Java Graphical User Interface(GUI): JFrame and JLabel functions Using Eclipse IDE
What Will I Learn?
- The user will learn the concept of JFrame and JLabel.
- The user will learn how JLabel is imported and put in a container.
- The user will also learn how to display a text when the mouse is hovered over another text.
Requirements
- A computer System is required for this tutorial.
- Java Software Development Kit(JDK) must be installed on your computer.
- An Integrated Development Environment(IDE) such as Eclipse or NetBeans is required to be installed on your computer.
Get JDK here
Get Eclipse here
Get NetBeans here
Difficulty
It would take some practice and do overs to master the codes, I would rate the difficulty level as Intermediate.
Tutorial Contents
WHAT IS JFRAME?
A frame, implemented as an instance of the JFrame class, is a window that has decorations such as a border, a title, and supports button components that close or iconify the window. Applications with a GUI usually include at least one frame. Applets sometimes use frames, as well.
WHAT IS JLABEL?
The JLabel Component descends from JComponent and is used to create text labels.
The object of JLabel class is a component for placing text in a container. It is used to display a single line of read only text. The text can be changed by an application but a user cannot edit it directly. It inherits JComponent class.
This program briefly illustrates how to create a JFrame container and include a JLabel object in it, therefore displaying a line of text in the JFrame container.
CODE BLOCK
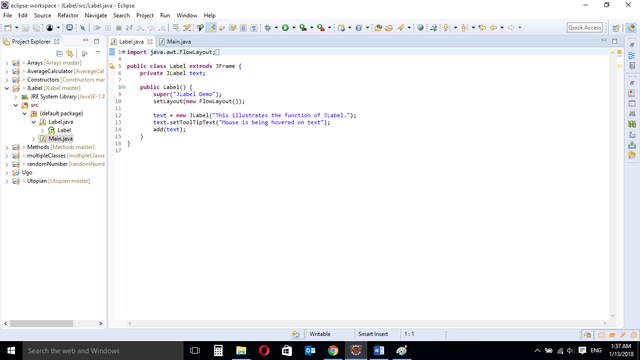
LABEL CLASS
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
public class Label extends JFrame {
private JLabel text;
private JLabel text1;
public Label() {
super("JLabel Demo");
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
text = new JLabel("This illustrates the function of JLabel.");
text.setToolTipText("Mouse is being hovered on text");
add(text);
}
}
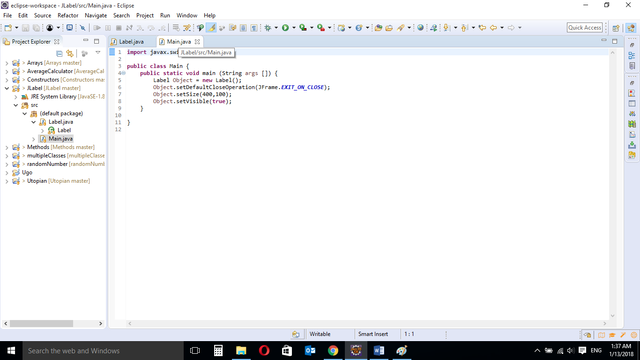
MAIN CLASS
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class Main {
public static void main (String args []) {
Label Object = new Label();
Object.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
Object.setSize(400,100);
Object.setVisible(true);
}
}
LABEL CLASS
Import java.awt.FlowLayout;
Import javax.swing.JFrame;
Import javax.swing.JLabel;
These are Import Statements. Import Statements are used to reference methods that are in other packages. Java numerous in built methods and these methods are in different packages. When the user imports a class, the user has access to all methods in the class because they are automatically imported.
public class Label extends JFrame {
This is the name of the current class. When you start a new class, it must be saved with a name. This class extends JFrame. In Java, it is possible for classes to inherit properties of another class. Here, this class inherits basic Frame properties like a window with close, maximize and minimize buttons from the JFrame class. The extends keyword is used to achieve this.
private JLabel text;
This is a variable declaration of JLabel type. The private keyword is used here, this means that this variable can only be accessed from within this class and not from other classes.
Public keyword is used if the user wants the variable to be accessed from anywhere.
Public Label() (
A Constructor is a block of code that lets you initialize variables immediately an object is created. Methods can be created and called later but with constructors, initialization is done immediately. Constructors have the same name as the class name and is called when an object of the class in created.
The above constructor does not carry any arguments and is created to hold the JFrame and JLabel components.
super(“JLabel Demo”);
The super keyword is used here to refer to properties of a superclass; in this case the JFrame class.
In this context, it is used to set the title of the newly created window. The title of the window is “JLabel Demo”
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
The FlowLayout class was imported earlier. This provides a basic layout that is used by JFrame components.
The FlowLayout class puts components in a row, sized at their preferred size. If the horizontal space in the container is too small to put all the components in one row, the FlowLayout class uses multiple rows.
Text = new JLabel(“”)
With the JLabel class, you can display unselectable text and images. If you need to create a component that displays a string, an image, or both, you can do so by using or extending JLabel. If the component is interactive and has a certain state, use a button instead of a label.
Here, JLabel is used to set the text that will appear on the screen and assign it to the JLabel variable text.
Text.setToolTipText(“”);
An additional functionality is added to the JLabel object. The .setToolTipText method is called using the JLabel variable and a dot(.) separator.
This displays a String message when the mouse is hovered over the JLabel text.
add(text)
Now that the window is created, the keyword add[] is used to add the text to the container so it will be visible to the user.
MAIN CLASS
Import javax.swing.JFrame;
This is an import statement. This statement is used specifically to import the JFrame class from Application Program Interface (API). This allows the user to use all methods contained in it.
public class Main {
This is just like creating a new file or document and saving it with a name. This is the name of the new class created.
Label Object = new Label();
An Object of the Label class is created. This enables the user to call in built GUI methods that will help to properly display the JLabel component to the screen.
Object.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
This inbuilt method needs to be called before the program is run . This method states the default behavior of the windows when the “close”(x) button is clicked.
Here, it tells the window to close.
Object.setSize(400,100);
This is to set the size of the object to the specified width and height. In this case, the specified dimensions are (400,100).
Normally the values of width and height are non-negative integers. The constructors that allow you to create a dimension do not prevent you from setting a negative value for these properties. If the value of width or height is negative, the behavior of some methods defined by other objects is undefined.
Object.setVisible(true);
This simply determines wether a component is displayed on the screen. It has two states. True and false.
With setVisible( false ), if the Component is not already marked invisible, setVisible calls invalidate() which invalidates the Container’s layout and the chain of parents since there is now more screen real estate in the Container and the positions of the siblings must be adjusted to flow into the freed space.
With setVisible( true ), if the Component is not already marked visible,setVisible calls invalidate() which invalidates the Container’s layout and the chain of parents since there is now less screen real estate in the Container and the positions of the siblings must be adjusted to squeeze in this new Component.
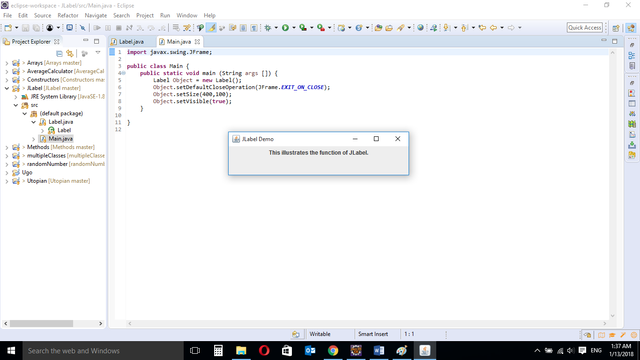
When the program is reun, it displays the JLabel Component to the screen
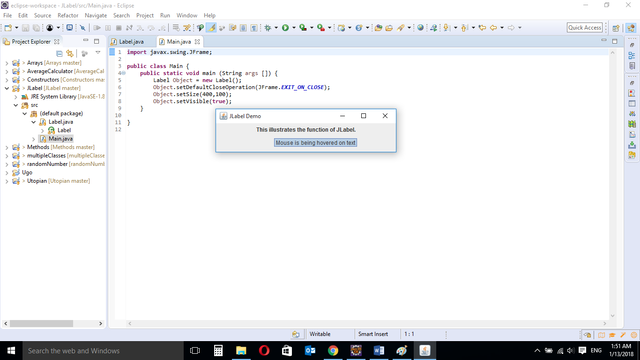
When the mouse is hovered on the text, it displays a String message
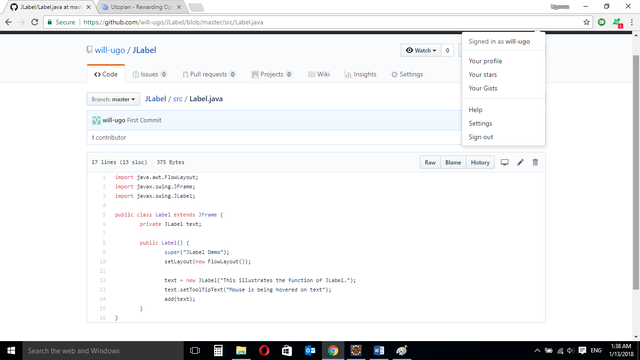
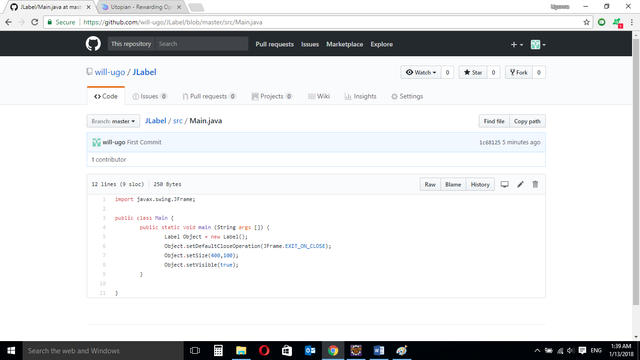
Source codes from GitHub Account
You can get the codes here if you want to try it on your own.
Curriculum
Similar posts already posted on Utopian are:
- Simple Java program to add two integer numbers inputted by the user
- Average Calculator using Eclipse IDE
- Java Constructors Using Eclipse IDE
- Random Number Generator: Guessing game using Eclipse IDE
Posted on Utopian.io - Rewarding Open Source Contributors
Thank you for the contribution. It has been approved.
You can contact us on Discord.
[utopian-moderator]
Thank you for this post
Hey @will-ugo I am @utopian-io. I have just upvoted you!
Achievements
Suggestions
Get Noticed!
Community-Driven Witness!
I am the first and only Steem Community-Driven Witness. Participate on Discord. Lets GROW TOGETHER!
Up-vote this comment to grow my power and help Open Source contributions like this one. Want to chat? Join me on Discord https://discord.gg/Pc8HG9x