UFOs Special Operations Mind Control Secret Projects Unclassified Part 2

What was the Kecksburg UFO incident?
The Kecksburg UFO incident occurred on December 9, 1965, at Kecksburg, Pennsylvania, United States. A large, brilliant fireball was seen by thousands in at least six U.S. states and Ontario, Canada. It streaked over the Detroit, Michigan – Windsor, Canada area, reportedly dropped hot metal debris over Michigan and northern Ohio, starting some grass fires, and caused sonic booms in the Pittsburgh metropolitan area. It was generally assumed and reported by the press to be a meteor after authorities discounted other proposed explanations such as a plane crash, errant missile test, or reentering satellite debris. However, eyewitnesses in the small village of Kecksburg, about 30 miles southeast of Pittsburgh, claimed something crashed in the woods. A boy said he saw the object land; his mother saw a wisp of blue smoke arising from the woods and alerted authorities. Another reported feeling a vibration and "a thump" about the time the object reportedly landed. Others from Kecksburg, including local volunteer fire department members, reported finding an object in the shape of an acorn and about as large as a Volkswagen Beetle. Writing resembling Egyptian hieroglyphs was also said to be in a band around the base of the object. Witnesses further reported that intense military presence, most notably the United States Army, secured the area, ordered civilians out, and then removed an object on a flatbed truck. The military claimed they searched the woods and found "absolutely nothing."The Tribune-Review from nearby Greensburg which had a reporter at the scene ran an article the next morning, "Unidentified Flying Object Falls near Kecksburg—Army Ropes off Area". The article continued, "The area where the object landed was immediately sealed off on the order of U.S. Army and State Police officials, reportedly in anticipation of a 'close inspection' of whatever may have fallen ... State Police officials there ordered the area roped off to await the expected arrival of both U.S. Army engineers and possibly, civilian scientists." However, a later edition of the newspaper stated that nothing had been found after authorities searched the area. The official explanation of the widely seen fireball was that it was a mid-sized meteor. However speculation as to the identity of the Kecksburg object (if there was one—reports vary) range from alien craft to debris from Kosmos 96, a Soviet space probe intended for Venus but which failed and never left the Earth's atmosphere. Similarities have been drawn between the Kecksburg incident and the Roswell UFO incident, leading to the former being referred to as "Pennsylvania's Roswell."

HyperSoar
The HyperSoar was an American hypersonic aircraft project developed at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL). It was to be capable of flying at around Mach 12 (9,200 mph, 14,700 km/h), allowing it to transit between any two points on the globe in under two hours. The HyperSoar was predicted to be a passenger plane capable of skipping outside the atmosphere to prevent it from burning up in the atmosphere. A trip from Chicago to Tokyo (10,123 kilometers) would take 18 skips, or 72 minutes. It was planned to use hydrocarbon-based engines outside the atmosphere and experimental jet engine technology with testing to begin by 2010. Later, the Hypersoar concept was acquired from LLNL by DARPA, and in 2002 it was combined with the USAF X-41 Common Aero Vehicle to form the FALCON program.
What is Prompt Global Strike?
Prompt Global Strike (PGS) is a United States military effort to develop a system that can deliver a precision-guided conventional weapon airstrike anywhere in the world within one hour, in a similar manner to a nuclear ICBM. Such a weapon would allow the United States to respond far more swiftly to rapidly emerging threats than is possible with conventional forces. A PGS system could also be useful during a nuclear conflict, potentially replacing the use of nuclear weapons against 30% of targets. The PGS program encompasses numerous established and emerging technologies, including conventional surface-launched missiles and air- and submarine-launched hypersonic missiles, although no specific PGS system has yet been finalized as of 2015. The PGS system is intended to complement existing American rapid-response forces, such as Forward Deployed Forces, Air Expeditionary Groups (which can deploy within 48 hours) and carrier battle groups (which can respond within 96 hours). Possible delivery systems for PGS warheads. In 2010, the United States Air Force prototyped a PGS system based on a modified Minuteman III ICBM. In March 2011, Air Force Major General David Scott stated that the service had no plans to use a sea- or land-based ICBM system for Prompt Global Strike, as they would be expensive to develop and potentially "dangerous." Instead, efforts would focus on a hypersonic glider. However, the following day, Chief of Staff of the United States Air Force Norton Schwartz said that an ICBM-based PGS system was still an option.

What is RQ-170?
RQ-170 Sentinel is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) developed by Lockheed Martin and operated by the United States Air Force (USAF) for the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). While the USAF has released few details on the UAV's design or capabilities, defense analysts believe that it is a stealth aircraft fitted with aerial reconnaissance equipment. The RQ-170 Sentinel was developed by Lockheed Martin's Skunk Works as a stealth Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV). Journalists have noted design similarities between the RQ-170 and previous stealth and UAV programs such as the RQ-3 DarkStar and Polecat. It is a tailless flying wing aircraft, with pods, presumably for sensors or SATCOMs, built into the upper surface of each wing. Few details of the UAV's characteristics have been released, but estimates of its wingspan range from approximately 65 feet (20 m) to 90 feet (27 m). In a December 2012 report, journalist David Axe stated that "20 or so" RQ-170s had been built. The "RQ" designation indicates that the RQ-170 Sentinel does not carry weapons. Aviation Week's David A. Fulghum believes that the UAV is probably a "tactical, operations-oriented platform and not a strategic intelligence-gathering design". The USAF confirmed the "grainy photos of a gray, flying-wing-typed unmanned airplane near Kandahar Airfield."Since then, this aircraft has been known as "The Beast of Kandahar" in relation to the discussion of the RQ-170 Sentinel on 4 December 2009. A USAF colonel subsequently commented that RQ-170 is separate from the MQ-X program, which has yet to determine stealth or powerplant requirements, and thus the Sentinel will not replace the MQ-1 Predator and MQ-9 Reaper drones. As of May 2011, the U.S. military had not released any statements concerning the Sentinel since December 2009.

What is UH-60 Black Hawk?
The Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk is a four-bladed, twin-engine, medium-lift utility helicopter manufactured by Sikorsky Aircraft. Sikorsky submitted the S-70 design for the United States Army's Utility Tactical Transport Aircraft System (UTTAS) competition in 1972. The Army designated the prototype as the YUH-60A and selected the Black Hawk as the winner of the program in 1976, after a fly-off competition with the Boeing Vertol YUH-61. Named after the Native American war leader Black Hawk, the UH-60A entered service with the U.S. Army in 1979, to replace the Bell UH-1 Iroquois as the Army's tactical transport helicopter. This was followed by the fielding of electronic warfare and special operations variants of the Black Hawk. Improved UH-60L and UH-60M utility variants have also been developed. Modified versions have also been developed for the U.S. Navy, Air Force, and Coast Guard. In addition to U.S. Army use, the UH-60 family has been exported to several nations. Black Hawks have served in combat during conflicts in Grenada, Panama, Iraq, Somalia, the Balkans, Afghanistan, and other areas in the Middle East. The UH-60 entered service with the U.S. Army's 101st Combat Aviation Brigade of the 101st Airborne Division in June 1979. The U.S. military first used the UH-60 in combat during the invasion of Grenada in 1983, and again in the invasion of Panama in 1989. Highly modified H-60s were employed during the U.S. Special Operations mission that resulted in the death of Osama bin Laden on 1 May 2011. One such MH-60 helicopter crash-landed during the operation, and was destroyed by the team before it departed in the other MH-60 and a backup MH-47 Chinook with bin Laden's remains. Two MH-47s were used for the mission to refuel the two MH-60s and as backups. News media reported that the Pakistani government granted the Chinese military access to the wreckage of the crashed 'stealth' UH-60 variant in Abbotabad; Pakistan and China denied the reports, and the U.S. Government has not confirmed Chinese access.

Project MKNAOMI
MKNAOMI was the code name for a joint Department of Defense/CIA research program lasting from the 1950s through the 1970s. Unclassified information about the MKNAOMI program and the related Special Operations Division is scarce. It is generally reported to be a successor to the MKDELTA project and to have focused on biological projects including biological warfare agents—specifically, to store materials that could either incapacitate or kill a test subject and to develop devices for the diffusion of such materials.

What is Project Sign?
Project Sign was an official U.S. government study of unidentified flying objects (UFOs) undertaken by the United States Air Force and active for most of 1948. The final report published in early 1949 stated that while some UFOs appeared to represent actual aircraft, there was not enough data to determine their origin. It was first disclosed to the public in 1956 via the book The Report on Unidentified Flying Objects by retired Air Force Captain Edward J. Ruppelt. The full files for Sign were declassified in 1961.
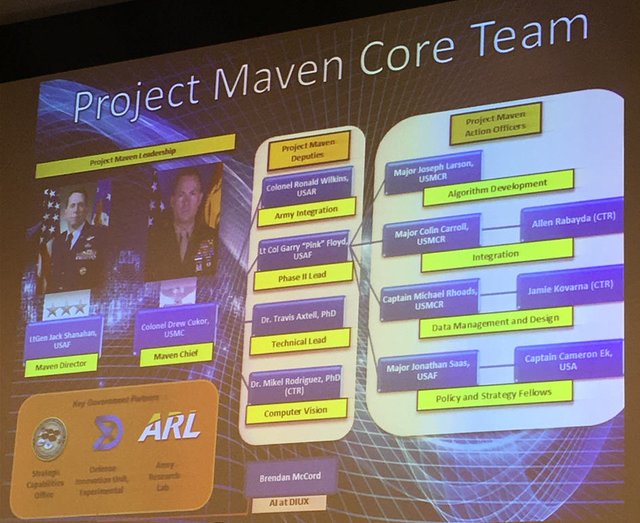
What is AWCFT?
he Algorithmic Warfare Cross-Functional Team (AWCFT) is a fast-moving effort launched in April 2017 by the U.S. Deputy Defense Secretary to accelerate the Department of Defense's integration of big data, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. Also known as Project MAVEN, the AWCFT's first task involved the development and integration of computer vision algorithms needed to augment and assist military and civilian analysts that are heavily encumbered by the sheer volume of Full-Motion Video (FMV) data the DoD collects. While the AWCFT's work against the FMV problem is ongoing, progress has been encouraging, and the AWCFT is now preparing to partner with industry to integrate big data and machine learning against other challenging problem sets across the Defense Intelligence Enterprise. In Project Maven Phase II, the AWCFT will continue to aggressively pursue its objective of turning the enormous volume of data available to the DoD into actionable intelligence and insights at speed.
What is Project Maven?
Project Maven is a crash Defense Department program that was designed to deliver AI technologies—specifically, technologies that involve deep learning neural networks—to an active combat theater within six months from when the project received funding.Project Maven have already been successfully deployed in the fight against ISIS and its success foreshadows enormous opportunities ahead—as well as enormous organizational, ethical, and strategic challenges. Project MAVEN, the AWCFT’s first task was to develop computer vision algorithms to help military and civilian analysts deal enormous amounts of full-motion video. Progress has been encouraging, and now the AWCFT is focusing on applying big data and machine learning against other challenging problems. Program experts are trying to apply computer vision algorithms to data processing, exploitation and dissemination. Efforts center on developing computer vision models for wide-area motion imagery; full-motion video from tactical unmanned aircraft; using cloud computing for video processing and dissemination; index and search for model output databases; artificial intelligence interfaces; and video support for forward-deployed warfighters. Researchers eventually want to expand a prototype from the analysis of vertical image and video to document analysis; natural language processing for machine translation and gisting; optical character recognition; horizontal still photo video object and persona identification; horizontal video object and persona identification; cognitive computing for target systems analysis and entity relationship identification; and other areas using machine learning approaches. Army researchers are inviting all businesses engaged in artificial intelligence and machine learning to submit their capabilities. This all-day event will allow businesses to engage their counterparts, create synergy, and ask questions.

What is Project RESISTANCE
U.S. that might pose threats to CIA facilities and personnel. From 1967 to 1973, many local police departments, college campus staff members, and other independent informants collaborated with the CIA to keep track of student radical groups that opposed the U.S. government's foreign policies on Vietnam. Project RESISTANCE and its twin program, Project MERRIMAC were both coordinated by the CIA Office of Security. In addition, the twin projects were branch operations that relayed civilian information to their parent program, Operation CHAOS.

What is Operation CHAOS?
Operation CHAOS or Operation MHCHAOS was the code name (CIA cryptonym) of a United States Central Intelligence Agency domestic espionage project targeting the American people from 1967 to 1974, established by President Johnson and expanded under President Nixon, whose mission was to uncover possible foreign influence on domestic race, anti-war and other protest movements. The operation was launched under Director of Central Intelligence (DCI) Richard Helms by chief of counter-intelligence James Jesus Angleton, and headed by Richard Ober. The "MH" designation is to signify the program had a worldwide area of operations.
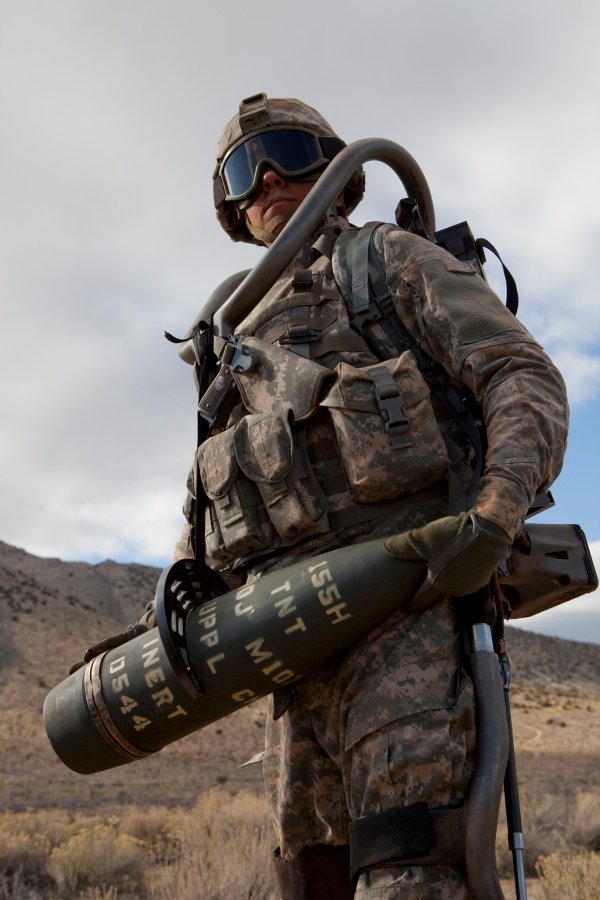

What is HULC?
Human Universal Load Carrier, or HULC, is an un-tethered, hydraulic-powered anthropomorphic exoskeleton developed by Professor H. Kazerooni and his team at Ekso Bionics. It is intended to help soldiers in combat carry a load of up to 200 pounds at a top speed of 10 miles per hour for extended periods of time. After being under development at Berkeley Robotics and Human Engineering Laboratory since 2000, the system was announced publicly at the AUSA Winter Symposium on February 26, 2009 when an exclusive licensing agreement was reached with Lockheed Martin. Although the exoskeleton is powered and can be used, the project was a failure as it hindered certain movements and actually increased strain on muscles, going directly against what a powered exoskeleton is supposed to do.

What is the AATIP?
The Advanced Aviation Threat Identification Program (AATIP) was a secret investigatory effort funded by the United States government to study unidentified flying objects, but it was not classified. It was first made public on December 16, 2017. The program began in 2007, with funding of $22 million over the five years until the available appropriations were ended in 2012. The program began in the U.S. Defense Intelligence Agency. Although the official AATIP program has ended, a related group of interested professionals have extended the effort in a nonprofit organization called, 'To the Stars Academy of Arts & Science.
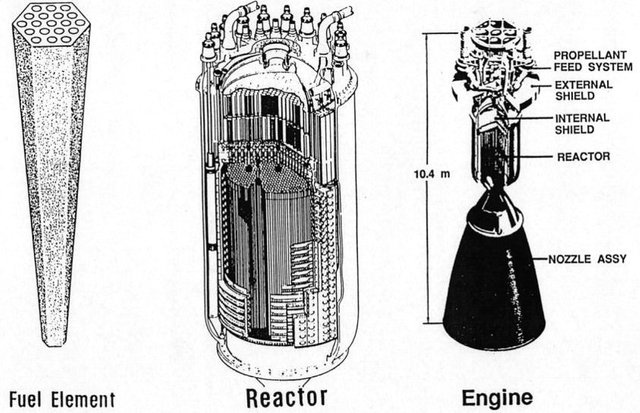
What is NERVA?
The Nuclear Engine for Rocket Vehicle Application (NERVA) was a U.S. nuclear thermal rocket engine development program that ran for roughly two decades. NERVA was a joint effort of the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) and NASA, managed by the Space Nuclear Propulsion Office (SNPO) until both the program and the office ended at the end of 1972. NERVA demonstrated that nuclear thermal rocket engines were a feasible and reliable tool for space exploration, and at the end of 1968 SNPO certified that the latest NERVA engine, the NRX/XE, met the requirements for a human mission to Mars. Although NERVA engines were built and tested as much as possible with flight-certified components and the engine was deemed ready for integration into a spacecraft, much of the U.S. space program was cancelled by Congress before a manned mission to Mars could take place.NERVA was considered by the AEC, SNPO and NASA to be a highly successful program; it met or exceeded its program goals. Its principal objective was to "establish a technology base for nuclear rocket engine systems to be utilized in the design and development of propulsion systems for space mission application". Virtually all space mission plans that use nuclear thermal rockets use derivative designs from the NERVA NRX or Pewee.
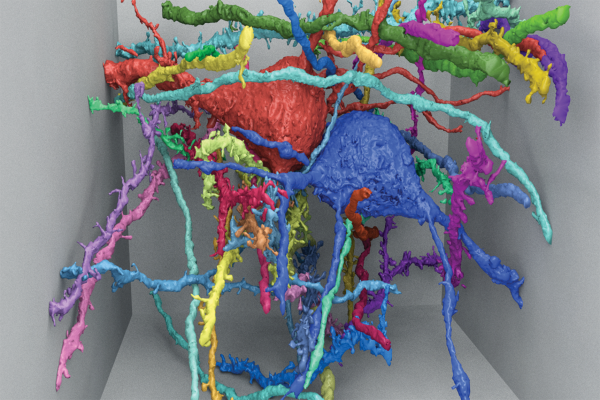
What is MICrONS
Machine Intelligence from Cortical Networks (MICrONS) seeks to revolutionize machine learning by reverse-engineering the algorithms of the brain. The program is expressly designed as a dialogue between data science and neuroscience. Participants in the program will have the unique opportunity to pose biological questions with the greatest potential to advance theories of neural computation and obtain answers through carefully planned experimentation and data analysis. Over the course of the program, participants will use their improving understanding of the representations, transformations, and learning rules employed by the brain to create ever more capable neurally derived machine learning algorithms. Ultimate computational goals for MICrONS include the ability to perform complex information processing tasks such as one-shot learning, unsupervised clustering, and scene parsing, aiming towards human-like proficiency. The Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA) MICrONS program (Machine Intelligence from Cortical Networks) is a five-year project with the goal of Reverse engineering one cubic millimeter of a rodent's brain tissue and use insights from its study to improve machine learning and artificial intelligence. The program is part of the White House BRAIN Initiative.

What is Desert Prowler?
The image of the Wraith from the Shangri-La album cover was used on a flight test patch for the Lockheed Martin Skunk Works' Black Ops Desert Prowler program.
The patch features the Wraith, with added red eyes, surrounded by six stars with the words "Desert Prowler, Alone and on the Prowl." The patch on the left says "Flight Test" on it, which is unlike other versions of the patch. The one on the right has lots of symbols on it. The figure on the Desert Prowler patch originally comes from an "Insane Clown Posse" album. "I'm not sure who used this image first, but I know that the EXACT same image was released on a significantly popular album release from the rap group "the Insane Clown Posse". The album was entitled "The Wraith", after the man on the cover of the album (the figure)... NOW... this group had been releasing albums in previous years, calling their first one their "1st Joker's Card", the second their "2nd Joker's Card", etc. etc.. When "The Wraith" was released, it was their final and "6th Joker's Card". This COULD explain why there are 6 stars surrounding the figure in the patch."The six stars depicted on the patch are also regularly associated with activities at "Area 51" (Five plus one = six stars, get it?) The U.S. Air Force assigns official names to its warplanes—and they’re sometimes pretty lame. A-10 Thunderbolt II. F-16 Fighting Falcon. B-52 Stratofortress. B-1 Lancer.Airmen inevitably give the planes unofficial nicknames that are way awesomer. A-10 Warthog. F-16 Viper. B-52 Buff. B-1 Bone. Now, four years after its public unveiling, we’ve confirmed the nickname of the secretive, radar-evading RQ-170 Sentinel drone that has snooped on Iran, North Korea and China and helped Navy SEALs find and kill Osama Bin Laden in Pakistan. It’s the RQ-170 Wraith. A wraith is a ghost. It’s a fitting name considering the Lockheed Martin-made drone’s ability to evade radar detection, thanks to its flying wing shape and, apparently, special radiation-absorbing coatings. The RQ-170 is the result of a crash program in the early 2000s to finally restore the Air Force’s ability to spy inside the borders of heavily armed enemies. The Mach-3 SR-71 Blackbird manned recon plane had performed that role from the 1960s until its retirement in the late 1990s. Lockheed built an estimated 20 or 30 RQ-170s and the Air Force assigned them to the 30th Reconnaissance Squadron at the remote Tonopah Test Range in Nevada. RQ-170s, presumably fitted with cameras and radars, were spotted flying over Iraq during the build-up to the 2003 U.S.-led invasion. The drones continued on to Afghanistan and were photographed several times starting in 2007 by journalists at NATO’s Kandahar Air Field in the country’s south. In 2009, the 30th Recon Squadron took its RQ-170s on a tour of America’s main Pacific bases, including a stopover in South Korea. The Air Force copped the spy ‘bot’s existence in December 2009. In 2010, the stealth drones were at Al Dhafra, the sprawling air base the U.S. leases from the United Arab Emirates for spy flights over Iran. When Navy SEALs raided Bin Laden’s Pakistan compound in May 2011, an RQ-170 was overhead. And in December 2011, one of the drones crashed on the Afghanistan-Iran border, presumably while surveilling Iranian targets—possibly including the country’s nuclear program. The wreckage was seized by Iranian agents and put on display for propaganda purposes. Tehran later claimed it could copy the drone’s technology. Buy ‘Shadow Wars: Chasing Conflict in an Era of Peace.’ The satellite-controlled RQ-170s have been fairly silent since the crash. There have been no further spottings and the Air Force has not provided more information on the drones’ deployments. According to Aviation Week reporters Amy Butler and Bill Sweetman, the Air Force is testing a bigger, stealthier RQ-180 drone, made by Northrop Grumman, to eventually replace the RQ-170. But for now the RQ-170s supposedly remain active. To find out more, we used the federal Freedom of Information Act to acquire Air Force Air Combat Command’s official annual history for 2010. While heavily redacted, the history does include a telling footnote. In January 2010, Air Combat Command circulated a document entitled “RQ-170 Sentinel ‘Wraith’ Capabilities Briefing.” It’s the only official mention we’ve seen of the drone’s nickname.

What is Operation Talpiot?
Talpiot program is an elite Israel Defense Forces (IDF) training program, for recruits who have demonstrated outstanding academic ability in the sciences and leadership potential. Graduates of the Talpiot program pursue double higher education while serving in the army, and then utilize their expertise to further IDF research and development in technological leadership positions. The program was inaugurated in 1979. The initiators of the program were Professor Felix Dothan and Professor Shaul Yatziv of the Hebrew University, who submitted the idea to the Israeli chief of staff Rafael Eitan. The idea was to harness human creativity, which peaks early,[citation needed] to develop new technologies for the army. The program is sponsored by the Israeli Air Force and IDF Administration for the Development of Weapons and the Technological Industry, and run under the auspices of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. During their initiation period, the cadets study for their B.Sc. in physics and mathematics (some of them in computer science – according to their choice) at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem in Air Force uniform, while also undergoing different periods of field training designed to familiarize them with all branches of the IDF (infantry level 04 basic training, combat engineering course, armored corps course, artillery corps course, instruction in military tactics etc.). At the end of the course, which lasts 40 months, the cadets receive the rank of first lieutenant (segen) and a B.Sc. and become integrated in R&D in the IDF and Israel Military Industries, or alternatively, in various combat positions, if they so choose. In addition to the three years obligated by the Israeli law, the service includes six years of standing army service in a wide variety of positions. The total program, including military service, is nine years.The first class had 25 cadets. Later, the class was increased to 50–60. The applicant pool consists of nearly ten-thousand top scorers in a test taken by all graduating high school seniors. 150–200 potential applicants are then subjected to a two-day series of tests. These include further IQ exams, as well as group-tasks designed to test one's social dynamics, all conducted under the supervision of trained psychologists and military personnel. For example, teams of applicants are given a specific task then the instructions are changed while the test is in progress, such as shortening the allotted time or changing the assigned tasks. Final acceptance into the program entails a high security clearance rating, given by the Air Force.In February 2016 a book called "Israel's Edge: The Story of IDF's Most Elite Unit - Talpiot" was released and written by CNBC executive producer Jason Gewirtz and published by Gefen in Jerusalem about the unit and the history of how it came into existence.

Project Ornithopter and Insectothopter
Similar to the Aquiline project, this was another attempt by the CIA to mimic the animal kingdom in the development of remote controlled aircraft. Project Ornithopter involved a birdlike drone designed to blend in with nature by flapping its wings. Another even smaller drone was designed to look like a crow that would land on window ledges and photograph, through the window, what was going on inside the building. Project Insectothopter took the concept to an even smaller animal – a drone designed to look like a dragonfly. Insectothopter was a green drone that flapped wings powered by miniature gas engines. Not satisfied with mimicking mother nature – the CIA also used actual animals to do surveillance, including pigeons with “pigeon-cams” attached to their necks. Unfortunately, the birds were tired out by the extra weight of the cameras and returned to the CIA base on foot – too tired to fly (the project was abandoned). Maybe the strangest project of all was Project Acoustic Kitty, which placed acoustic listening devices on household cats. That project was abandoned when the cats strayed too far off target searching for food, and one was run over by a car.

What is Reaction Engines Scimitar?
The Reaction Engines Scimitar is a derivative of the SABRE engine technology, but intended for jet airliners (the Reaction Engines A2 concept), rather than space launch applications. Consequently, most of the Scimitar engine technology is similar to SABRE but designed for much longer life. Both engines are designed around existing gas turbine,[citation needed] and ramjet technology, but the Scimitar engine lacks the rocket features and has high bypass features for greater efficiency. The engines burn liquid hydrogen as fuel. The incorporation of lightweight heat exchangers in the main thermodynamic cycles of these engines is a new feature to aerospace propulsion.[citation needed] Similar studies of intercoolers used on jet engines show significant improvement of efficiency.

What is IARPA?
The Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA) is an organization within the Office of the Director of National Intelligence responsible for leading research to overcome difficult challenges relevant to the United States Intelligence Community. IARPA characterizes its mission as follows: "To envision and lead high-risk, high-payoff research that delivers innovative technology for future overwhelming intelligence advantage." IARPA funds academic and industry research across a broad range of technical areas, including mathematics, computer science, physics, chemistry, biology, neuroscience, linguistics, political science, and cognitive psychology. Most IARPA research is unclassified and openly published. IARPA transfers successful research results and technologies to other government agencies. Notable IARPA investments include quantum computing, superconducting computing, and forecasting tournaments.IARPA is known for its programs to fund research into anticipatory intelligence, using data science to make predictions about future events ranging from the political elections to disease outbreaks to cyberattacks, some of which focus on open-source intelligence. IARPA has pursued these objectives not only through traditional funding programs but also through tournaments and prizes. Other projects involve analysis of images or video that lacks metadata by directly analyzing the media's content itself. Examples given by IARPA include determining the location of an image by analyzing features such as placement of trees or a mountain skyline, or determining whether a video is of a baseball game or a traffic jam. Another program focuses on developing speech recognition tools that can transcribe arbitrary languages. IARPA is also involved in high-performance computing and alternative computing methods. In 2015, IARPA was named as one of two foundational research and development agencies in the National Strategic Computing Initiative, with the specific charge of "future computing paradigms offering an alternative to standard semiconductor computing technologies". One such approach is cryogenic superconducting computing, which seeks to use superconductors such as niobium rather than semiconductors to reduce the energy consumption of future exascale supercomputers. Several programs at IARPA focus on quantum computing and neuroscience. IARPA is a major funder of quantum computing research due to its applications in quantum cryptography. As of 2009, IARPA was said to provide a large portion of quantum computing funding resources in the United States. Quantum computing research funded by IARPA was named Science Magazine's Breakthrough of the Year in 2010, and physicist David Wineland was a winner of the 2012 Nobel Prize in Physics for quantum computing research funded by IARPA. IARPA is also involved in neuromorphic computation efforts as part of the U.S. BRAIN Initiative and the National Nanotechnology Initiative's Grand Challenge for Future Computing. IARPA's MICrONS project seeks to reverse engineer one cubic millimeter of brain tissue and use insights from its study to improve machine learning and artificial intelligence.

What is Blackswift?
The Blackswift was a proposed aircraft capable of hypersonic flight designed by the Lockheed Martin Skunk Works, Boeing, and ATK. The USAF states that the "Blackswift flight demonstration vehicle will be powered by a combination turbine engine and ramjet, an all-in-one power plant. The turbine engine accelerates the vehicle to around Mach 3 before the ramjet takes over and boosts the vehicle up to Mach 6." Dr. Steven Walker, the Deputy Director of DARPA's Tactical Technology Office (acting Director as of January, 2017), will be coordinating the project. In October 2008 it was announced that HTV-3X or Blackswift did not receive needed funding in the fiscal year 2009 defense budget and had been canceled. The Hypersonic Cruise Vehicle program will continue with reduced funding.

2037 Bomber
The 2037 Bomber is the unofficial name given to a heavy strategic bomber planned by the United States Air Force, intended to serve as a replacement for the Northrop Grumman B-2 Spirit. The aircraft is projected to enter service in 2037 as a stealth, supersonic, long-range bomber aircraft with capability for unmanned operation. With the ending of B-2 Spirit production in 2000, the U.S. Air Force was left with a gap in its bomber development. A new bomber would be needed in the 2037 time frame to replace retiring B-52s and B-1 Lancers according to the Air Force's Bomber Roadmap, released in 1999.This was considered too long to wait, so the Air Force commenced the Next-Generation Bomber program (later the Long Range Strike Bomber program).

What is the Falcon Project?
The DARPA Falcon Project (Force Application and Launch from CONtinental United States) is a two-part joint project between the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) and the United States Air Force (USAF) and is part of Prompt Global Strike. One part of the program aims to develop a reusable, rapid-strike Hypersonic Weapon System (HWS), now retitled the Hypersonic Cruise Vehicle (HCV), and the other is for the development of a launch system capable of accelerating an HCV to cruise speeds, as well as launching small satellites into earth orbit. FALCON (Force Application and Launch from CONtinental United States) program announced in 2003 had two major components: a small launch vehicle for carrying payloads to orbit or launching the hypersonic weapons platform payload, and the hypersonic vehicle itself. This two-part program was announced in 2003 and continued into 2006.
I am always curious about UFO! Thanks for your post! upvoted
Thanks for the upvote! I like UFO's too!

Lots of interesting information, Steven Greer said that there could be an alien false flag attack by the secret global government(my own words),if so what type of technology do you think they would use.
Really is- like as soon as I post this list all of a sudden "russia" has everything way better than "us". Things like FIRESIGN and others do have implications for upcoming false flags stay tuned in for more about that.