UFOs Special Operations Mind Control Secret Projects Unclassified Part 1

What is a Conspiracy Theory?
A conspiracy theory is an explanation of an event or situation that invokes an unwarranted conspiracy, generally one involving an illegal or harmful act carried out by government or other powerful actors. Conspiracy theories often produce hypotheses that contradict the prevailing understanding of history or simple facts. The term is often a derogatory one. According to the political scientist Michael Barkun, conspiracy theories rely on the view that the universe is governed by design, and embody three principles: nothing happens by accident, nothing is as it seems, and everything is connected. Another common feature is that conspiracy theories evolve to incorporate whatever evidence exists against them, so that they become, as Barkun writes, a closed system that is unfalsifiable, and therefore "a matter of faith rather than proof". A conspiracy theory may take any matter as its subject, but certain subjects attract greater interest than others. Favored subjects include famous deaths, government activities, new technologies, terrorism and questions of alien life. Among the longest-standing and most widely recognized conspiracy theories are notions concerning the assassination of John F. Kennedy, the 1969 Apollo moon landings and the 9/11 terrorist attacks, as well as numerous theories pertaining to alleged plots for world domination by various groups both real and imaginary.

What is a UFO?
A UFO is an" unidentified flying object", these flying objects that are usually disc shaped or similar to the TR-3B aircraft created by the United States military. lets start off with the disc type UFOs.The disc shaped UFOs typically come from the zeta reticuli which is the home star system from the grays which are the typical looking aliens with big grey heads and big black eyes.These discs are powered by a cyclotron bombarding element 115 with protons. when protons fuse with 115 it becomes element 116 but it immediately decays back into element 115 when it decays it releases 2 anti protons this generates energy because when antimatter collides with normal matter it exerts energy.The method of propulsion is kind of interesting because it taps into a gravity wave that we will call gravity A. the gravity A wave is amplified and propagated in a lens method from each of the 3 gravity amplifiers the amplifiers pulse sequentially at a counter clockwise motion at a rate of about 7.46Hz One configuration known as omicron configuration is used when flying near planets. this is possible by lensing the gravity A wave towards by the B wave propagated outward from the planet changing pitch of the gravity A wave determines lift or attraction. in omicron mode only 1 amplifier is needed to hover. however you need a second one to actually move. Another interesting thing is maximum distortion. in this state the gravity. A wave propagated outward from the craft enshrouds the craft is a sort of gravity bubble. in this state the craft is nearly invisible since the light behind the craft bends around the gravity bubble. once the craft achieves maximum distortion, the metal of the craft becomes invisible as well making a sort of windshield. There is also writing on the craft that is not seen anywhere on this planet. Another configuration known as delta configuration. Delta configuration is achieved by focusing the amplified gravity A wave toward a distant point in space time. the crafts reactor is a capable of amplifying the strong nuclear force of the gravity A wave emanating from the element 115, and capable of bending space-time and pulling it towards the intersection of the craft. The craft then makes a small jump to the now near space time and shuts the amplifiers off. So far this is all that is known about the disc like crafts from zeta reticuli.

What is Area 51?
The United States Air Force facility commonly known as Area 51 is a highly classified remote detachment of Edwards Air Force Base, within the Nevada Test and Training Range. According to the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), the correct names for the facility are Homey Airport (ICAO: KXTA) and Groom Lake, though the name Area 51 was used in a CIA document from the Vietnam War. The facility has also been referred to as Dreamland and Paradise Ranch, among other nicknames. The special use airspace around the field is referred to as Restricted Area 4808 North (R-4808N). The base's current primary purpose is publicly unknown; however, based on historical evidence, it most likely supports the development and testing of experimental aircraft and weapons systems (black projects). The intense secrecy surrounding the base has made it the frequent subject of conspiracy theories and a central component to unidentified flying object (UFO) folklore. Although the base has never been declared a secret base, all research and occurrences in Area 51 are Top Secret/Sensitive Compartmented Information (TS/SCI). On 25 June 2013, following a Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) request filed in 2005, the CIA publicly acknowledged the existence of the base for the first time, declassifying documents detailing the history and purpose of Area 51. Area 51 is located in the southern portion of Nevada in the western United States, 83 miles (134 km) north-northwest of Las Vegas. Situated at its center, on the southern shore of Groom Lake, is a large military airfield. The site was acquired by the United States Air Force in 1955, primarily for the flight testing of the Lockheed U-2 aircraft. The area around Area 51, including the small town of Rachel on the "Extraterrestrial Highway", is a popular tourist destination. The original rectangular base of 6 by 10 miles (9.7 by 16.1 km) is now part of the so-called "Groom box", a rectangular area measuring 23 by 25 miles (37 by 40 km), of restricted airspace. The Yucca Mountain nuclear waste repository is 44 miles (71 km) southwest of Groom Lake.

What is Groom Lake?
Nevada Test Range topographic chart centered on Groom Lake. Groom Lake is a salt flat[citation needed] in Nevada used for runways of the Nellis Bombing Range Test Site airport (KXTA) on the north of the Area 51 USAF military installation. The lake at 4,409 ft (1,344 m) elevation is approximately 3.7 miles (6.0 km) from north to south and 3 miles (4.8 km) from east to west at its widest point. Located within the namesake Groom Lake Valley portion of the Tonopah Basin, the lake is 25 mi (40 km) south of Rachel, Nevada.

What is Stargate Project?
The Stargate Project was the code name for a secret U.S. Army unit established in 1978 at Fort Meade, Maryland, by the Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) and SRI International (a California contractor) to investigate the potential for psychic phenomena in military and domestic intelligence applications. The Project, and its precursors and sister projects, went by various code names—GONDOLA WISH, GRILL FLAME, CENTER LANE, SUN STREAK, SCANATE—until 1991 when they were consolidated and rechristened as "Stargate Project". Stargate Project work primarily involved remote viewing, the purported ability to psychically "see" events, sites, or information from a great distance. The project was overseen until 1987 by Lt. Frederick Holmes "Skip" Atwater, an aide and "psychic headhunter" to Maj. Gen. Albert Stubblebine, and later president of the Monroe Institute. The unit was small-scale, comprising about 15 to 20 individuals, and was run out of "an old, leaky wooden barracks". The Stargate Project was terminated and declassified in 1995 after a CIA report concluded that it was never useful in any intelligence operation. Information provided by the program was vague, included irrelevant and erroneous data, and there was reason to suspect that its project managers had changed the reports so they would fit background cues. The program was featured in the 2004 book and 2009 film entitled The Men Who Stare at Goats, although neither mentions it by name. Information in the United States on psychic research in some foreign countries was sketchy and poorly detailed, based mostly on rumor or innuendo from second-hand or tertiary reporting, attributed to both reliable and unreliable disinformation sources from the Soviet Union. The CIA and DIA decided they should investigate and know as much about it as possible. Various programs were approved yearly and re-funded accordingly. Reviews were made semi-annually at the Senate and House select committee level. Work results were reviewed, and remote viewing was attempted with the results being kept secret from the "viewer". It was thought that if the viewer was shown they were incorrect it would damage the viewer's confidence and skill. This was standard operating procedure throughout the years of military and domestic remote viewing programs. Feedback to the remote viewer of any kind was rare; it was kept classified and secret. Remote viewing attempts to sense unknown information about places or events. Normally it is performed to detect current events, but during military and domestic intelligence applications viewers claimed to sense things in the future, experiencing precognition.

What is Operation Mockingbird?
Operation Mockingbird was an alleged large-scale program of the United States Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) that began in the early 1950s and attempted to manipulate news media for propaganda purposes. It funded student and cultural organizations and magazines as front organizations.According to writer Deborah Davis, Operation Mockingbird recruited leading American journalists into a propaganda network and oversaw the operations of front groups. CIA support of front groups was exposed after a 1967 Ramparts magazine article reported that the National Student Association received funding from the CIA. In the 1970s, Congressional investigations and reports also revealed Agency connections with journalists and civic groups. None of these reports, however, mentions an Operation Mockingbird coordinating or supporting these activities.A Project Mockingbird is mentioned in the CIA Family Jewels report, compiled in the mid-1970s. According to the declassified version of the report released in 2007, Project Mockingbird involved the wire-tapping of two American journalists for several months in the early 1960s.
.jpg)
What is Project MkUltra?
Project MKUltra, also called the CIA mind control program, is the code name given to a program of experiments on human subjects, at times illegal, designed and undertaken by the United States Central Intelligence Agency. Experiments on humans were intended to identify and develop drugs and procedures to be used in interrogations and torture in order to weaken the individual to force confessions through mind control. Organized through the Scientific Intelligence Division of the CIA, the project coordinated with the Special Operations Division of the U.S. Army's Chemical Corps. The operation began in the early 1950s, was officially sanctioned in 1953, was reduced in scope in 1964, further curtailed in 1967, and officially halted in 1973. The program engaged in many illegal activities, including the use of unwitting U.S. and Canadian citizens as its test subjects, which led to controversy regarding its legitimacy. MKUltra used numerous methods to manipulate people's mental states and alter brain functions, including the surreptitious administration of drugs (especially LSD) and other chemicals, hypnosis, sensory deprivation, isolation and verbal abuse, as well as other forms of psychological torture.

The Monarch Project ?
Mind control program developed by the CIA, under Project MKULTRA. Monarch represents an important pillar of the New World Order. After the Illuminati saw some of their puppets slipping and expose some truth, all important authorities and celebrities have been replaced by Monarch slaves. Those include moderators, musicians, politicians, actors, sportsmen and more. Those are being mercilessly misused for the Illuminati agenda, to exemplify the human a wrong way of life and condition them on the satanic age.Trauma based mind control, besides HAARP, is a favourite weapon of the Illuminati. Although it is an important mind control instrument, there are more. Also in use are efficient propaganda methods combined with NLP through mass media, systematic mass hypnosis of mankind by subliminal messages with targeted conditioning on the satanic world government, neurochip implantation into innocent people ("targeted individuals" or, TI's) and manipulation of thoughts by HAARP via frequency modulation. Causes "Triggers" Hence the mind of the Monarch slave contains different memory fragments, or even personalities, there's a need for so called "trigger", which can switch the victims alter from one to another. For staying undetected in public, those have to be inconspicuous.Triggers are also being called "keys". Theoretically, any kind of stimulus can be utilised as a trigger. The only thing that matters, is that the slave has to notice it. If, for instance, a victim gets induced a new alter by an electro shock, the electro shock will be the temporary trigger. After the slave spontaneously relapses into the original alter (called: core) by leaving the just created alter, a similar electro shock would trigger him into the same, already existing alter.

What is Project Iceworm?
Project Iceworm is located in Greenland it was the code name for a top secret United States Army program during the Cold War to build a network of mobile nuclear missile launch sites under the Greenland ice sheet. The ultimate objective of placing medium-range missiles under the ice close enough to strike targets within the Soviet Union — was kept secret from the Danish government. To study the feasibility of working under the ice, a highly publicized "cover" project, known as Camp Century, was launched in 1960. Unsteady ice conditions within the ice sheet caused the project to be canceled in 1966. Details of the missile base project were secret for decades, but first came to light in January 1995 during an enquiry by the Danish Foreign Policy Institute (DUPI) into the history of the use and storage of nuclear weapons in Greenland. The enquiry was ordered by the Danish parliament following the release of previously classified information about the 1968 Thule Air Base B-52 crash that contradicted previous assertions by the Danish government. To test the feasibility of construction techniques a project site called "Camp Century" was started by the United States military, located at an elevation of 6,600 feet (2,000 m) in northwestern Greenland, 150 miles (240 km) from the American Thule Air Base. The radar and air base at Thule had already been in active use since 1951. Project Iceworm Coordinates: 77°10′N 61°08′W
What is Project FUBELT?
Project FUBELT (also known as Track II) is the codename for the secret Central Intelligence Agency operations that were to prevent Salvador Allende's rise to power before his confirmation and to promote a military coup in Chile. The highlights of Project FUBELT are cited in declassified US government documents released by the National Security Archive on September 11, 1998, 25 years after the coup, as well as in papers uncovered by a 1975 congressional inquiry. CIA memoranda and reports on Project FUBELT include meetings between United States Secretary of State Henry Kissinger and CIA officials, CIA cables to its Santiago station, and summaries of secret action in 1970, detailing decisions and operations to undermine the election of Salvador Allende in September 1970 and to promote a military coup. In November 1970, the US National Security Council issued National Security Decision Memorandum 93, which replaced FUBELT. Handwritten notes, taken by CIA director Richard Helms, record the orders of President Richard Nixon, to foster a coup in Chile. In the first meeting between Helms and high agency officials on the secret operations codenamed "FUBELT", a special task force under the supervision of CIA Deputy Director for Plans, Thomas Karamessines, is established, headed by veteran agent David Atlee Phillips. The memorandum notes that the CIA must prepare an action plan for National Security Advisor Henry Kissinger within 48 hours. Henry Kissinger, Thomas Karamessines and Alexander Haig (military assistant to Henry Kissinger), in a meeting on October 15, 1970, discuss promoting a coup in Chile, known as "Track II" of covert operations. Kissinger orders the CIA to "continue keeping the pressure on every Allende weak spot in sight. In a secret cable, Thomas Karamessines conveyed Kissinger's orders to CIA station chief in Santiago, Henry Hecksher: "It is firm and continuing policy that Allende be overthrown by a coup." The CIA ran a series of secret operations intended to push President Eduardo Frei Montalva to support "a military coup which would prevent Allende from taking office on 3 November." After Salvador Allende's election, the United States considered trying to get Chile expelled from the Organization of American States. Embassy officers and the State Department Policy Planning office called for the cutting off of economic and military assistance to Pinochet's government on human rights grounds, but were overruled by the Ambassador and officials of The Pentagon and Treasury Department.

What is Project Mogul?
Project Mogul (sometimes referred to as Operation Mogul) was a top secret project by the US Army Air Forces involving microphones flown on high-altitude balloons, whose primary purpose was long-distance detection of sound waves generated by Soviet atomic bomb tests. The project was carried out from 1947 until early 1949. The project was moderately successful, but was very expensive and was superseded by a network of seismic detectors and air sampling for fallout, which were cheaper, more reliable, and easier to deploy and operate. Project Mogul was conceived by Maurice Ewing who had earlier researched the deep sound channel in the oceans and theorized that a similar sound channel existed in the upper atmosphere: a certain height where the air pressure and temperature result in minimal speed of sound, so that sound waves would propagate and stay in that channel due to refraction. The project involved arrays of balloons carrying disc microphones and radio transmitters to relay the signals to the ground. It was supervised by James Peoples, who was assisted by Albert P. Crary. One of the requirements of the balloons was that they maintain a relatively constant altitude over a prolonged period of time. Thus instrumentation had to be developed to maintain such constant altitudes, such as pressure sensors controlling the release of ballast. The early Mogul balloons consisted of large clusters of rubber meteorological balloons, however, these were quickly replaced by enormous balloons made of polyethylene plastic. These were more durable, leaked less helium, and also were better at maintaining a constant altitude than the early rubber balloons. Constant-altitude-control and polyethylene balloons were the two major innovations of Project Mogul.

What is Roswell?
In mid-1947, a United States Army Air Forces balloon crashed at a ranch near Roswell, New Mexico. Following wide initial interest in the crashed "flying disc", the US military stated that it was merely a conventional weather balloon. Interest subsequently waned until the late 1970s, when ufologists began promoting a variety of increasingly elaborate conspiracy theories, claiming that one or more alien spacecraft had crash-landed, and that the extraterrestrial occupants had been recovered by the military, who then engaged in a cover-up. In the 1990s, the US military published two reports disclosing the true nature of the crashed object: a nuclear test surveillance balloon from Project Mogul. Nevertheless, the Roswell incident continues to be of interest in popular media, and conspiracy theories surrounding the event persist. Roswell has been described as "the world's most famous, most exhaustively investigated, and most thoroughly debunked UFO claim" The sequence of events was triggered by the crash of a Project Mogul balloon near Roswell.

What is the Bell?
Die Glocke "The Bell" was a purported top secret Nazi scientific technological device, secret weapon, or Wunderwaffe. Described by Polish journalist and author Igor Witkowski in Prawda o Wunderwaffe (2000), it was later popularized by military journalist and author Nick Cook as well as by writers such as Joseph P. Farrell (fr) and others who associate it with Nazi occultism and antigravity or free energy research.

What is S.E.T.I
SETI is an acronym for the Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence. It is the science of using telescopes, radio and optical, to search the skies for signals from alien civilizations. The search for extraterrestrial intelligence is a collective term for scientific searches for intelligent extraterrestrial life, for example, monitoring electromagnetic radiation for signs of transmissions from civilizations on other planets.The idea of SETI began in 1959 with the publication of a paper in the British journal Nature by Giuseppe Cocconi and Philip Morrison.

What is The Manhattan Project?
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project was under the direction of Major General Leslie Groves of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Nuclear physicist Robert Oppenheimer was the director of the Los Alamos Laboratory that designed the actual bombs. The Army component of the project was designated the Manhattan District; "Manhattan" gradually superseded the official codename, Development of Substitute Materials, for the entire project. Along the way, the project absorbed its earlier British counterpart, Tube Alloys. The Manhattan Project began modestly in 1939, but grew to employ more than 130,000 people and cost nearly US $2 billion (about $22 billion in 2016 dollars). Over 90% of the cost was for building factories and to produce fissile material, with less than 10% for development and production of the weapons. Research and production took place at more than 30 sites across the United States, the United Kingdom, and Canada.Two types of atomic bombs were developed concurrently during the war: a relatively simple gun-type fission weapon and a more complex implosion-type nuclear weapon. The Thin Man gun-type design proved impractical to use with plutonium so a simpler gun-type called Little Boy was developed that used uranium-235, an isotope that makes up only 0.7 percent of natural uranium. Chemically identical to the most common isotope, uranium-238, and with almost the same mass, it proved difficult to separate the two.

What is Majestic 12?
In UFO conspiracy theories, Majestic 12 (or MJ-12) is the code name of an alleged secret committee of scientists, military leaders, and government officials, formed in 1947 by an executive order by U.S. President Harry S. Truman to facilitate recovery and investigation of alien spacecraft. The concept originated in a series of supposedly leaked secret government documents first circulated by ufologists in 1984. Upon examination, the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) declared the documents to be "completely bogus", and many ufologists consider them to be an elaborate hoax. Majestic 12 remains popular among some UFO conspiracy theorists and the concept has appeared in popular culture including television, film and literature.

Operation Merlin
United States covert operation under the Clinton Administration to provide Iran with a flawed design for a component of a nuclear weapon ostensibly in order to delay the alleged Iranian nuclear weapons program, or to frame Iran.

Operation Paperclip
Secret program of the Joint Intelligence Objectives Agency (JIOA) in which more than 1,600 German scientists, engineers, and technicians, such as Wernher von Braun and his V-2 rocket team, were recruited in post-Nazi Germany and taken to the U.S. for government employment, primarily between 1945 and 1959; many were former members and some were former leaders of the Nazi Party. The primary purpose for Operation Paperclip was U.S. military advantage in the Russo–American Cold War, and the Space Race. The Soviet Union were more aggressive in forcibly recruiting (at gunpoint) some 2,000 German scientists with Operation Osoaviakhim during one night.[citation needed] The Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) established the first secret recruitment program, called Operation Overcast, on July 20, 1945, initially "to assist in shortening the Japanese war and to aid our postwar military research". The term "Overcast" was the name first given by the German scientists' family members for the housing camp where they were held in Bavaria. In late summer 1945, the JCS established the Joint Intelligence Objectives Agency (JIOA), a subcommittee of the Joint Intelligence Community, to directly oversee Operation Overcast and later Operation Paperclip. The JIOA had one representative of each member agency of the Joint Intelligence Committee: the army's director of intelligence, the chief of naval intelligence, the assistant chief of Air Staff-2 (air force intelligence), and a representative from the State Department. In November 1945, Operation Overcast was renamed Operation Paperclip by Ordnance Corps (United States Army) officers, who would attach a paperclip to the folders of those rocket experts whom they wished to employ in America. In a secret directive circulated on September 3, 1946, President Truman officially approved Operation Paperclip and expanded it to include one thousand German scientists under "temporary, limited military custody"

Operation Washtub
Top-secret program In the event of a Russian invasion of Alaska, the FBI and U.S. Air Force had a plan: make ordinary, average Alaskans into federal agent–like spies that could report back to Washington and survive in hiding from the enemy.

Project 1794
As part of a mass declassification of a number of secrets in 2012, the U.S. Air Force revealed that its Aeronautical Systems Division had plans to produce a UFO-style aircraft back in the 1950s. (Of course, they didn’t release the reason why they needed one, but we’ll leave that up to your imagination.) The flying disc–shaped vehicle was supposed to reach speeds of Mach 4; an altitude of 100,000 feet; and have a range of over 1,000 nautical miles. The brakes were put on the project in 1961.
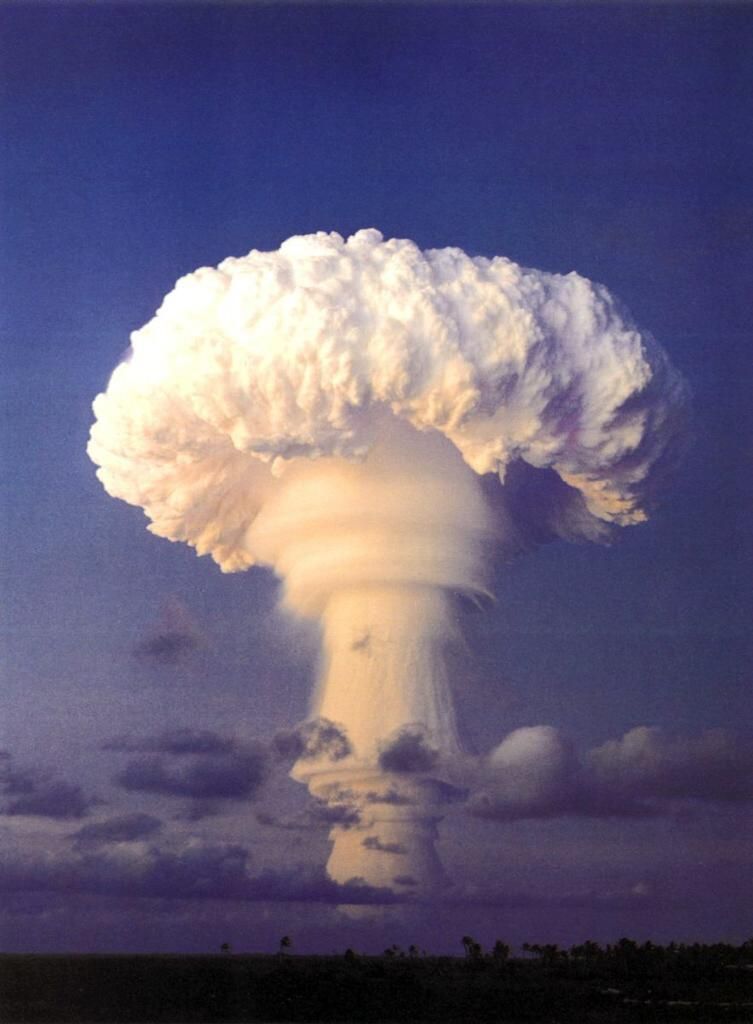

Operation Argus
High-altitude nuclear tests were conducted, these under Operation Argus was Nuclear tipped missiles were fired from ships for the first time as part of Argus. On August 27, 30 and September 6, 1950, nuclear warheads were shot into space by X-17 rockets from the deck of a US warship anchored off South Africa. These missiles went 300 miles out into space. The reason for these nuclear tests in outer space? One scientist theorized that exploding nuclear bombs in the Earths magnetic field (but above the Earth’s atmosphere) could create an electronic pulse that would render incoming Russian ICBM’s inoperative. Though a magnetic pulse was created by the nuclear explosions, the pulse was not large enough to have any affect on the ICBM’s. The project was another dangerous, and ultimately futile, experiment.

What is Project Orion?
Project Orion was a study of a spacecraft intended to be directly propelled by a series of explosions of atomic bombs behind the craft (nuclear pulse propulsion). Early versions of this vehicle were proposed to take off from the ground with significant associated nuclear fallout; later versions were presented for use only in space. 6 tests were launched.
The idea of rocket propulsion by combustion of explosive substance was first proposed by Russian explosives expert Nikolai Kibalchich in 1881, and in 1891 similar ideas were developed independently by German engineer Hermann Ganswindt. General proposals of nuclear propulsion were first made by Stanislaw Ulam in 1946, and preliminary calculations were made by F. Reines and Ulam in a Los Alamos memorandum dated 1947. The actual project, initiated in 1958, was led by Ted Taylor at General Atomics and physicist Freeman Dyson, who at Taylor's request took a year away from the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton to work on the project.The Orion concept offered high thrust and high specific impulse, or propellant efficiency, at the same time. The unprecedented extreme power requirements for doing so would be met by nuclear explosions, of such power relative to the vehicle's mass as to be survived only by using external detonations without attempting to contain them in internal structures. As a qualitative comparison, traditional chemical rockets—such as the Saturn V that took the Apollo program to the Moon—produce high thrust with low specific impulse, whereas electric ion engines produce a small amount of thrust very efficiently. Orion would have offered performance greater than the most advanced conventional or nuclear rocket engines then under consideration. Supporters of Project Orion felt that it had potential for cheap interplanetary travel, but it lost political approval over concerns with fallout from its propulsion.Such later proposals have tended to modify the basic principle by envisioning equipment driving detonation of much smaller fission or fusion pellets, although in contrast Project Orion's larger nuclear pulse units (nuclear bombs) were based on less speculative technology.

Dr Freezelove
Not a project really but a mission. On January 21, 1968, a fire started on board a B52G bomber during a secret mission over Greenland. Most of the crew bailed out and the aircraft smashed into the Greenland ice sheet. On impact, the high explosives in at least three of the atomic bombs on board exploded. This spread radioactive plutonium, tritium and uranium over a large area. The CIA and US military now had a real Project 57 on their hands. The fire melted the ice and at least one atomic bomb fell into North Star Bay and below the ice covered sea. Apparently the US tried to recover the bomb but was unsuccessful. Even though project 57 had provided lots of data about what happens when a nuclear warhead explodes and spreads radioactive contamination over a wide area, the military and CIA still did not have a permanent emergency response unit dedicated, equipped and trained to respond to these dirty bomb like disasters. So an ad-hoc group of scientists and military people were put together and sent to Greenland for what would become the toughest dirty bomb clean up operation in history. With temperatures dropping to – 70 F and winds up to 100 mph, the conditions made it all but impossible for the men to clean up all of the radioactive contamination. Less than 50% of the radioactive material was recovered. The crew cleaned and froze for eight months and when they were done had cleaned up 10,500 tons of radioactive ice, snow and crash debris, which was flown to South Carolina for disposal. The crew would call themselves “Dr Freezelove”.

What is Project 57
This was a “safety test” conducted at the Nevada Test Site to simulate what would happen if an airplane carrying an atomic bomb crashed and released radioactive material into the environment. In this way, Project 57 would become America’s first “dirty bomb” experiment. Scientists theorized that the detonation of the high explosives surrounding a nuclear warhead (but that did not initiate a full chain reaction) would release plutonium into the environment. But they did not know for certain, nor did they know how much plutonium would be released, how far the plutonium would travel, etc. The military and CIA felt the test was needed because more and more American nuclear warheads were being carried by more and more aircraft. Sooner or later (and it would come sooner than anyone thought), an airplane accident was bound to happen when the aircraft was carrying live nuclear weapons. A part of the test site called Area 13 was selected and workers began to set up thousands of “sticky pans”, steel pans sprayed with a sticky resin that would capture and hold plutonium particles released into the air by the explosion of the bomb. Mock cities were set up to determine what would happen if the explosion occurred in an urban area. Fourteen hundred blocks of asphalt streets were laid, and cars parked at various locations on the asphalt. Nine burros, 109 beagles, 10 sheep and 31 rats were placed in cages to measure the physical impact of the plutonium release. At 6:27 AM on April 24, 1957, the nuclear warhead was fired in such a way as to mimic a plane crash. When the radioactive dust settled, 895 square acres had been contaminated. Plutonium is one of the most deadly substances known to man; one millionth of a gram of plutonium is lethal if it is inhaled. Plutonium remains deadly for 20,000 years. Scientists learned much about how plutonium acts by studying the effects on the test animals, but the actual data is still classified. They also found that the plutonium did not move far – it tended to settle on the top of the soil and stay there. After a year of study, Project 57 was shut down and the area never cleaned up. It was fenced off, the material (including the cars) were buried. That was it, or so the scientists thought, until the following year when another scientist authored a paper theorizing that earth worms passing through the contaminated area would move the plutonium with them, out of the restricted zone (as would birds which ate the worms and flew off with the radioactivity in them).

Kiwi
In the 1960’s, the US was on its way to the moon. Lesser known is the fact that, at area 25 (a sister top secret site to Area 51) of the Nevada Test Site, NASA and AEC scientists were working on something even more ambitious – a trip to Mars on a nuclear powered rocket. This was called project Nuclear Engine Rocket Vehicle Application or NERVA. Sixteen stories tall, the rocket ship, called Orion, would send 150 men to Mars in only 124 days. Orion would blast off from eight 250-foot-tall towers out of a cloud of radioactivity generated by a powerful nuclear reactor and engine aboard the ship. When running at full power the nuclear engine operated at 3,680 degrees Fahrenheit; it had to be cooled by liquid hydrogen gas. To test such a monster engine and reactor it had to be bolted down to the earth. When tested, the NERVA engine would shoot into the atmosphere a plume of hydrogen exhaust that had passed through a super-heated uranium fission reactor. The Los Alamos scientists then decided they wanted to know what would happen if scientists lost control of one of these nuclear engines, and it exploded. Thus was born Kiwi – a test to deliberately blow up one of these reactor/engines. On January 12, 1965, a nuclear rocket engine, codenamed Kiwi, was allowed to overheat. At a temperature of 4,000 degrees Centigrade, the reactor burst – shooting radioactive fuel skyward, glowing every color of the rainbow. The explosion blew a 100-pound chunk of radioactive fuel a quarter mile away. The radioactive plume rose to 2,600 feet, and the wind eventually carried the radioactive cloud west, passing over Los Angeles and out to sea. Scientists were airborne with instruments measuring the amount of radiation that was released into the atmosphere, but as of today that data remains classified. Though this was passed off as another “safety test”, the release of so much radiation into the atmosphere possibly violated the Limited Test Ban Treaty of 1963, that banned the airborne explosion of atomic bombs. But scientists now knew what they needed. If the rocket engine exploded on the launch pad – anyone standing within 100 feet would die almost immediately from radiation exposure. Anyone within 400 feet would receive a serious does of radiation that could be fatal, and anyone within 1000 feet would be overexposed to radiation. Five months later, the real thing took place when another design of the nuclear rocket engine, code named Phoebus, did overheat. It exploded when one of the liquid hydrogen cooling tanks accidentally ran dry.

Project Kempster-Lacroix
In the development of America’s first stealth aircraft, dubbed “Oxcart”, all manner of new technology was created at Area 51 to make the aircraft invisible to radar, or at least as small a radar image as could be achieved. Materials that would absorb radar, space age design and electronic counter measures were all employed. Yet when President Kennedy gave Oxcart it’s mission to fly surveillance over Cuba to look for nuclear missiles being secretly installed there by the Soviet Union, the aircraft was still not quite ready. Researchers and scientists redoubled their efforts, but it was decided that Oxcart was still not stealthy enough. Some other way had to be found to make it all but invisible to enemy radar.Project Kemper-Lacroix was one possible solution. At Area 51, scientists came up with the idea of attaching two giant electron guns, one on either side of the aircraft. The guns would shoot out a 25-foot wide ion cloud of highly charged particles in front of the aircraft (an aircraft which was already moving at speeds above Mach 3). The ion gas cloud would further absorb enemy radar waves coming up from the ground, providing the plane with more stealth. Testing on scale models of the Oxcart aircraft showed the theory would work. Testing the electron beam guns on the full scale Oxcart aircraft, the researchers soon discovered the radiation given off by the guns would kill the pilot. So more engineers worked on developing an x-ray shield the pilots could wear to protect them from the radiation. But the first test pilot to wear the shield said it was too cumbersome to allow the pilots to fly the aircraft. Project Kemper-Lacroix was abandoned.

Project Teak and Orange
Perhaps the most wrong-headed, ill-advised and dangerous of all the atmospheric nuclear explosions by the US, Projects Teak and Orange were right out of a science fiction story about mad scientists and their crazy experiments leading to the destruction of the planet.Teak and Orange were two massive, 3.8 megaton nuclear devices which would be detonated in the Earths upper atmosphere over the Johnston Atoll, 750 miles west of Hawaii. Teak was exploded at 50 miles and Orange was exploded at 28 miles in the upper atmosphere. The purpose of these tests was to give the US a measuring stick to use so as to determine if the Soviet Union did the same thing (exploded a nuclear device high in the Earths atmosphere). As if such an explosion would be difficult to detect? It seems mad now, looking back, that such tests were green-lighted, but that was the mood of the Cold War in the 1950’s and 1960’s. Test first, ask questions later. How obvious is it to explode a 3.8 megaton nuclear device 28-50 miles up? The fireballs produced burned the retinas of any living thing within a 225 mile radius of the blast. Anything that had been looking at the sky when the blast occurred, without protective goggles was blinded. This included hundreds of monkeys and rabbits flown in aircraft nearby. The animals had their heads locked into devices that forced them to look at the blast. From Guam to Wake Island to Maui, the blue sky turned red, white and gray, creating an aura over a 2,100 mile section of the meridian. Radio communication throughout a huge part of the Pacific went dead. One of the weapons test engineers stated it chillingly – “we almost blew a hole in the ozone layer”. In fact, prior to the explosions scientists had warned that it would be possible to blast a hole in the Earths protective ozone layer, but Teak and Orange went ahead regardless.

Project Aquiline
This project began sometime in the late 1960’s and involved some of the first remote controlled aircraft experiments that would later become the Predator drones that are operating in the Middle East, today. It was a six-foot remote controlled drone designed to look like an eagle or buzzard in flight. It carried a television camera in the nose, as well as sensors and electronic surveillance equipment. The project began as an attempt to investigate a mysterious watercraft the Soviet Union had constructed and was spotted testing (by satellite reconnaissance) on the Caspian Sea (that they later nicknamed the Caspian Monster). The project remains classified today, but a British documentary uncovered what is thought to have been the target for the Aquiline drone – a Soviet hydrofoil called Ekranopian. The Aquiline drone was designed to track in on its target following established communication lines in foreign countries, and be launched from a submarine. The Aquiline drone was built and tested (it crash landed often) but the CIA eventually canceled the program.

Project Nutmeg
Top-secret project that gave birth to the Nevada Test and Training Range. Prior to testing atomic devices on US soil, nuclear bombs were tested in the Pacific Ocean at what was called the Pacific Proving Grounds. While this afforded the US a remote (and huge) area to test secret atomic devices, the cost involved in sending men, materials and equipment half way around the world, was staggering. America felt it had to find someplace secure, yet within its borders that was reasonably close to where most atomic scientists were working at that time (such as Los Alamos, New Mexico). Project Nutmeg was authorized by the President to locate such an area. An ideal location was a region of desolate desert that had been a wildlife reservation. This area also had the benefit of already having a landing strip nearby, left over from military training exercises during WWII. The selected site in Nevada became 687 square miles of government-controlled land, and what we know today as the Nevada Test Site (of which Area 51 is the most well know, and most secret, parcel of land).
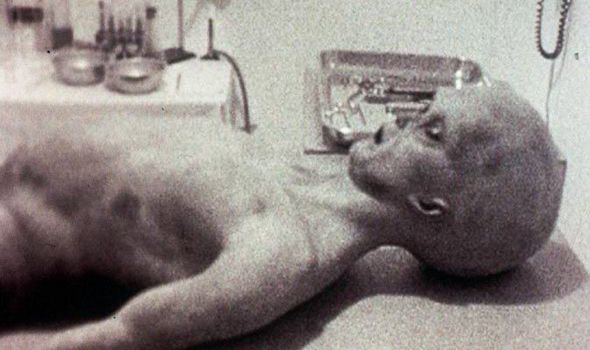
Sigma-Four
In July 1947, the US military and Army intelligence recovered something that crashed at Roswell, New Mexico. The initial report was it was a crashed flying saucer and the bodies that were recovered were alien. The military quickly changed this story to it being a weather balloon, and so began the mystery of what really happened at Roswell, and the most famous UFO incident in American history. The author of “Area 51” postulates that it was what was really recovered at Roswell that led to the creation of Area 51, in 1951. Something so stunning that an entire secret area had to be established for it to be studied. Immediately after the crash, the recovered material and bodies were sent to Wright Field (later called Wright-Patterson Air Force Base) in Ohio. The Atomic Energy Commission, under the direction of Vannevar Bush, then took over, created Area 51 and moved it all to Area 51, in Nevada. According to the author, what the US really recovered at Roswell was not a spacecraft with aliens from outer space, but a Soviet aircraft with unknown and mysterious flying capabilities. The US knew the crashed aircraft was of Soviet, and not other-worldly, design because Russian language lettering had been found on the crashed remains. The aircraft had capabilities no one in Area 51, or anyone else, had ever seen. The aircraft could both hover and fly. No US technology at the time could do such a thing. Vannevar Bush ordered six selected engineers, working in total secrecy, to reverse engineer it and figure out how it worked. The project would be so secret, it would remain black forever, it would never be known outside a mere handful of people, such as Bush. The operation would have no name, it would simply go by a letter-number designation, S-4 or Sigma-Four. But there was more……..The engineers also had to reverse engineer the bodies recovered from the crash scene. Not alien bodies, human bodies. But human bodies like none ever seen – mutated, surgically altered children. Two of the child-size aviators were still “alive”, but not conscious, in a comatose state. They were kept alive in life-support chambers at Area 51, so they could be studied. They were tiny even for children, and had very large heads compared to the rest of their bodies. They were estimated to be thirteen years old, and also had oversized eyes. The engineers who would experiment on these aviators were told it was possible Nazi doctor Joseph Mengele had operated on them (in exchange for a promise by Stalin to get his own laboratory in Russia, a promise Stalin did not keep) before he escaped Europe for South America. But why would the Soviet Union send their cutting edge technology aircraft, with their biologically/surgically modified alien looking tiny human children, to the US? The author states the engineers were told Stalin believed the craft would land, and the children-aliens would emerge and send the US into a panic far worse than had occurred only a decade earlier, with the fake alien attack during the radio broadcast of “War of the Worlds”. Stalin believed the US populace would panic at the sight of “real aliens”.
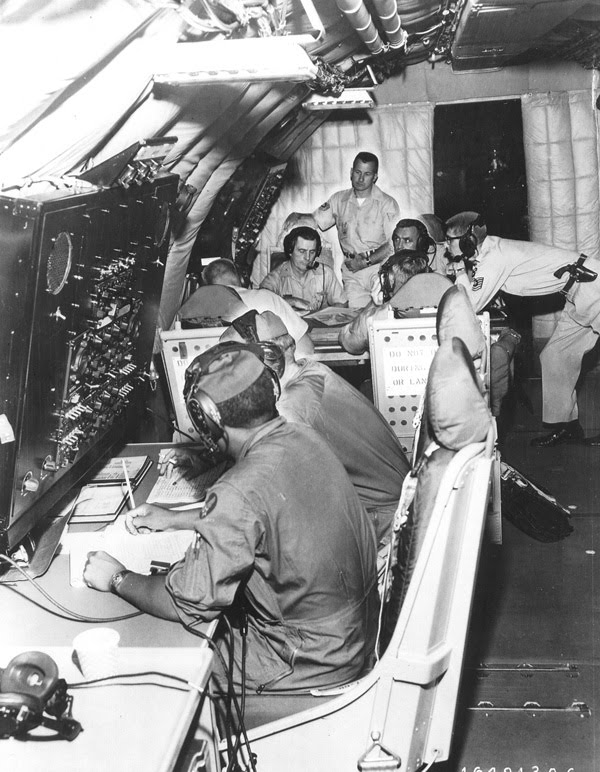

Operation Looking Glass
Code name for an airborne command and control center operated by the United States. In more recent years it has been more officially referred to as the ABNCP (Airborne Command Post). It provides command and control of U.S. nuclear forces in the event that ground-based command centers have been destroyed or otherwise rendered inoperable. In such an event, the general officer aboard the Looking Glass serves as the Airborne Emergency Action Officer (AEAO) and by law assumes the authority of the National Command Authority and could command execution of nuclear attacks. The AEAO is supported by a battle staff of approximately 20 people, with another dozen responsible for the operation of the aircraft systems. The name Looking Glass, which is another word for a mirror, was chosen for the Airborne Command Post because the mission operates in parallel with the underground command post at Offutt Air Force Base.

What is the F-117?
The Lockheed Have Blue prototype stealth fighter (a smaller proof-of-concept model of the F-117 Nighthawk) first flew at Groom in December 1977. In 1978, the Air Force awarded a full-scale development contract for the F-117 to Lockheed Corporation's Advanced Development Projects. On 17 January 1981 the Lockheed test team at Area 51 accepted delivery of the first full Scale Development (FSD) prototype 79–780, designated YF-117A. At 6:05 am on 18 June 1981 Lockheed Skunk Works test pilot Hal Farley lifted the nose of YF-117A 79–780' off the runway of Area 51. Meanwhile, Tactical Air Command (TAC) decided to set up a group-level organization to guide the F-117A to an initial operating capability. That organization became the 4450th Tactical Group (Initially designated "A Unit"), which officially activated on 15 October 1979 at Nellis AFB, Nevada, although the group was physically located at Area 51. The 4450th TG also operated the A-7D Corsair II as a surrogate trainer for the F-117A, and these operations continued until 15 October 1982 under the guise of an avionics test mission.Flying squadrons of the 4450th TG were the 4450th Tactical Squadron (Initially designated "I Unit") activated on 11 June 1981, and 4451st Tactical Squadron (Initially designated "P Unit") on 15 January 1983. The 4450th TS, stationed at Area 51, was the first F-117A squadron, while the 4451st TS was stationed at Nellis AFB and was equipped with A-7D Corsair IIs painted in a dark motif, tail coded "LV".

Project A119
A Study of Lunar Research Flights (Project A119), was a top-secret plan developed in 1958 by the United States Air Force. The aim of the project was to detonate a nuclear bomb on the Moon which would help in answering some of the mysteries in planetary astronomy and astrogeology. If the explosive device detonated on the surface, not in a lunar crater, the flash of explosive light would have been faintly visible to people on earth with their naked eye, a show of force resulting in a possible boosting of domestic morale in the capabilities of the United States, a boost that was needed after the Soviet Union took an early lead in the Space Race and was also working on a similar project.
The project was never carried out, being cancelled primarily out of a fear of a negative public reaction, with the potential militarization of space that it would also have signified, and because a moon landing would undoubtedly be a more popular achievement in the eyes of the American and international public alike. A similar project by the Soviet Union also never came to fruition.The existence of the US project was revealed in 2000 by a former executive at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), Leonard Reiffel, who led the project in 1958. A young Carl Sagan was part of the team responsible for predicting the effects of a nuclear explosion in vacuum and low gravity and in evaluating the scientific value of the project. The project documents remained secret for nearly 45 years, and despite Reiffel's revelations, the United States government has never officially recognized its involvement in the study.

What is Aurora?
Rumored in the mid-1980s as an American reconnaissance aircraft. There is no substantial evidence that it was ever built or flown and it has been termed a myth. The U.S. government has consistently denied such an aircraft was ever built. Aviation and space reference site Aerospaceweb.org concluded, "The evidence supporting the Aurora is circumstantial or pure conjecture, there is little reason to contradict the government's position." Former Skunk Works director Ben Rich confirmed that "Aurora" was simply a myth in "Skunk Works", a book detailing his days as the director. Mr. Rich wrote that a young Colonel working in the Pentagon arbitrarily assigned the name "Aurora" to the funding for the B-2 bomber design competition and somehow the name was leaked to the media. Others come to different conclusions. In 2006, veteran black project watcher and aviation writer Bill Sweetman said, "Does Aurora exist? Years of pursuit have led me to believe that, yes, Aurora is most likely in active development, spurred on by recent advances that have allowed technology to catch up with the ambition that launched the program a generation ago." The Aurora legend started in March 1990, when Aviation Week & Space Technology magazine broke the news that the term "Aurora" had been inadvertently included in the 1985 U.S. budget, as an allocation of $455 million for "black aircraft production" in FY 1987. According to Aviation Week, Project Aurora referred to a group of exotic aircraft, and not to one particular airframe. Funding of the project allegedly reached $2.3 billion in fiscal 1987, according to a 1986 procurement document obtained by Aviation Week. In the 1994 book Skunk Works, Ben Rich, the former head of Lockheed's Skunk Works division, wrote that the Aurora was the budgetary code name for the stealth bomber fly-off that resulted in the B-2 Spirit.
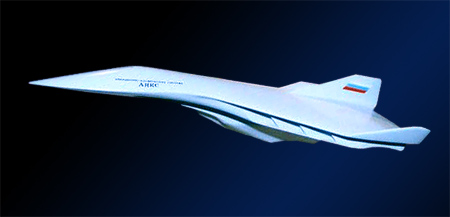
What is Ayaks?
The Ayaks (Russian: АЯКС, meaning also 'Ajax') is a hypersonic aircraft program started in the Soviet Union and currently under development in Russia by the Saint Petersburg Institute for the Hypersonic Systems of Leninets Holding Company.In the early 1980s, Soviet scientists began to explore a new type of aircraft. The Ayaks was to be a new Soviet spaceplane capable of flying and conducting a wide range of missions in the mesosphere, for both military and civilian purposes. The original concept revolved around a hypersonic reconnaissance aircraft project, but later was expanded into the wider concept of hypersonic multi-purpose military and civilian jets, as well as a platform for launching satellites. The mesosphere is the layer of the Earth's atmosphere from 50 kilometres (160,000 ft) to 85 kilometres (279,000 ft) high, above the stratosphere and below the thermosphere. It is very difficult to fly in the mesosphere — the air is too rarefied for aircraft wings to generate lift, but sufficiently dense to cause aerodynamic drag on satellites. In addition, parts of the mesosphere fall inside the ionosphere, meaning the air is ionized due to solar radiation. When the aircraft reaches hypersonic speed, it uses the heating energy from air friction to increase the heat capacity of the fuel ("reform" the fuel). The aircraft has double shielding between which water and ordinary, cheap kerosene circulates. The energy of surface heating is used to break up water into hydrogen and oxygen. Thus, the heating capacity of the fuel increases, and the surface of the aircraft cools down. The whole concept is named "Magneto-plasmo-chemical engine"

What is SR-72?
The Lockheed Martin SR-72 is a conceptualized hypersonic UAV intended for intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance proposed by American company Lockheed Martin to succeed the retired Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird.

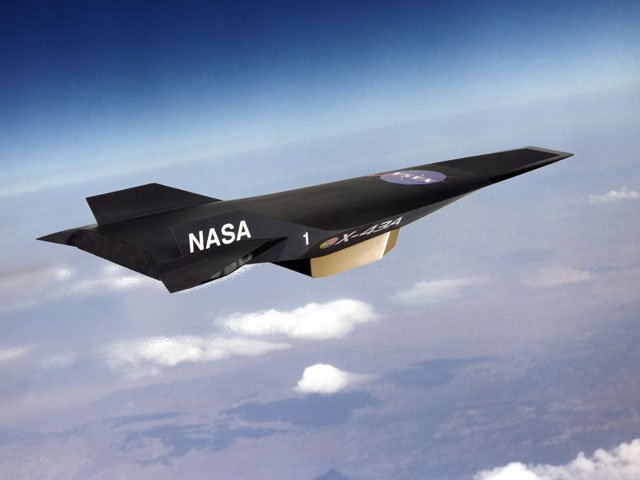
What is X-51
The Boeing X-51 Waverider is an unmanned research scramjet experimental aircraft for hypersonic flight at Mach 5 (3,300 mph; 5,300 km/h) and an altitude of 70,000 feet (21,000 m). The aircraft was designated X-51 in 2005. It completed its first powered hypersonic flight on 26 May 2010. After two unsuccessful test flights, the X-51 completed a flight of over six minutes and reached speeds of over Mach 5 for 210 seconds on 1 May 2013 for the longest duration powered hypersonic flight. Waverider refers in general to aircraft that take advantage of compression lift produced by their own shock waves. The X-51 program was a cooperative effort by the United States Air Force, DARPA, NASA, Boeing, and Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne. The program was managed by the Aerospace Systems Directorate within the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL). X-51 technology is proposed for use in the High Speed Strike Weapon (HSSW), a Mach 5+ missile which could enter service in the mid-2020s. In the 1990s, the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) began the HyTECH program for hypersonic propulsion. Pratt & Whitney received a contract from the AFRL to develop a hydrocarbon-fueled scramjet engine which led to the development of the SJX61 engine. The SJX61 engine was originally meant for the NASA X-43C, which was eventually canceled. The engine was applied to the AFRL's Scramjet Engine Demonstrator program in late 2003. The scramjet flight test vehicle was designated X-51 on 27 September 2005.
X-51A under the wing of a B-52 at Edwards Air Force Base, July 2009 In flight demonstrations, the X-51 is carried by a B-52 to an altitude of about 50,000 feet (15 km; 9.5 mi) and then released over the Pacific Ocean. The X-51 is initially propelled by an MGM-140 ATACMS solid rocket booster to approximately Mach 4.5 (3,000 mph; 4,800 km/h). The booster is then jettisoned and the vehicle's Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne SJY61 scramjet accelerates it to a top flight speed near Mach 6 (4,000 mph; 6,400 km/h). The X-51 uses JP-7 fuel for the SJY61 scramjet, carrying some 270 lb (120 kg) on board.

What is a ScramJet?
A scramjet (supersonic combusting ramjet) is a variant of a ramjet airbreathing jet engine in which combustion takes place in supersonic airflow. As in ramjets, a scramjet relies on high vehicle speed to compress the incoming air forcefully before combustion (hence ramjet), but whereas a ramjet decelerates the air to subsonic velocities before combustion, the airflow in a scramjet is supersonic throughout the entire engine. That allows the scramjet to operate efficiently at extremely high speeds.