Building a Food Ordering System with MEAN Stack (Mongo, Express, Angular and Nodejs.
Today, we would be building a web app which can help user to other a particular set of food from a resturant. We would be using Nodejs, express, and typescript for our server side client.
and AngularJs for our front-end.
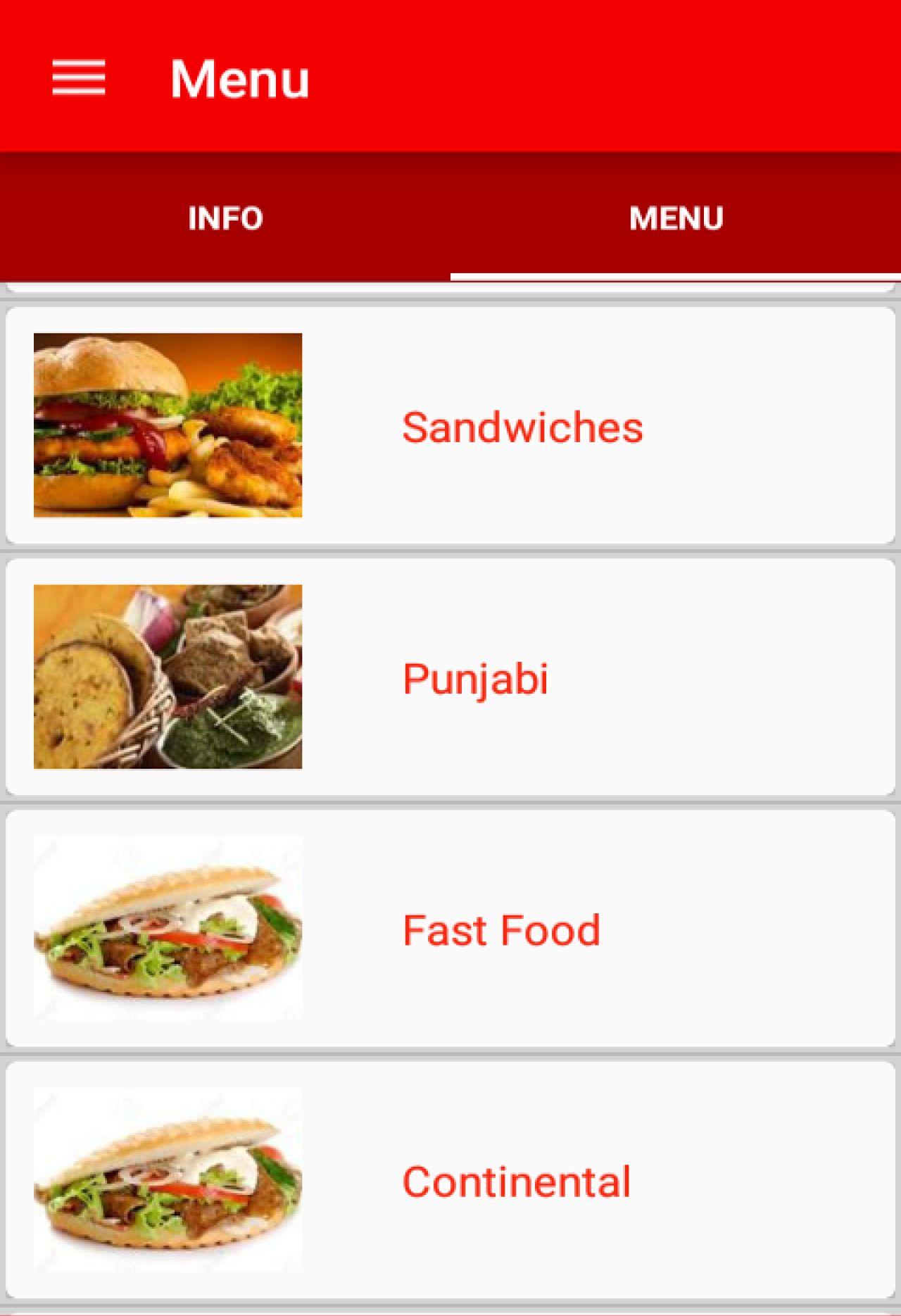
When we are done, our web app would look like the image below.
Image
Overview.
In this installment, we would design our database schema, in RDBMS and convert it to a NoSQL schema (Mongodb), run installation, cofigure our application, and build our model.
Requirement.
- Typescript version 2.4.2
- Node version version 8.9.4
- Npm version 5.6.0
- Express version ^4.15.3.
- Repository
Difficulty
This tutorial is rated intermediate
Table of content.
- What is a food menu app?
- What is the difference between NoSql (mongodb) and Sql
- Designing the database in MySql and adapting for MongoDb
- Configuration and setting up our application.
- Installation and running mongoDb server on windows
- Setting up Express.ts file and connecting to the database.
1. What is a food menu app?
It is quite possible, that you don't eat in a restaurant or even order a slice of Pizza from a near by restaurant. I bet there are some persons that can't do without this.
A food menu app is an application a costumer or a user can use in checking the various prices of food a particular time and of a specified location. This application makes the experience of getting or acquiring food very easy and simplified.
2. What is the difference between NoSql (mongodb) and Sql.
Lets start with mySql, mySql database gives opinions and relationship when designing the database. for example, lets assume we want to build a car, in mySql, it is assumed that this car can has different parts which includes the tyres, the wheel, the engine the Car-case. All these components brought together would makeup the car. This is how mySql sees things, in component manner. There are relationships between tables in a database.
While in Nosql like Mongodb, we have collections in a database which has no opinion or whatsoever. it gives you whatever you give to the database or lets call it document.
In NoSql it is assumed the the car already has its component embedded in the car-case which makes the actual car.
3. Designing the database in MySql and adapting for MongoDb.
To design the Database, we must have in mind what the application is about to do, and the features of this application.
For Voltron, we are going to have the following features:
- Users Feature, which has the whole authentication system.
- ListItems Feature
- Order/checkout feature.
We would start by the designing the database in an RDBMS format before conversion to NoSql
Lets take a close look at the relationships
- A user should be able to login in an check all the items available from a restaurant.
- A user should able to checkout and pay for the order that has been created. In a whole, we should be able to track a particular user transaction in the database.
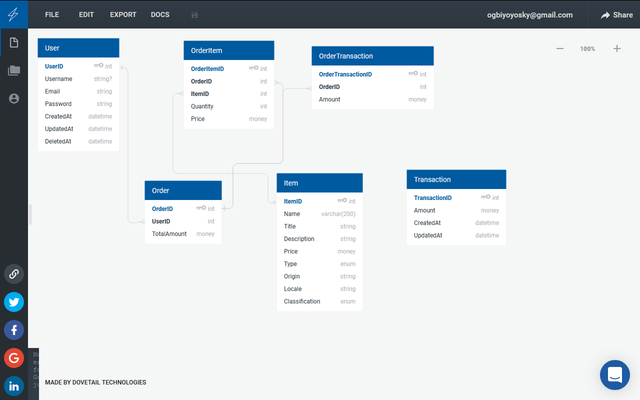
In MySql design
I would be design this Database using QuickDatabaseDesign
User
-
UserID PK int
Username string null
Email string
Password string
CreatedAt datetime
UpdatedAt datetime
DeletedAt datetime
Order
-
OrderID PK int
UserID int FK >- User.UserID
TotalAmount money
OrderItem as oi
----
OrderItemID PK int
OrderID int FK >- Order.OrderID
ItemID int FK >- i.ItemID
Quantity int
Price money
# Table documentation comment 1 (try the PDF/RTF export)
Item as i # Table documentation comment 2
------------
ItemID PK int
# Field documentation comment 1
# Field documentation comment 2
Name varchar(200) # Field documentation comment 3
Title string
Description string
Price money
Type enum
Origin string
Locale string
Classification enum
OrderTransaction as ot
----
OrderTransactionID PK int
OrderID int FK >- Order.OrderID
Amount money
Transaction
----
TransactionID int pk
Amount money
CreatedAt datetime
UpdatedAt datetime
Source: https://app.quickdatabasediagrams.com/#/schema/jYQKX0i5cUueryLU4_eIIQ
Looking at the design above, the userId is referenced on the order table, we have a bunch of relationship you can study by looking at the line connection.
Database Design in NoSql (MongoDb).
The design for MongoDb as i said, should not be in relational form.
We are going to have three collections. which are:
- User Collection
- Item Collection
- Order Collection.
User collection
We are going to have a separate user collection because we are going to be creating an authentication system.We should be able to query all the users separately without other information. Below is an example.
{
"_id": "5abb8e9019c576bade205923",
"name": "micheal Ogbiyoyo",
"updatedAt": "2018-03-28T14:37:16.861Z",
"createdAt": "2018-04-06T15:32:10.647Z",
"password": "miracle123",
"username": "sirfreeman",
"email": "[email protected]"
},
Item Collection
It would also be nice to keep all items separately due to the limit of mongoDb which is 16Mb,
the item collection should posses the price, description and Amount in Stock of the item.
the items can be kept separately to avoid passing the size of a mongo collection.
Example Below
{
"_id": "5ac35a4e817b4317f840f9f7",
"id": 1,
"title": "Fried yam",
"price": 1999.99,
"__v": 0,
"updatedAt": "2018-04-03T10:40:09.105Z",
"createdAt": "2018-04-03T10:40:09.105Z",
"inStock": 2,
"photo": "beans.jpg",
"desc": "Fried Rice",
"type": "food"
}
Order collection
This collection Should posses the user, the items or item added by the user, the Quantity and price of the item. This practice is called embedding in Mongo/ NoSql
Below is the example of how a user object is embedded in the order collection.
{
"id": "5ac35a4e817b4317f840f9f7",
"user": {
"username": "sirfreeman"
},
"items": [
{
"item": {
"title": "Fried rice",
"price": 1999.90
},
"qty": 2
}
]
}
Explaining the relationships between documents or tables.
To build any software, we must first go and look at our requirements before moving to the database design.
Our food order system must do the following
1. Users should be able to authenticate themselves into t.
2. Users should be able to view all items with their prices
3. It must scale—that means it must perform as well for a thousand users as well as it would for two users.
Our limitations:
- We must make the experience accessible to all browser regardless of their level of support for Javascript and (or) WebSockets.
- We must ensure our food order System is well optimized for high performance.
- We also have to ensure our users get the very best experience possible within our limitations.
Explaination of fields
Lets start with the users collection
- _id: The id is auto-generated by mongodb.
- name: The name field shows the users name.
- password: stores the users' password.
- username and email: stores the email and the username of which are unique values and type as strings.
Item collection
- _id: stores a auto-generated string from mongo
- title: The items title, which has its type as string.
- price: The iitem price has a type of Number.
- photo: It has a type of String, which is link to the image name in the image directory.
- type: which is a string
Order collection
The order collection has the item embedded along side with the user and the items
- items: which is an array of objects that contain the item from the item collection
- the user object is passed to the order collection to know which user order an item.
- qty: this is the qantity of an item order which has a type of number.
4. Configuration and setting up our application (voltron-api).
Yes, it's time for some organization of our project.We are going to be using matheusdavidson express-typescript-mongoose-starterpack . The starter pack is going to help us with the organization of our project
We begin by cloning the repository into our local machine.
git clone https://github.com/matheusdavidson/express-typescript-mongoose-starter.git
next up we run the command below to install our node_modules. The following packages would be installed.
- body-parser version"^1.17.2",
- cookie-parser version "^1.4.3",
- dotenv version "^4.0.0",
- ejs version "^2.5.7",
- express version "^4.15.3",
- mongoose version"^4.11.5",
- morgan version "^1.8.2",
- path version "^0.12.7"
You can get rid of ejs since we are building an Api. ejs which is for server side templating.
npm install
Adding configurations and packages on the Starter pack
We run the command below and pass the flag of --save to save dependencies
the following packages should be installed.
- bcrypt version "^1.0.3",
- bcrypt-nodejs version "0.0.3"
- compression version "^1.7.2",
- cors version "^2.8.4",
- express version "^4.15.3",
- helmet version "^3.12.0",
- jsonwebtoken version "^8.2.0",
- jwt-simple version "^0.5.1"
- mongoose-unique-validator version "^2.0.0"
- passport "^0.4.0",
- passport-jwt "^4.0.0",
- passport-local "^1.0"path": "^0.12.7",
- validator "^9.4.1"
We can simply add the above packages to the package.json file and run the command npm install
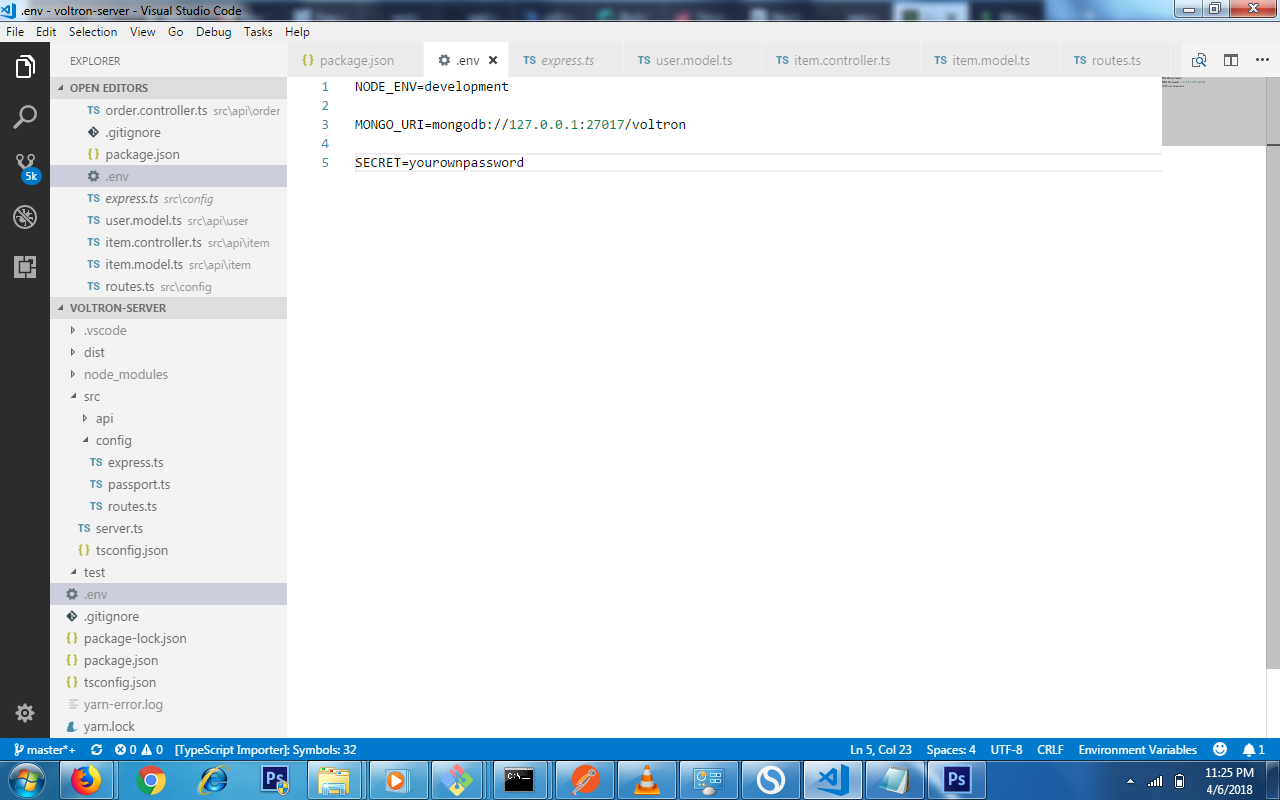
Lastly on configuration, we are going to add some variables for our .env file which we rename the .env.example to .env and add the snippet below.
NODE_ENV=development
MONGO_URI=mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/voltron
SECRET=yourownpassword
5. Installation and running mongoDb server on windows
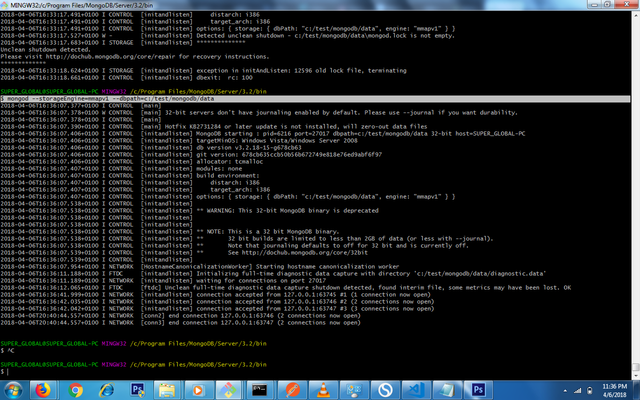
To run installation, you can download MongoDB binary and run installation
after installation, goto to /c/Program Files/MongoDB/Server/3.2/bin and open the command line and enter the command below to run the mongo server
mongod --storageEngine=mmapv1 --dbpath=c:/test/mongodb/data
Above, we are passing two flags to store the dbpath and the storageEnginr to be used.
lastly, we need to create our voltron database which we added to the .env
open another command prompt on thesame directory and enter the command below to initiate the mongodb
mongo.exe
next up to create the database enter the command on the shell
use voltron
6. Setting up Express.ts file and connecting to the database.
This file iss the binder for our application, The framework express gives no opinion unlike Adonisjs which is organized in MVC pattern.
so lets begin with this file.
the file shole be created in the config folder with the name express.ts
open up the file and import the following module at the top which we have installed from Npm.
import * as bodyParser from "body-parser";
import * as express from "express";
import * as logger from "morgan";
import * as path from "path";
import * as mongoose from "mongoose";
import * as cors from "cors";
import * as compression from "compression";
import * as passport from "passport";
import * as helmet from "helmet";
import Routes from "./routes";
import * as Passport from "./passport";
Next up lets create a class to initiate express. In this class we are going to be using all this modules. The following would be done;
- Settingup the .env file
- intializing passport, which is for api authentication
- connecting to the voltron database
- setting middlewares
- setting up our routes
below is the content of the class, i will explain each part.
class Express {
public app: express.Express;
private envFile = 'src/.env';
constructor () {
this.app = express();
this.setupEnv();
this.initializePassport();
this.setupMongo();
this.setupMiddleware();
this.setupRoutes();
}
private setupEnv() {
//
// Add NODE_ENV to path if is not production
// if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') this.envFile += '.' + process.env.NODE_ENV;
//
// Set env from file
require('dotenv').config();
}
private initializePassport() {
this.app.use(passport.initialize());
}
private setupMongo() {
//
// Connect to mongo using mongoose
// @todo: fix "open()" DeprecationWarning warning
mongoose.connect(process.env.MONGO_URI, {
db: { safe: true }
});
}
private setupRoutes() {
new Routes(this.app);
}
private setupMiddleware() {
this.app.use(logger("dev"));
this.app.use(bodyParser.json());
this.app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: false }));
this.app.use(cors());
this.app.use(helmet());
this.app.use(compression());
}
}
export default new Express().app;
The first line, we have a variable called app which is a type of express.Express
we also set the .env file from the root directory
Next up in our constructor method, we kickoff everything.
constructor () {
this.app = express();
this.setupEnv();
this.initializePassport();
this.setupMongo();
this.setupMiddleware();
this.setupRoutes();
}
lets create each of the methods above and use the modules.
below we are initializing passport by using the module
private initializePassport() {
this.app.use(passport.initialize());
}
Next we need the method to connect to the db
private setupMongo() {
//
// Connect to mongo using mongoose
// @todo: fix "open()" DeprecationWarning warning
mongoose.connect(process.env.MONGO_URI, {
db: { safe: true }
});
}
Remember to add the variable MONGO_URI to the .env file which is written as
MONGO_URI=mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/voltron connection done.
setting up the middleware, we just need to use a bunch of modules
private setupMiddleware() {
this.app.use(logger("dev"));
this.app.use(bodyParser.json());
this.app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: false }));
this.app.use(cors());
this.app.use(helmet());
this.app.use(compression());
}
to set the Route we just need to create a need instance of the router
private setupRoutes() {
new Routes(this.app);
}
Lastly Export the class and import in the server.js. which is done by default if you are using the Davison's starter pack.
export default new Express().app;
If you are having any issue, drop a comment or confirm from the repository
Conclusion
In this installment, we successfully created and designed our database, setup our project with typescript and run the mongo server and database. in the Next installation, we are going to get our hands dirty with some real code and design our mongoose models, and set up the routing system with controllers.
cheers!!!
We have successfully created the database.
Posted on Utopian.io - Rewarding Open Source Contributors
Great article.
Running the code. I came across an error. The error message I received gave a printed log containing the message "Mongod.lock is corrupt". How do i fix this? Great article by the way.
that's easy, simply go to the local disk :c click the test folder and head over to the data folder and delete the mongod.lock file and restart the server.
Hey @sirfreeman I am @utopian-io. I have just upvoted you!
Achievements
Utopian Witness!
Participate on Discord. Lets GROW TOGETHER!
Up-vote this comment to grow my power and help Open Source contributions like this one. Want to chat? Join me on Discord https://discord.gg/Pc8HG9x
We can order food from any restaurant using this web app. You have used Nodejs, express, and typescript for the server-side client.
and AngularJs for the front-end. It's working great. I have also recently ordered a Resolution that is the guest-oriented restaurant Reservation management system. You can use it for online and walk-in customers to reserve tables. It has built-in features like floor set up, number of seats, profile management, notifications, etc. Visit alignminds to get it now.