The Oscillator Feedback Oscillator Principles
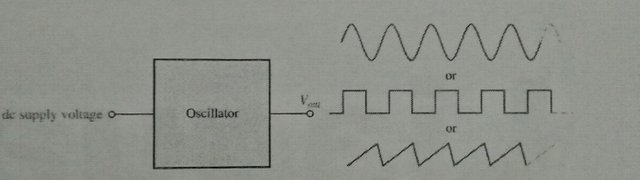
An oscillator is a circuit that produces a periodie waveform on its output with only the dc supply voltage as an input. A repeuitive input signal is not required except to synchronize oscillations in some applications. The output voltage can be either sinusoidal or nonsinusoidal. depending on the type of oscillator. Two major classifications for oscillators are feedback oscillators and relaxation oscillators. After completing this section, you should be able to Describe the basic operating principles of an oscillator Explain the purpose of oscillator List the basic elements of an oscillator Diseuss two important oscillator classifications
Feedback oscillators
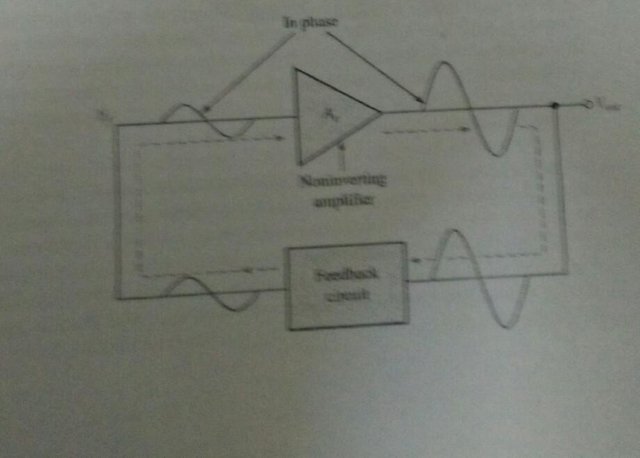
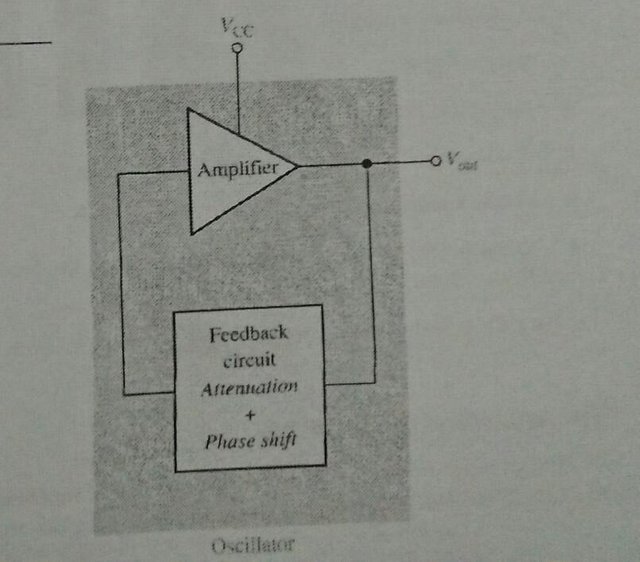
one type of oscillator is the reedback oscillator, which returns a fraction of the output signal to the input with no net phase shift, resulting in a reinforcement of the output signal. After oscillations are started. the loop gain is maintained at 10 to main- tain oscillations. A feedback oscillator consists of an amplifier for gain(either a discrete transistor or an op-amp) and a positive feedback circuit that produces phase shift and pro- vides attenuation, as shown in Figure
Relaxation oscillators
A second type of oscillator is the relaxation oscillator. A relax- ation oscillator uses an Rcuming circuit to generate a waveform that is generally a square wave or other nonsinusoidal waveform. Typically, a relaxation oscillator uses a Schmitt trigger or other device that changes states to altemately charge and discharge a capacitor through a resistor. Relaxation oscillators are discussed in Section
FEEDBACK osCILLATOR PRINCIPLES
on the principle of positive feedback. In section, we examine this general conditions required for oscillation to occur. Feedback ascillators are widely used to generate sinusoidal waveformas. After completing this section, you should be able to Discuss the main principle on which feedback oscillators is based Explain positive faedback Describe the conditions for oscillation Discuss the start-up conditions
Positive Feedback
Positive feedback is charactorized by the condition wherein an in-phase portion the out- put voltage of an amplifier is fed back to the input with no net phase shift resulting in arr- infaroament of the output signal. This basic idea is illustrated in Figure 16-3. As you can see the in-phuse feedback voltage, v is amplified no produce the output voltage, which turn produces the foadback vol Thal is, a loop is created in which the signal sustains itself and a continuous sinusoidal output is produced This phenomenon is called oscillatan.