyzes results. Prior to 9/11 Narus worked on building carrier-grade tools to analyze IP network traffic for billing purposes, to prevent what NARUS called "revenue leakage". Post-9/11 Narus added more "semantic monitoring abilities" for surveillance. In 1997, Ori Cohen, Vice President of Business and Technology Development for VDONet, founded Narus with Stas Khirman in Israel. Presently, they are employed with Deutsche Telekom AG and are not members of Narus' Executive Team. In 2010, Narus became a subsidiary of Boeing, located in Sunnyvale, California. In 2014, Narus was sold to Symantec. Narus is noted for having created NarusInsight, a supercomputer system, whose installation in AT&T's San Francisco Internet backbone gave rise to a 2006 class action lawsuit by the Electronic Frontier Foundation against AT&T, Hepting v. AT&T. A single NarusInsight machine can monitor traffic equal to the maximum capacity (10 Gbit/s) of around 39,000 256k DSL lines or 195,000 56k telephone modems. But, in practical terms, since individual internet connections are not continually filled to capacity, the 10 Gbit/s capacity of one NarusInsight installation enables it to monitor the combined traffic of several million broadband users. According to a year 2007 company press release, the latest version of NarusInsight Intercept Suite (NIS) is "the industry's only network traffic intelligence system that supports real-time precision targeting, capturing and reconstruction of webmail traffic... including Google Gmail, MSN Hotmail and Yahoo! Mail". However, currently most webmail traffic can be HTTPS encrypted, so the content of messages can only be monitored with the consent of service providers. NarusInsight can also perform semantic analysis of the same traffic as it is happening, in other words analyze the content, meaning, structure and significance of traffic in real time. The exact use of this data is not fully documented, as the public is not authorized to see what types of activities and ideas are being monitored. Ed Snowden's June 2013 releases about PRISM (surveillance program) have made clear however that Narus has played a central role.
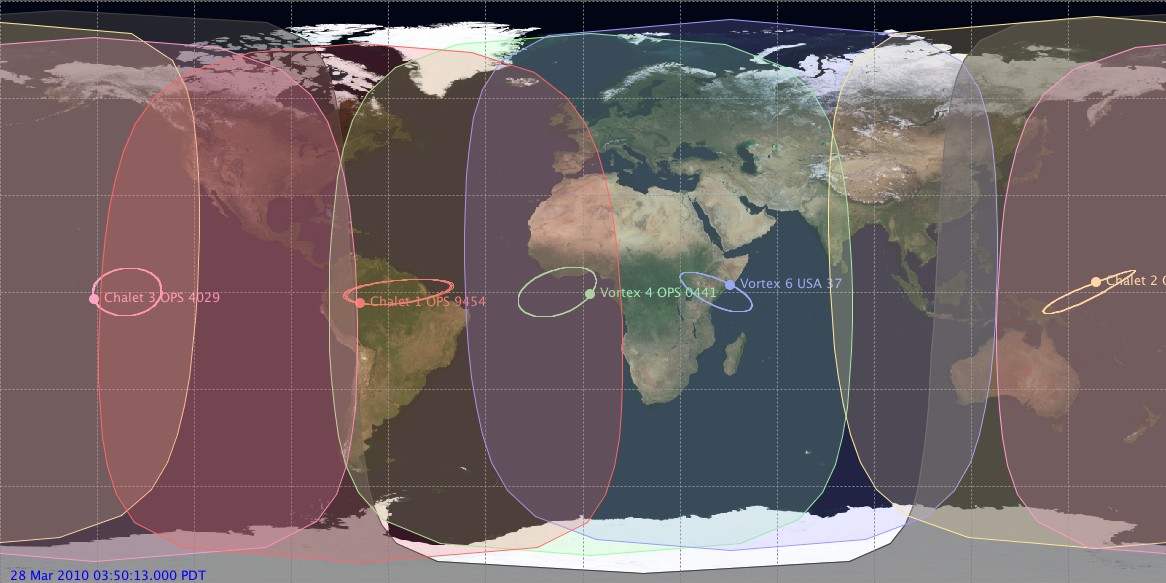
Vortex
Vortex, previously known as Chalet, was a class of spy satellite operated by the United States during the 1980s and 1990s to collect signals intelligence (SIGINT) from high Earth orbit. The Vortex satellites were operated by the National Reconnaissance Office for the United States Air Force and listened to radio transmissions originating from Earth or space. The intercepted data is believed to have been fed into and analyzed by the National Security Agency ECHELON system. The satellites each had a mass of approximately 1,800 kilograms and are operated from non-stationary geosynchronous orbits. Each reportedly carried a 38-meter-diameter umbrella-like reflecting dish to collect radio signals from Earth. At least six launch attempts were made of Chalet/Vortex satellites between 1978 and 1989. The Chalet/Vortex satellites replaced the older generation of Canyon satellites, and were superseded by the larger, more capable Mercury satellites.

MYSTIC
MYSTIC is a formerly secret program used since 2009 by the US National Security Agency (NSA) to collect the metadata as well as the content of phone calls from several entire countries. MYSTIC operates under the legal authority of Executive Order 12333. Its RETRO tool, short for “retrospective retrieval,” and related projects reached full capacity against the first target nation in 2011. The MYSTIC program started in 2009, but reached its full extent, the capability to record the content of phone calls for an entire country for 30 days, in 2011. Documents from 2013 say the surveillance program could be extended to other countries. On March 18, 2014, the existence of the program was first revealed by The Washington Post, based upon documents leaked by Edward Snowden. It was reported that the NSA had the capability to record all the phone calls from an unidentified foreign country. On May 19, 2014, the website The Intercept published the name of one country of which the phone calls were recorded, and also identified three other countries of which only the telephony metadata were collected .
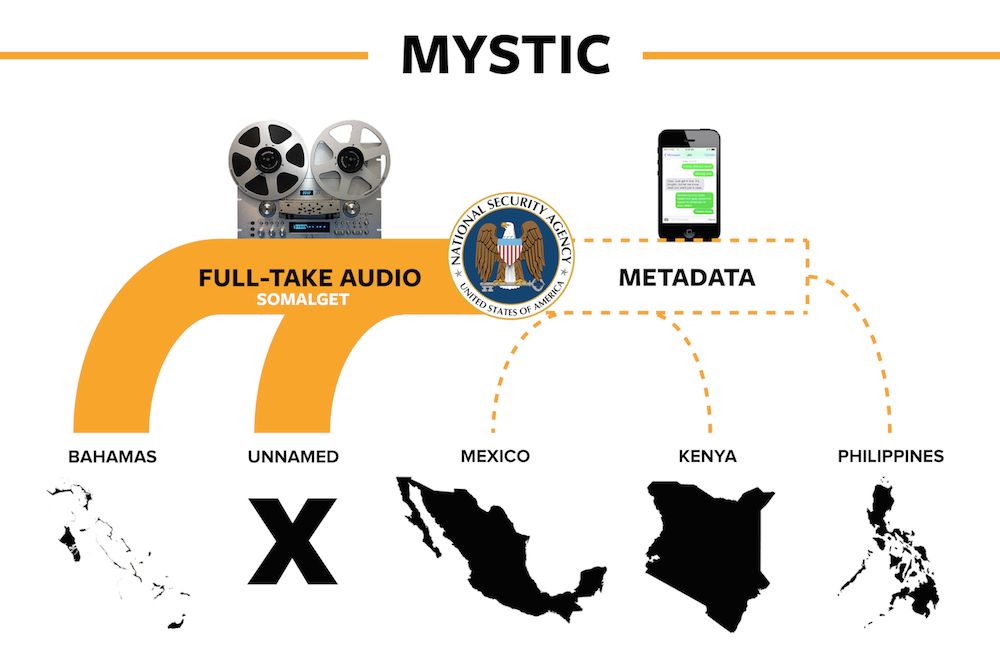
SOMALGET
SOMALGET is part of a broader NSA program called MYSTIC, which The Intercept has learned is being used to secretly monitor the telecommunications systems of the Bahamas and several other countries, including Mexico, the Philippines, and Kenya. But while MYSTIC scrapes mobile networks for so-called “metadata” – information that reveals the time, source, and destination of calls – SOMALGET is a cutting-edge tool that enables the NSA to vacuum up and store the actual content of every conversation in an entire country.

Can the Government read my mind?
It appears so, MINDPRISM," as “The Ultimate in Upstream Collection.” A combination of the agency’s most powerful and sophisticated signals intelligence capacities and a new neuroscience program has given the agency the ability to capture communications---before they are even communicated. “NSA can no longer afford to operate at network speed,” the slide reads. “With MINDPRISM, we can stay one step of communication itself. If the target can think it, we can collect it. NSA official familiar with the program describes it as the most forward-leaning of the NSA programs compromised by Snowden and complained that senior Al Qaeda leaders and Vladimir Putin had all begun changing the way and the amount that they think in response to the disclosures. MINDPRISM extracts thoughts and information in the Powerpoint slides about who is thinking about what. Broadly speaking, however, the slides describe a program that taps human thought through implants in dental work, beaming thought signals for satellite pickup to NSA’s network of supercomputers. A single implant can capture the thoughts of hundreds of people in the target’s vicinity, including Americans whose thoughts are not specifically targeted but are incidentally collected in large volume through the program. Kim Jong Un really is obsessed with basketball. It’s literally all he thinks about. And that’s important to know. MINDPRISM obviously stands to complicate the Obama Administration’s efforts at diplomatic rehabilitation. When asked if the surveillance would strain ties between the United States and Germany, German Chancellor Angel Merkel---whose telephone NSA had tapped---said, "you read my mind."

Executive Order 12333
Executive Order 12333, signed on December 4, 1981 by U.S. President Ronald Reagan, was an Executive Order intended to extend powers and responsibilities of U.S. intelligence agencies and direct the leaders of U.S. federal agencies to co-operate fully with CIA requests for information. This executive order was titled United States Intelligence Activities. It was amended by Executive Order 13355: Strengthened Management of the Intelligence Community, on August 27, 2004. On July 30, 2008, President George W. Bush issued Executive Order 13470 amending Executive Order 12333 to strengthen the role of the DNI. Executive Order 12333 has been regarded by the American intelligence community as a fundamental document authorizing the expansion of data collection activities. The document has been employed by the National Security Agency as legal authorization for its collection of unencrypted information flowing through the data centers of internet communications giants Google and Yahoo!. In July 2014 chairman David Medine and two other members of the Privacy and Civil Liberties Oversight Board, a government oversight agency, indicated a desire to review Executive Order 12333 in the near future, according to a report by journalist Spencer Ackerman of The Guardian. In July 2014, former State Department official John Tye published an editorial in The Washington Post, citing his prior access to classified material on intelligence-gathering activities under Executive Order 12333, and arguing that the order represented a significant threat to Americans' privacy and civil liberties.

COINTELPRO
COINTELPRO (acronym for COunter INTELligence PROgram) (1956-1971) was a series of covert, and at times illegal, projects conducted by the United States Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) aimed at surveilling, infiltrating, discrediting, and disrupting domestic political organizations. FBI records show that COINTELPRO resources targeted groups and individuals that the FBI deemed subversive, including the Communist Party USA, anti-Vietnam War organizers, activists of the civil rights movement or Black Power movement (e.g., Martin Luther King Jr. and the Black Panther Party), feminist organizations, independence movements (such as Puerto Rican independence groups like the Young Lords), , and a variety of organizations that were part of the broader New Left. The FBI has used covert operations against domestic political groups since its inception; however, covert operations under the official COINTELPRO label took place between 1956 and 1971. COINTELPRO tactics are still used to this day, and have been alleged to include discrediting targets through psychological warfare; smearing individuals and groups using forged documents and by planting false reports in the media; harassment; wrongful imprisonment; and illegal violence, including assassination. The FBI's stated motivation was "protecting national security, preventing violence, and maintaining the existing social and political order. The program was successfully kept secret until 1971, when the Citizens' Commission to Investigate the FBI burgled an FBI field office in Media, Pennsylvania, took several dossiers, and exposed the program by passing this material to news agencies. Many news organizations initially refused to publish the information. Within the year, Director J. Edgar Hoover declared that the centralized COINTELPRO was over, and that all future counterintelligence operations would be handled on a case-by-case basis.

What is a strawman?
A strawman is a fictitious legal entity, created with the hope that as the child grows up, he will be fooled into believing that he is actually the strawman (which he most definitely is not) and pay all sorts of imaginary costs and liabilities which get attached to the strawman by con artists.
How is a strawman created?
Well the mechanism involves that unnecessary birth certificate which the parents imagine is about, and belongs to, their baby (neither of which is actually true). If the baby has been named James and the family name is Martin, then you would expect the birth certificate to have the name James Martin written on it. If that is what is written on it, then all is well and it is a genuine birth certificate. However, if any other name is there, then the document is not a birth certificate but instead is the creation of a strawman masquerading as James Martin. The alternative entries might be any of the following examples: "JAMES MARTIN", "Mr James Martin", "Martin, Mr James" or anything else which is not exactly "James Martin" and nothing else.
Why create a strawman?
The answer is 'in order to charge the strawman imaginary costs and penalties and fool the human James Martin into paying those amounts'. These imaginary charges include 'Income Tax', 'Council Tax', 'Inheritance Tax', 'Capital-Gains Tax', 'Road Tax', 'Import Tax', 'Value-Added Tax', 'Fuel Levy', 'Loan Interest', 'Bank Charges' and anything else that full-time professionals can think up and are confident that you will not notice that you never agreed to pay and don't need to pay.
Extremely Over-informative and spooky as always.
Cheers!
You my friend are a riot! Lmfao Thanks
If you had a penny for every smart thing you said on here you would have around 20$ by now..
My estimates was extremely close! 19.36$ Keep up the good work!
HIGHLY RESTEEMED!
Highly Re-bacon.

HiGHLY APPRECiATED !THANKS BACON!
