A Study of the Human Cardiovascular System - Section one
Circulatory System (License : Public Domain, Author: LadyofHats, Mariana Ruiz Villarreal ) Wikimedia commons
The human body is no doubt a complex one. When i think of how the inner body functions it truly amazes me. I remember during my primary school days, i and my friends would hold a side of our chest as to check or count our heart beat and we would like; how is the heart like? is it big or small? What is this stuff beating on our chest? and all of that. We will make fun of it, and move on.
Biology and biological related subject is one of my best subjects, and I feel thrilled writing it or making presentations on it . "A Study of the Human Cardiovascular System " isn't an exception. The broadness of this topic has propelled me to compartmentalize it into sections. I will be writing on this topic section by section, This section is more like an introductory section, in the end of this topic we will be able to recall or gain more knowledge about our inner body as it regards to the circulatory system.
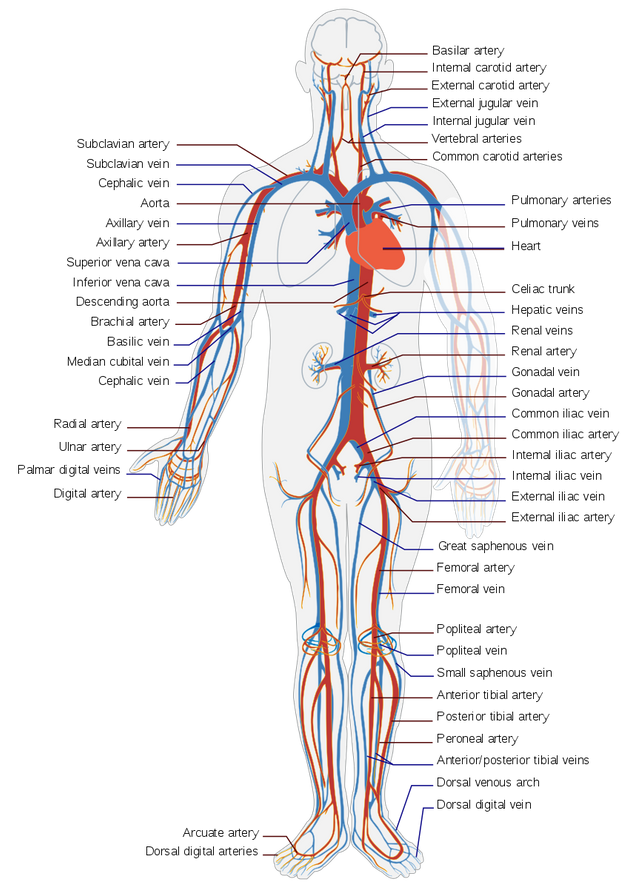
The cardiovascular system could be referred to the circulatory or vascular system. What it does is to allow the circulation of blood as well as the transportation of nutrients like electrolytes and amino acids, oxygen, hormones, carbon dioxide and blood cells in the body. It also provides nourishment and protect the body from diseases, keep the body temperature and pH stable. The cardiovascular systems of human body is usually closed, in the sense that the blood never leaves the interconnection of the blood vessels.
The blood system supplies the cells of the body with oxygen and nutrients, and carries away waste materials. The heart is the vital center of this, being the pump that drives blood through the body. It weighs under a pound, measures on average about 5 inches long by 3 1/2 inches wide and comprises four muscular chambers. The heart is positioned under the rib cage and in front of the lungs. It lies on the center line of the body but not symmetrically . One end slants out to a point just to the left of the breastbone (sternum). The heartbeat is most noticeable here, giving the impression that the heart lies on the left side of the body.
The heart is really two pumps. One pump receives blood from the body and sends it out to the lungs, where the waste product, carbon dioxide, is exchanged for fresh oxygen. The other pump receives back the oxygenated blood from the lungs, and speeds it on its way to the rest of the body.
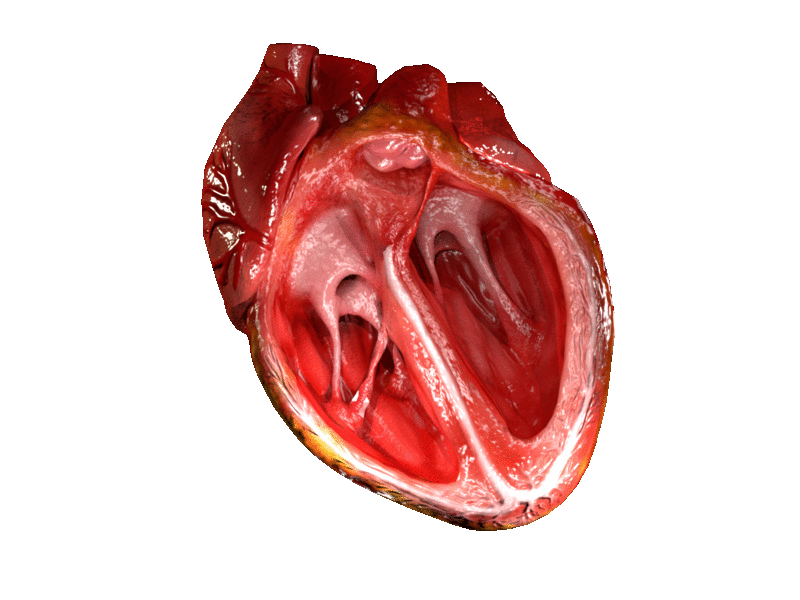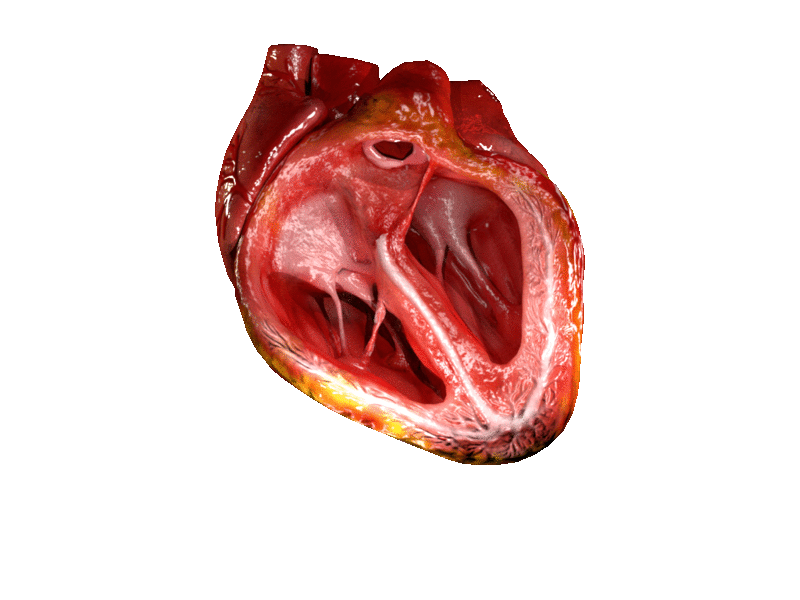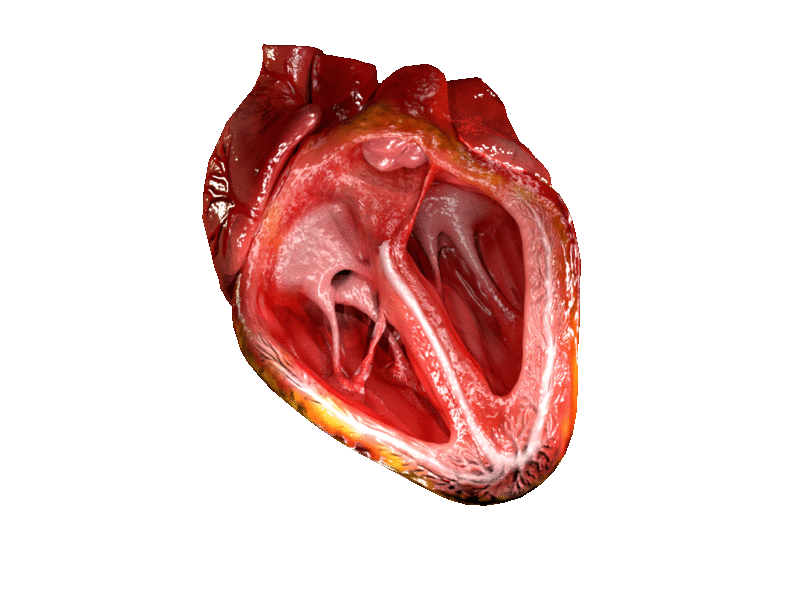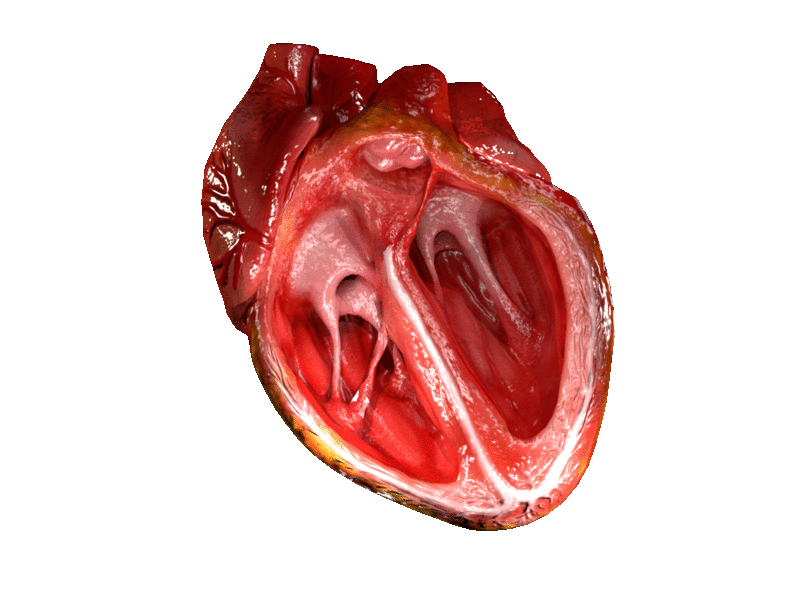
CG Heart (License: CC-BY-SA 4.0, Author : DrJanaOfficial) Wikimedia Commons
The adult heart beats 60 to 80 times a minute, and about 40 million times a year. The smaller the heart, the faster it beats. An average male heart is about 10 ounces in weight, and a female heart 8 ounces. This means that a woman's heart makes about 6 to 8 more beats a minute than a man's heart. At each beat the heart takes in and discharges over 1/4 pint of blood (130cc). It pumps over 2000 gallons a day, and 50 million gallons in a lifetime. In a healthy man during exercise, the heartbeat may increase to 180 beats a minute, pumping 40 pints a minute.
Blood pressure is expressed in two figures that indicate the pressures in the aorta. One is on concentration called the systolic pressure and the other is on relaxation, called the diastolic pressure. For a healthy young man or woman at rest, the systolic pressure is usually between 100 and 120mm Hg, and the diastolic between 70 and 80mm Hg. These are expressed as 100/70 or 120/80. Pressure in the right ventricle only rises to about 20mm Hg. This is enough to send blood through the lungs and back to the left ventricle.
How the Heart Works
The heartbeat is in two stages. One is contraction and the other is relaxation. As the heart begins to contract, both atria and both ventricles are already full of blood. The left atrium and ventricle contain deoxygenated blood, while the right contains oxygenated blood. The atria contract slightly before the ventricles. This builds up the pressure in the ventricles. The back pressure eventually closes the valves between the atria and ventricles. The ventricles contract, and pressure forces open the valves between the ventricles and the arteries that lead from them. From the right ventricles, deoxygenated blood is sent into the lungs. From the left oxygenated blood from the lungs is sent out to the body.
When most of the blood has passed, the valves close, because there is no longer enough pressure to keep them open. The heart relaxes and atria and ventricles begin to fill with blood. After about 0.4 seconds, a nerve impulse triggers off the next contraction.
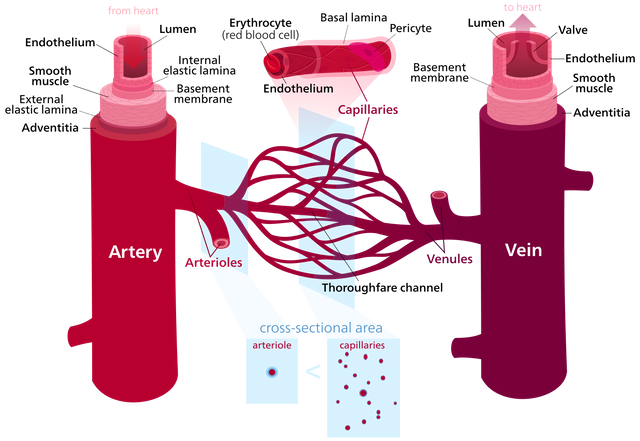
Blood Vessels and Where the Blood Goes
The blood vessels can be said to be the body's public road that enables the blood to flow speedily and resourcefully from the heart to all part of the body and return back. The dimension of blood vessels is equivalent to the blood that passes through the vessel.
Blood vessels are of three types. Which are arteries, veins and capillaries. The arteries carry oxygenated blood from the heart to all parts of the body. They have a strong elastic walls that squeeze the blood along with the waves of contraction. After profuse branching the blood passes through the tissues of the body in tiny capillaries, where nutritive substances and oxygen are exchanged for waste products. The blood is then conveyed back to the heart along veins. These have thinner walls than the arteries, and contain valves to prevent a back flow of blood.
The distribution of blood to various organs of the body is done during exertion or by rest. When at rest, it will take the heart-lung-heart route 6 seconds, the heart-brain-heart route takes 8 seconds and the heart-toe-heart route takes 16 seconds for the distribution.
But note that the three major functions of the cardiovascular system is firstly, the transportation of materials, secondly, the regulation of the body's internal environment and protection from pathogens.
*** To be continued in section two...
[1 ] Circulatory System-wikipedia
[2] Cardiovascular System -innerbody
[3] Anatomy of the Heart and Cardiovascular System
[4] Circulatory System: Facts, Function & Diseases
[5] Functions of the Cardiovascular System
[6] Cardiovascular System Anatomy
For those writing STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) related posts, consider to be part of #steemSTEM community. The link to #steemSTEM community discord room is here. For STEM writers from Nigeria, include #stemng tag in your posts in addition to using normal #steemstem tag. You can check this blog by @stemng for more information. You can visit this post by @steemstem on how to become a member of STEM community. Visit this link for helpful guidelines on writing #steemstem targeted posts. In order not to violate copyright laws in your use of images, consider checking out this post by @steemstem team.

.png)
.png)
It is so amazing that how the complicated tiny inner organs make a human alive and we don't even know properly how they functions.This a great art work done by Almighty.
Yeah. Sometimes we need to look at our body structures and internal environment as to keep the memory fresh and know the basic things to do in order to stay healthy. God is great indeed!
Thanks for your feedback!
You are most welcome
A friend's sister had preeclampsia in her pregnancy and the blood pressure shot to the roof. It was only timely medical attention that saved her life. It was a wonder how the local maternity where she was doing antenatal did not see it earlier with all the symptoms such as swollen body parts, high BP, etc.
Only few women experience preeclampsia in pregnancy and the only cure is to put to birth. Though some measures can be taken to relieve the patient. Because such situation could lead to failure of the entire organs and even death.
Trust nothing happened to her?
Congratulations! This post has been upvoted from the communal account, @minnowsupport, by masterwriter from the Minnow Support Project. It's a witness project run by aggroed, ausbitbank, teamsteem, theprophet0, someguy123, neoxian, followbtcnews, and netuoso. The goal is to help Steemit grow by supporting Minnows. Please find us at the Peace, Abundance, and Liberty Network (PALnet) Discord Channel. It's a completely public and open space to all members of the Steemit community who voluntarily choose to be there.
If you would like to delegate to the Minnow Support Project you can do so by clicking on the following links: 50SP, 100SP, 250SP, 500SP, 1000SP, 5000SP.
Be sure to leave at least 50SP undelegated on your account.
This post has been voted on by the steemstem curation team and voting trail.
There is more to SteemSTEM than just writing posts, check here for some more tips on being a community member. You can also join our discord here to get to know the rest of the community!