Do It Yourself: Continuous power supply with an output range of 0 V to 28 V
Hello Steemians !
In this project, it covers the systematic process in creating a continuous power supply having a range of 0 to 28 V. We made this project as for the fulfillment of the subject in “Power Electronics”. If you want to know how we did this, so just hold on and do not forget to write down notes

What is a Power supply?
Maybe some of you are wondering what is a power supply, so let’s define it first :)
Let’s begin !
Step 1: Design of your circuit diagram
On this step, prepare the circuit diagram to be place in Multisim. You may use also Proteus for your convenience but I find Multisim much easier to use.
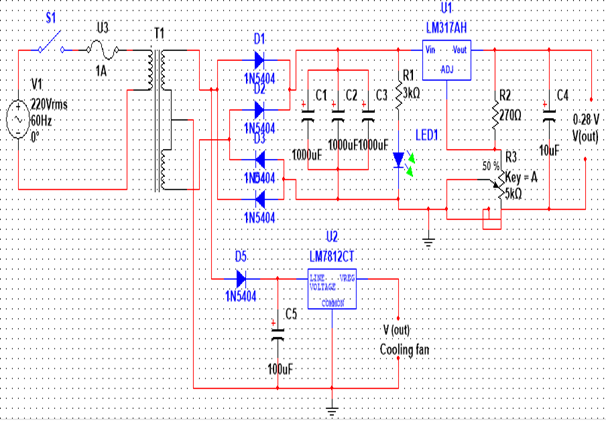
(Photo is mine)
Power supply mechanism
The obtain AC power is 220 Vrms with 60 Hz and controlled by a switch and a fuse. The center-tapped transformer that has specification of approximately 24V will be directed to a full-bridge rectifier. A rectifier is use to convert the transformer output voltage to a varying DC voltage, which in turn is passed through an electronic filter to convert it to an unregulated DC voltage.A pulsating DC output will be filtered to the three 1000 µF 50 V capacitors. The output will be fed to input of the adjustable LM317 regulator. Also, it goes to the circuit of the cooling having an output of 12V coming from the center connection of the transformer. It also uses LM7412 voltage regulator. Cooling fan is used to lessen the heat dissipated from the components. The 10µF is a decoupler capacitor, which serves as filter to filter out noise for smooth DC output voltage. With that, better results of the output is obtain. Also there is a cooling fan to lessen the heat in the system when used.
Step 2: Prepare the needed materials.
Prepare the following materials or components. Complete first the needed materials before jumping to the next procedure.
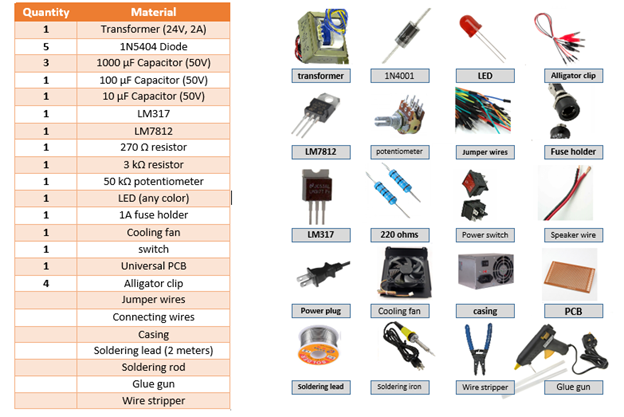
(Note: Photos of each components are not mine, I edited it and made a collage)
LM317 - is an adjustable three-terminal positive-voltage regulator capable of supplying more than 1.5 A over an output-voltage range of 1.25 V to 37 V
LM7812 – is a three terminal device positive voltage regulator with a fixed output voltage of 12 V.
Transformer - converts the 120 V rms line voltage into an ac voltage that will produce a rectified voltage.
Take note: Once you buy resistor and capacitor, check for their respective ratings. All capacitor must be 50 V rating while resistor is one half watt.
Step 3: Construct on breadboard
Once the materials are gathered, construct it on the breadboard first for initial tests. Do not immediately put on the universal PCB to avoid difficulties if there are adjustments to make.
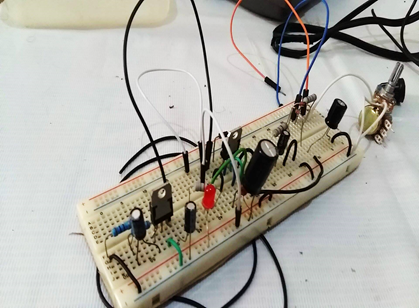
Take note of the pin configuration of the following to avoid damages in components:
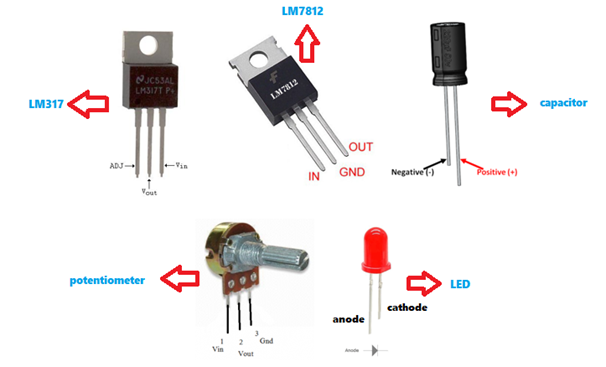
(Note: Photo of each components are not mine, I just edited it and made a collage)
Always check for the connection if there are still components missing and not connected to each other. Most importantly, check the output of the power supply. It must range from 0 V – 28 V.
Step 4: PCB placement and soldering of components in the PCB
If the desired output of 0 – 28 V has met, put the components one by one in the universal PCB. Never forget to inspect the connection of each components. Once placed, it is now ready for the soldering process. Be carefully upon soldering to avoid accidents. Ask for assistance if needed. The efficiency of the power supply depends on the circuitry you made, so attain for the good quality of soldering. Always see the circuit diagram as your guide to lessen faultiness. To ensure that wires are on the proper connection, put a glue to lock it up. As you can see some sticky glue into the connection of the transformer.
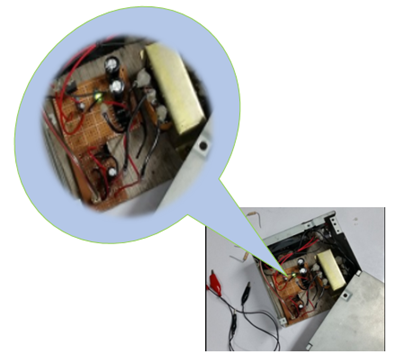
(Photo is mine)
Step 5: Transferring the PCB and other necessary components inside the casing
In this step, you are almost on the finish line. Prepare the casing of your device and carefully transfer the circuitry into it. As much as possible, fixed the tangled wires or use cable ties in fixing them.
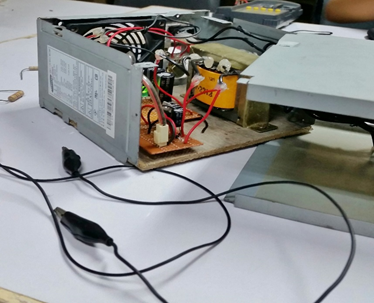
(Photo is mine)
Step 6: Finishing
Lastly, check the connections for the last time. Do not forget the outside appearance of your power supply. Put the potentiometer knob and alligator clip for the connection of your output. Test the final output for validation. Then you are done
I hope you learned something about this post and help you solve some questions in your mind. Remember, knowledge is power. Try it on yourself to see results.
(Some of the photos I used are not mine)
See you on my next tutorials :)