How stuff works : Pulleys
As with levers and fulcrums, pulleys are there to make tasks easier for ourselves. Without having to lift heavy objects and run the risk of injuring ourselves badly, there are other ways to do things that aren't always "do-able" ourselves. If you've missed my post about levers and linkages, feel free to view it here.
A pulley, also called a block, is a mechanism composed of a wheel (called a sheave) with a groove between two flanges around the wheel’s circumference. A rope, cable or belt usually runs inside the groove. A pulley system consists of two or more pulleys and a drive belt. The pulleys and belts can come in a variety of shapes and materials. The simplest pulley system is one with one pulley and a rope.
Examples:
- Pulley and belt drivers are used in many everyday household machines, such as sewing machines, washing machines and vacuum cleaners.
- Cranes use pulleys to lift heavy loads.
Mechanical advantage in pulleys
Mechanical advantage can be defined as the ratio of load to effort. Pulley system rely on this important relationship between load and effort. The higher the mechanical advantage, the easier it is to lift a load.
- In a single pulley, the load and the effort are equal, so there is no mechanical advantage. With a single pulley, the pulley must be able to move so that mechanical advantage can be increased.
Example:
Mechanical advantage is the ratio of the output force to the input force. It tells us how much effort is needed to lift the load
If the load IS 20N and the effort is 10N, then:
MA= load / effort
= 20N / 10N
= 2 / 1
This means that we only need half the effort (10N) to lift the load (20N).
Types of pulley systems
A fixed or first-class pulley
We can think of a single fixed pulley as a first-class lever: the fulcrum is at the centre and the load and effort arm have the same length. A fixed or first-class pulley has a fixed axle. This means the axle stays in one place. If the block of the pulley is fixed to a beam or to the ceiling, the pulley will not move and is called fixed pulley. A flagpole is an example of a fixed pulley.
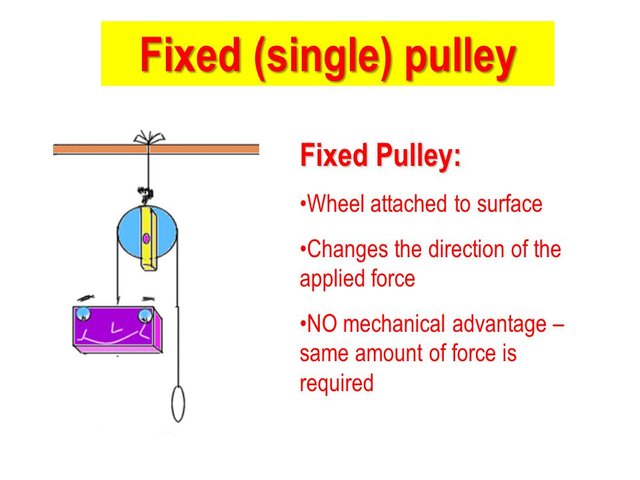
A fixed pulley
A movable or second-class pulley
A movable or second-class pulley has a free axle. This means that the axle is free to move in space. A movable pulley can multiply forces.
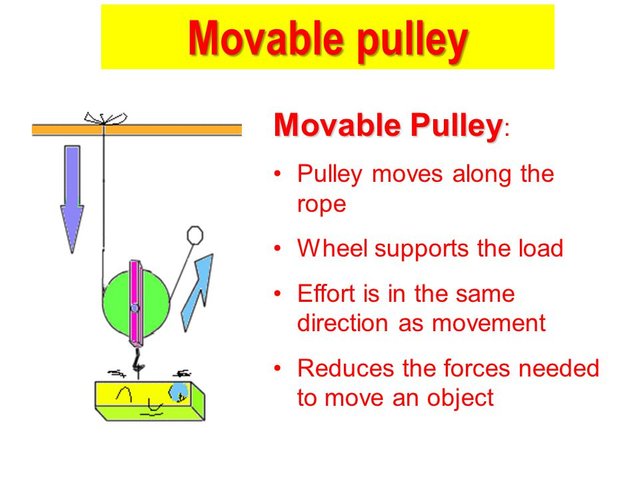
A movable pulley
- A movable pulley has a mechanical advantage of 2: if one end of the rope is anchored, pulling on the other end of the rope will apply a double force to the load that is attached to the pulley.
- A movable pulley system moves with the load: the pulley is suspended from a rope, with a section of the rope on either side of the pulley. Each section of the rope supports half the load
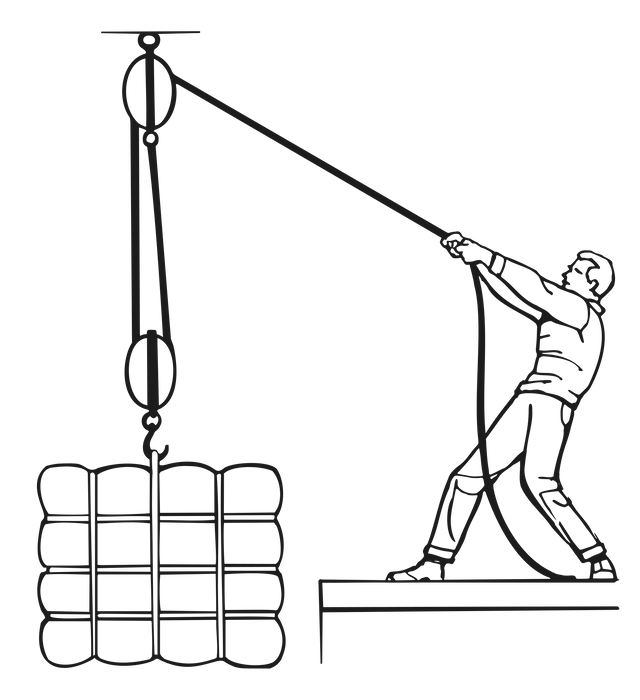
A compound pulley
A compound pulley system is a combination of a fixed and a movable pulley system.
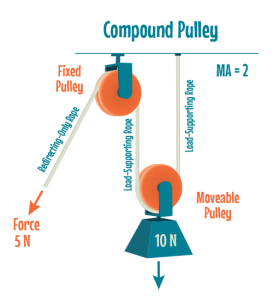
A compound pulley
- A block and tackle is a compound pulley where several pulleys are mounted on each axle, further increasing the mechanical advantage. It is an assembly of a rope and pulleys that is used to lift loads. A number of pulleys are assembled together to form the blocks. The rope is threaded through the pulleys to provide mechanical advantage that amplifies the force applied to the rope.
Activity
Design a simple pulley of your own choice with easy accessible items from home.
Example:
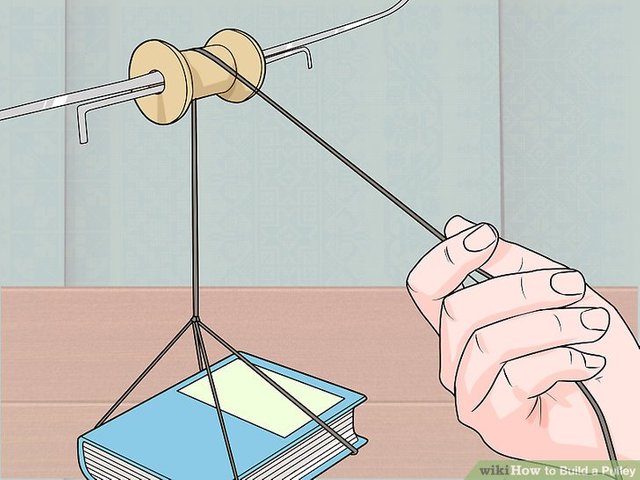
Image source
Bibliography & Extra reading:
- Pulleys
- Sheaves
- Block and tackle
- Machines
- Pulleys and lifting
- Mechanical advantage
- Simple machines
- How pulleys work
- Mechanical advantage device
- Calculating mechanical advantages
- Work and simple machines
- Work, energy and machines
- E classroom pulleys

Thanks, very informative. Enjoyed it!