Learn how to program with Python #2 - Solving Puzzles from Advent of Code 2018
Repository
What will I learn
- .strip()
- Counting characters
- True == 1 and False == 0
- Nested loop
- .pop()
Requirements
- Python 3.7.2
- Pipenv
- git
Difficulty
- basic
Tutorial
Preface
This tutorial is part of a course where solutions to puzzles from Advent of Code 2018 are discussed to explain programming techniques using Python. Each puzzle contains two parts and comes with user specific inputs. It is recommended to try out the puzzle first before going over the tutorial. Puzzles are a great and fun way to learn about programming.
While the puzzles start of relatively easy and get more difficult over time. Basic programming understanding is required. Such as the different type of variables, lists, dicts, functions and loops etc. A course like Learn Python2 from Codeacademy should be sufficient. Even though the course is for Python two, while Python 3 is used.
This tutorial will look at puzzle 2
Setup
Download the files from Github and install the virtual environment
$ cd ~/
$ git clone https://github.com/Juless89/tutorials-aoc
$ cd tutorials-aoc
$ pipenv install
$ pipenv shell
$ cd part_2
Part one
To make sure you didn't miss any, you scan the likely candidate boxes again, counting the number that have an ID containing exactly two of any letter and then separately counting those with exactly three of any letter. You can multiply those two counts together to get a rudimentary checksum and compare it to what your device predicts.
To solve this puzzle the frequency of each character inside the string has to be counted. Then those characters that appear 2 or 3 times their counts have to counted as well.
.strip()
First the data has to be imported and formatted in the correct form. A list of strings is the most efficient.
The text file is many lines of strings:
lsrivfotzgdxpkefaqmuiygchj
lsrivfotzqdxpkeraqmewygchj
lsrivfotzbdepkenarjuwygchj
lsrivfotwbdxpkeoaqmunygchj
Reading these lines from the file once again adds a \n to each line. This time the lines will be used in a string format. .strip() can be used to remove the newlines. Doing this inside a list comprehension returns a list.
# read input file and convert to list
# remove `\n`
with open('input.txt', 'r') as file:
lines = [x.strip() for x in file]
[x.strip() for x in file] is equal to:
list = []
for x in file:
list.append(x.strip())
Counting characters
A string is basically a list and can be used in a similar way. This means accessing a character at a specific index:
string = 'test'
print(string[0])
t
And iterating over each character inside a string with a for loop. To store the count for each character a dict can be used. Where the character is the key. If the key is already inside the dict the value can be increased by 1, if not the key can be added and set to 1.
# go over each line
for line in lines:
# store each character's count
count = {}
# check if c already in count
for c in line:
if c in count:
count[c] += 1
else:
count[c] = 1
True == 1 and False == 0
Count now contains the frequency of each character.
{'l': 1, 's': 1, 'r': 1, 'i': 1, 'v': 2, 'f': 1, 'o': 1, 't': 1, 'z': 1, 'b': 1, 'd': 1, 'x': 1, 'p': 1, 'h': 2, 'e': 1, 'n': 1, 'a': 1, 'q': 1, 'm': 1, 'u': 1, 'w': 1, 'y': 1, 'g': 1, 'j': 1}
Only the values are needed. These can be extracted with .values().
dict_values([1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1])
When adding a Boolean statement True equals 1 and False equals 0.
# store results
results = {'2': 0, '3': 0}
# if 2/3 in values, statement is true
# increment with 1
results['2'] += 2 in count.values()
results['3'] += 3 in count.values()
# return amount of 2s * 3s
return results['2'] * results['3']

Part two
The boxes will have IDs which differ by exactly one character at the same position in both strings. What letters are common between the two correct box IDs?
To solve this puzzle all lines have to be compared with each other.
Nested loop
The straight forward way would be to create a nested loop where each line gets compared to each line.
for line1 in lines:
for line2 in lines:
# compare line1 and line2
However this would mean that lines will be checked against each other and themselves multiple times. When dealing with a lot lines can increase the run time significantly.
.pop()
Another solution is to remove the line from the list with .pop() and compare that with the remainder of the list. This way each comparison will only be made once.
# loop until lines is empty or answer
# is found
while len(lines) > 0:
# remove line from list
line1 = lines.pop(0)
# loop through remaining list
for x in range(0, len(lines)):
line2 = lines[x]
# compare line1 and line2
The lines are compared on a character by character basing, this guarantees the same order. For each character that is different 1 gets added to difference. When the difference is 1 the line is returned
difference = 0
# compare each character, for each
# character that is different add 1
# to difference
for c in range(0, len(line1)):
if line1[c] != line2[c]:
difference += 1
# if difference is 1 return id
if difference == 1:
return line1

Running the code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# read input file and convert to list
# remove `\n`
with open('input.txt', 'r') as file:
lines = [x.strip() for x in file]
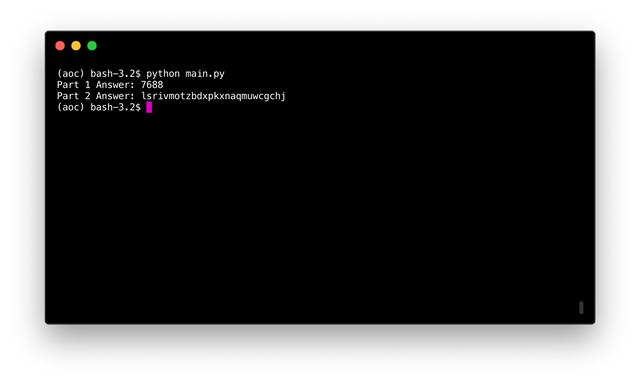
print(f'Part 1 Answer: {part_1(lines)}')
print(f'Part 2 Answer: {part_2(lines)}')
Run the code with:
python main.py
Curriculum
The code for this tutorial can be found on Github!
This tutorial was written by @juliank.

Thank you for your contribution @steempytutorials.
After reviewing your tutorial we suggest the following points listed below:
We suggest that you don't repeat information that you put in the previous tutorials. For example, the Setup section.
Thanks for following our suggestions to improve your tutorials.
Looking forward to your upcoming tutorials.
Your contribution has been evaluated according to Utopian policies and guidelines, as well as a predefined set of questions pertaining to the category.
To view those questions and the relevant answers related to your post, click here.
Need help? Chat with us on Discord.
[utopian-moderator]
Thanks for the feedback!
Thank you for your review, @portugalcoin! Keep up the good work!
Excellent blog post on the world of programming. 👏
Hi @steempytutorials!
Your post was upvoted by @steem-ua, new Steem dApp, using UserAuthority for algorithmic post curation!
Your post is eligible for our upvote, thanks to our collaboration with @utopian-io!
Feel free to join our @steem-ua Discord server
Hi, @steempytutorials!
You just got a 0.26% upvote from SteemPlus!
To get higher upvotes, earn more SteemPlus Points (SPP). On your Steemit wallet, check your SPP balance and click on "How to earn SPP?" to find out all the ways to earn.
If you're not using SteemPlus yet, please check our last posts in here to see the many ways in which SteemPlus can improve your Steem experience on Steemit and Busy.
Hey, @steempytutorials!
Thanks for contributing on Utopian.
We’re already looking forward to your next contribution!
Get higher incentives and support Utopian.io!
Simply set @utopian.pay as a 5% (or higher) payout beneficiary on your contribution post (via SteemPlus or Steeditor).
Want to chat? Join us on Discord https://discord.gg/h52nFrV.
Vote for Utopian Witness!