Understanding Motor Nameplate | revealing the essential information in a single nameplate
Good day Steemians..
It’s been days since my last post. Today’s post is somewhat different from what is been used to, which is #tutorials. This post is more on theoretical information about electrical motors. It talks about all the information written in a nameplate.
When we buy a brand-new gadgets or appliances, we are looking for is specifications. Specifications may be written on a small piece of paper or in a booklet. These specifications tell the consumer what he need to know about the gadget. Usually, consumers are looking first for the specifications before the price. In electrical motors, this information is written in a nameplate.

source
Motor nameplate must be present in all electrical motors and it should be clear. Understanding its information can be hard in some ways because some are written in codes, but this is essential. Most countries require the manufacturers to display all information on the nameplate, but often not the case maybe because all information will not fit in a single nameplate.
Here are the 19 essential information on the nameplate
- Voltage
- Frequency
- Phase
- Current
- Type
- Power factor
- kW or Horsepower
- Full-load Speed
- Efficiency
- Duty
- Insulation Class
- Maximum ambient temperature
- Altitude
- Enclosure
- Frame
- Bearings
- NEMA – Letter code
- NEMA – Design letter
- NEMA – Service factor
This 19 information can be categorized in the following:
- Electrical Input
- Mechanical Input
- Performance
- Reliability
- Construction
- NEMA
Let’s discuss the information
Electrical Input
1. Voltage
This data tells us what voltage is needed for the motor to operate. The parameters of motors such as efficiency, torque, current is rated at voltage and frequency. Motor will failed its performance when use at different voltages.
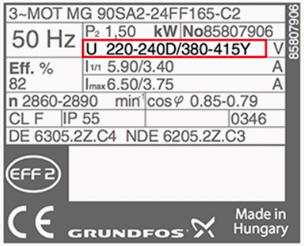
2. Frequency
Motor input frequency is usually rated at 50 or 60 Hertz. Changing the frequency will also change some parameters of motor, same happen with voltage.
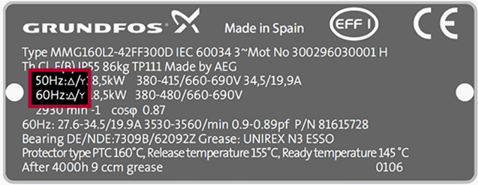
3. Phase
It represents number of AC power lines. Motors can operate in single or three phase ac power lines and these are the standard power lines.

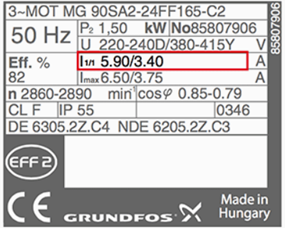
4. Current
It corresponds to the rated power output together with frequency and voltage. This also may deviate from the nameplate rating if phases are not balanced or voltage turns lower.
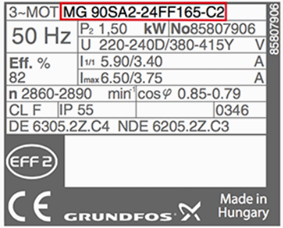
5. Type
It defines motor as single phase or poly phase, single speed or multi speed or the construction type.
6. Power factor
It is the expression of the ratio of active power to apparent power in percentage. Indicated on nameplate as “PF” or “P.F” or Cosine of phi.
Mechanical Input
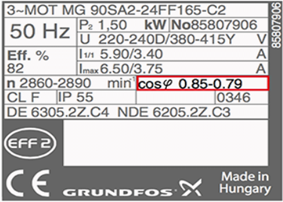
1. kW or Horsepower
it is the motor’s mechanical output rating which is the ability to deliver torque need for load.
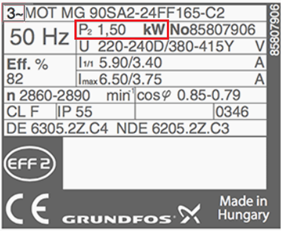
2. Full-load speed
The speed at rated full-load torque delivered at rated output power. Normally given RPM (revolution per minute)
Performance
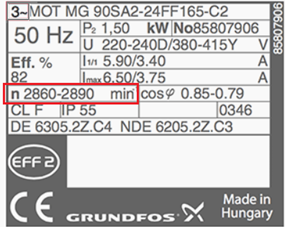
1. Efficiency
The output power of motor divided by input power multiplied by 100, usually in percentage.

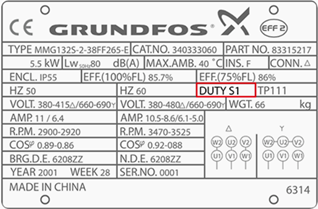
2. Duty
Defines length of time at which motor can carry its nameplate rating safely.
Reliability
1. Insulation Class
An expression of standard classification on thermal tolerance of motor winding.
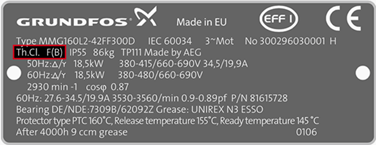
2. Maximum Ambient temperature
It is the maximum ambient temperature in which the motor can operate. For EFF2 motors the maximum is 40 °C and for EFF1 motors is 60 °C
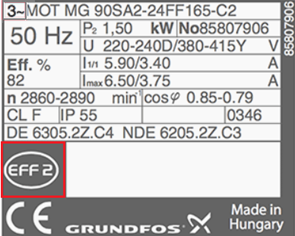
3. Altitude
Shows the maximum height above sea level which motor remains within design temperature rise. If not indicated, maximum height is 1000 meters.
Construction
1. Enclosure
Classifies a motor to its degree of protection from environment and method of cooling. Shown as IP or ENCL on nameplate
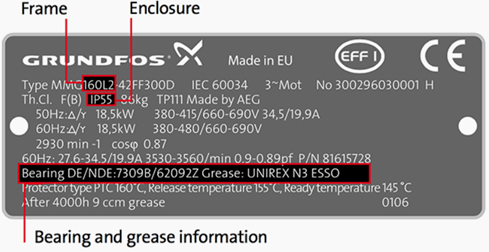
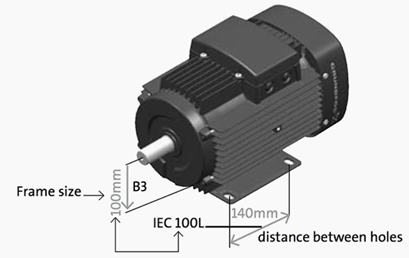
2. Frame
Frame size is an important information on nameplate. it determines the mount dimensions such as foot hole mount pattern and shaft height. It is often part of type designation which can be difficult in interpreting because special shaft or mount configurations are being used.
3. Bearings
This is the component in motor that requires maintenance often. Information usually given for both drive-end (DE) bearing and non drive-end (NDE)
NEMA
1. Letter Code
It defines the locked rotor current kVA on a per horsepower basis. Letter code consists of letters from A to V. Farther away from letter code A, it means higher inrush current per horsepower.
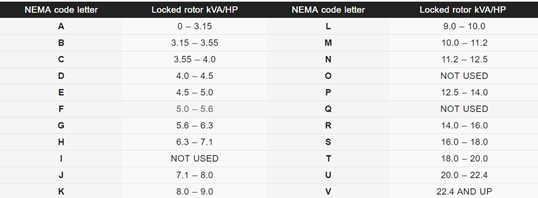
2. Letter Design
It covers the characteristics of both torque and current of motor. Design letter (A, B, C or D) defines in different category. Usually motors are design in A or B motors.
3. Service Factor
When a motor is designed to operate nameplate power rating has a service factor of 1, this means the motor can operate at 100% of rated power.
Here is my source. You can check on this for more information
http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/19-essential-information-you-can-find-on-motor-nameplate
Thank you for your time. Have a great day.
Best wishes,
@thinkingmind
@originalworks take a look
This is really useful! I will keep it handy.
thank you